|
|
|
| |
Adobe RTMP requests
Overview
RTMP is a binary client-server data transfer protocol used by certain Adobe Flash applications. The optional Adobe RTMP (Real Time Messaging Protocol) module allows load testing Adobe Flash applications programmed using the Adobe RTMP technology.
There are several versions of the RTMP binary protocol:
- RTMP, the basic data transfer protocol that works on top of TCP/IP;
- RTMPT, RTMP protocol encapsulated within the HTTP protocol requests/responses;
- RTMPS, identical to RTMPT but using HTTPS.
- RTMPE, RTMP protocol encrypted using proprietary Adobe algorithms. This protocol is not supported by NeoLoad.
To be able to handle RTMP requests, you will need to purchase the optional Adobe RTMP and Adobe AMF modules. These modules are included in the demo version of NeoLoad.
- Warning: Recording a RTMP application in NeoLoad is subject to certain limitations. See Limitations.
- Warning: To communicate with the server using RTMPT, the Flash client uses the system proxy settings, not the browser settings. With Windows, and when recording with a browser other than Internet Explorer, the Internet Explorer proxy settings must be changed for NeoLoad to be able to see the RTMPT requests.
Dependent libraries
When recording RTMP-type requests, you will need to load the Java classes for the objects exchanged. See Adobe RTMP.
Recording
The following diagram shows how the Adobe RTMP module works during recording:

The RTMP data exchanged between the client and server is captured by NeoLoad. The Adobe RTMP module comes into play, analyzing and decoding the requests. Once translated into XML, the requests are inserted in the project.
Runtime
The following diagram shows how the Adobe RTMP module works during a test run:
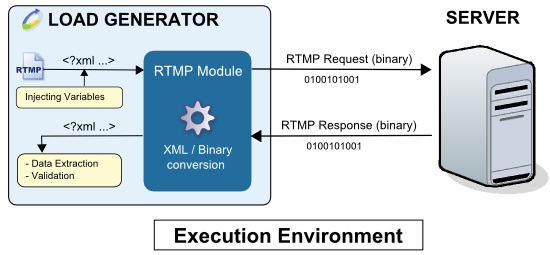
The XML request variables are evaluated and the module engine translates the XML to binary data. This data is then sent to the server. The binary response received is translated into XML and the validity checks and Variable Extractors of the played request are executed.