Activity building blocks: triggers, targets, and actions
When you build a marketing activity using the Activity Builder, your building blocks are triggers, targets, and actions. These building blocks are represented as icons, or elements, in the palette. You select elements from the palette and place them in a precise order along a flow that represents the marketing activity.Basic rules for using triggers, targets, and actions in marketing activities
- The activity must start with a trigger; otherwise, the activity will not start.
- All web activities start with the E-Marketing Spot trigger.
- Dialog activities start with a trigger you choose from the palette, such as the Customer Registers trigger or Customer Places Order trigger.
- The activity must contain an action; otherwise, the activity will not do anything.
- Optionally, the activity can contain a target, placed to the left of an action. The target defines which customers experience the action.
Examples
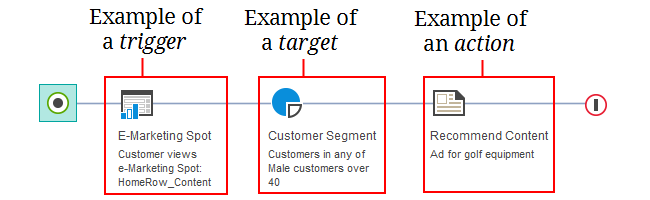
Here is an example of a web activity built with a trigger, a target, and an action:Example 1: When a customer views the e-Marketing Spot on the store home page, if that customer belongs to the Male customers over 40
customer segment, display an
advertisement for golf equipment.
Here is another example; in this case, it is a dialog activity that is built with a trigger, a target, and two actions: Example 2: When a customer places an order, check the customer's purchase history. If this order is the fifth order, then:
- Send the customer an email informing them of their new Preferred Customer status and its benefits.
- Add the customer to the Preferred Customer customer segment.

The following sections describe the purpose of triggers, targets, and actions, as well as some guidelines for using them.
Triggers
Use triggers to define the event that causes your activity to start or continue.For a complete list of dialog activity triggers, see Triggers in dialog activities.
Guidelines for using triggers:
- In web activities:
- Web activities always start with the E-Marketing Spot trigger, as shown in the previous Example 1. By default, the e-Marketing Spot trigger is included as the first element in all standard web activity templates. The web activity is triggered when a customer views the page containing the e-Marketing Spot.
- Only the e-Marketing Spot trigger is applicable to web activities.
- We cannot include more than one trigger in a web activity.
- In dialog activities:
- Dialog activities can start with any trigger that is available in the palette. In most cases, triggers are customer events, for example, a customer registers or places an order. Additionally, a trigger can be an elapsed period of time, for example, a week. When the trigger you specify occurs, the dialog activity proceeds.
- We can include more than one trigger in a dialog activity.
Targets
Use targets to define which customers experience your marketing activities. When a customer reaches a target in the activity flow, the customer is evaluated against the target criteria. For example, the criteria for a Purchase History target might be that the customer has placed exactly 5 orders, as shown in the previous Example 2. If the customer matches the target criteria, the customer continues to the next element in the activity flow. Targets are typically based on a customer's behavior and segmentation.For a complete list of available targets, see Targets in marketing activities.
Guidelines for using targets:
- Targets are optional elements in activities. If you do not include targets in an activity, then the activity applies to all customers.
- Place a target before an action in the activity flow; as a result, only customers who meet the requirements of the target experience the action.
- We can include more than one target in an activity.
- We can have two or more consecutive targets; as a result, customers must meet the requirements of all consecutive targets to experience the action.
- A target cannot be the first element in an activity.
Actions
Use actions to define what to do, based on the previous sequence of triggers and (optionally) targets in the activity flow. An action is a step to do as part of the activity flow.- In a web activity, an action typically displays something in an e-Marketing Spot.
- In a dialog activity, an action can send the customer an email or text message, issue the customer a coupon, or add the customer to a customer segment.
For a complete list of available actions, see Actions in marketing activities.
Guidelines for using actions:
- All activities must include at least
one action; otherwise, the activity will not result in any communication with a customer.
- The standard web activity templates include an action by default, for example, the Recommend Content action.
- For dialog activities, you choose the action, for example, the Send Message action.
- Place an action to the right of a trigger in the activity flow; however, we can place a target between a trigger and an action.
- An action cannot be the first element in an activity.
- We can include more than one action in an activity.
- We can have two or more consecutive actions. All consecutive actions apply to the customer.
Related concepts
Web activities
Related tasks
Creating a dialog activity
Creating a web activity
Manage web activities
Manage email activities
Browsing for activities using lists and calendars
Changing the priority of a Web activity
Activating or deactivating an activity
Viewing the web activities scheduled for an e-Marketing Spot
Manage e-Marketing Spots
Related reference
Troubleshooting: Web activity does not display in store preview