Process: Working with single seller RFQ
Flow
Objective
Request For Quote (RFQ) trading mechanism for a single seller.
Description
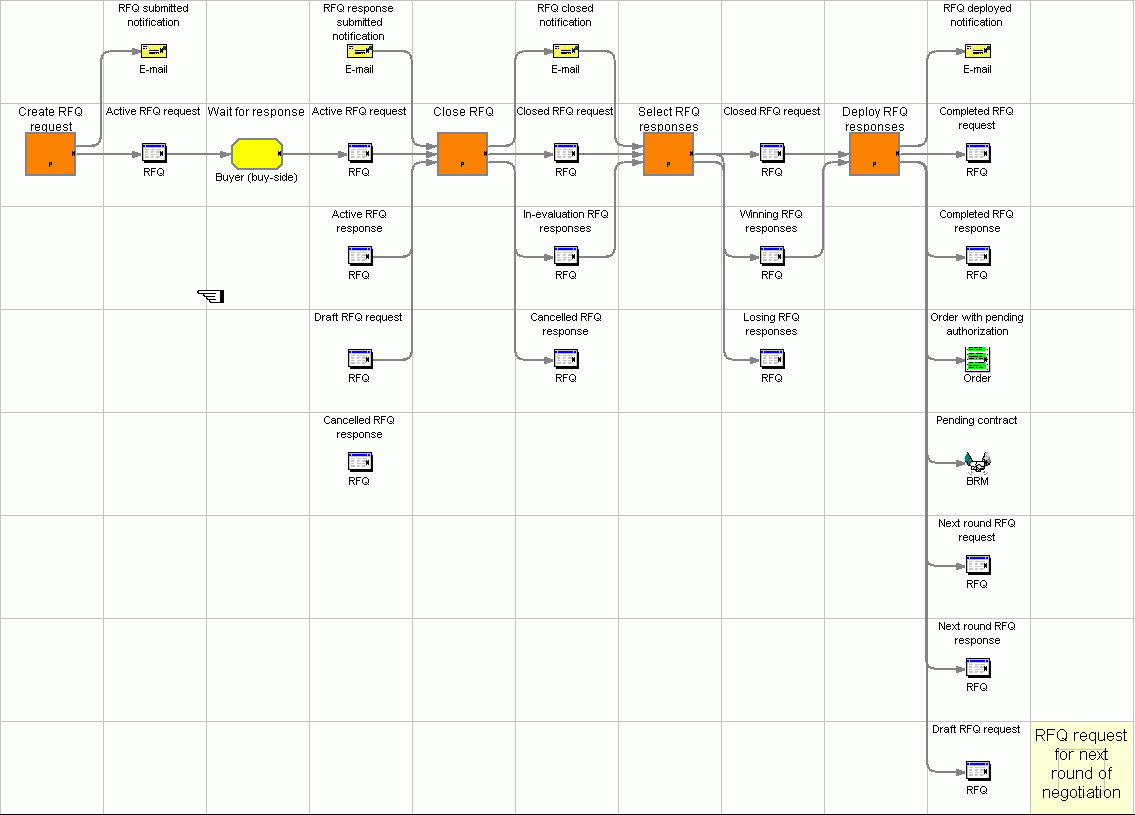
The Request for Quote (RFQ) process is a business flow comprised of many stages or states that the trading partners must pass through as they negotiate. The final state in a successful negotiation is a contract or order, as specified by the buyer.
A buyer can create an RFQ for unique variations of goods and services that are offered in the catalog. If buyers cannot find a product matching their needs in the catalog, they can select attributes from the personalized attributes dictionary to precisely define the product specifications.
Buyers can include multiple products in one RFQ, and define unique specifications for each product. They can include attachments on the RFQ or product specification level. They can also specify the terms and conditions for the transaction. When the buyer submits an RFQ request, it is placed into a "future" or "active" state. A seller can view the RFQ and submit a response when the request is in an "active" state. A buyer can also change or cancel an RFQ.
When sellers respond to an RFQ, they have the option of responding to each attachment, terms and conditions, and product, as well as to each product specification or comment. They have the option of substituting a product if the buyer has provided that option in the request. A seller can also modify or cancel a response.
Once sellers have responded to the RFQ, the buyer closes the RFQ and evaluates the responses to select a winner, or multiple winners. When the RFQ response is accepted by the buyer and the seller is notified, the RFQ transaction is completed through one of the following processes:
- The buyer places an order that contains the RFQ information.
- A contract containing the RFQ information is created.
- The RFQ can go to the next round.
Features
- The customer can select organization to work on behalf of.
- RFQ attachments
- Terms and conditions
- Catalog products
- Made-to-order items
- Customized product specifications
Edition
Enterprise
Subprocesses
Tasks
| Task | Description | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Wait for response |
When a buyer has activated an RFQ, the seller can respond to the terms and conditions and product descriptions specified by the buyer. The seller can either accept the RFQ as received, or can present counterproposals in their response. For example, the seller may want to propose another delivery date, another product, or change the value of a changeable product specification. |
Buyer (buy-side) |
Business artifacts
- Active RFQ request
- Active RFQ response
- Cancelled RFQ response
- Closed RFQ request
- Completed RFQ request
- Completed RFQ response
- Draft RFQ request
- In-evaluation RFQ responses
- Losing RFQ responses
- Next round RFQ request
- Next round RFQ response
- Order with pending authorization
- Pending contract
- RFQ closed notification
- RFQ deployed notification
- RFQ response submitted notification
- RFQ submitted notification
- Winning RFQ responses
(C) Copyright IBM Corporation 1996, 2006. All Rights Reserved.