Create a deployment manager profile
Overview
This topic describes creating a runtime environment for a deployment manager.
Before using the Profile Management tool, install the core product files.
The Profile Management tool is the graphical interface to the manageprofiles command.
You must provide enough system temporary space to create a profile.
After installing the core product files for the ND product, create a profile.
It can be...
This procedure describes creating a deployment manager profile using the graphical user interface that is provided by the Profile Management tool.
The deployment manager provides a single administrative interface to a logical group of appservers on one or more machines.
Procedure
- Start the Profile Management tool to create a new runtime environment. Several ways exist to start the wizard:
- At the end of installation, select the check box to launch the Profile Management tool.
- From the command line...
app_server_root/bin/ProfileManagement/pmt.[bat|sh]
- Select the Profile Management tool from the First steps console.
- cd profile_root/firststeps
./firststeps.bat|sh -
On Windows use the Start menu to access the Profile Management tool.
For example, click...
Start | Programs or All Programs | IBM WebSphere | your product | Profile Management tool
- On Linux use the OS menus to start the Profile Management tool.
- At the end of installation, select the check box to launch the Profile Management tool.
- Click Next on the Welcome panel.
The wizard displays the Profile type selection panel.
- Select the option for creating a deployment manager and click Next.

- Select either...
- Typical profile creation
- Advanced profile creation
...click Next.
The Typical profile creation option creates a profile that uses default configuration settings. With the Advanced profile creation option, you can specify your own configuration values for a profile.
If you chose not to deploy the administrative console, the console ports are grayed out on the Ports panel.
-
If you selected Typical profile creation, go to the step on administrative security.
- If you selected Advanced profile creation, optionally select to deploy the console, then click Next.
- Specify a name for the profile and the directory path for the profile directory, or accept the defaults, then click Next.

Double-byte characters are supported.
Do not use any of the following characters...
- Spaces
- Illegal special characters that are not supported within the name of a directory on your operating system, such as *&?
- Slashes (/) or (\)
The first profile that you create on a machine is the default profile.
The default profile is the default target for commands that are issued from...
appserver_root/bin
When only one profile exists on a machine, every command works on the only server process in the configuration. To make another profile the default profile during subsequent profile creation, check...
Make this profile the default
...on the Profile name and location panel of the Advanced profile creation path.
When two or more profiles exist on a machine, certain commands require the use of the parameter...
-profileName
...to identify which profile to address.
You can avoid the use of -profileName by running the commands in the bin directory of each profile.
-
profile_root/profile/bin
Scripts in the profile/bin directory contain two lines. The first line sets the...
WAS_USER_SCRIPT
...environment variable for the command window, which sets up the command environment to address the profile. The second line calls the actual command in...
-
app_server_root/bin
The actual command queries the command shell to determine the calling profile and to autonomically address the command to the calling profile.
The default profile name is...
profileTypeX
...where...
profileType Value of... - AppSrv
- DMgr
- Custom
X sequential number The default profile directory is...
app_server_root/profiles
- On the Node, host, and cell names panel, specify a unique node name, the actual host name of the machine, and a unique cell name. Click Next.
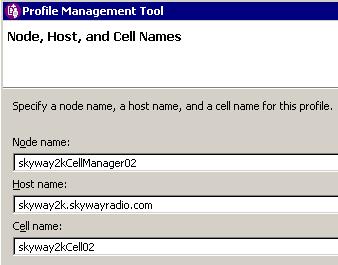
The deployment manager node has the following characteristics.
Field name Default value Constraints Description Node name shortHostNameCellManagerNodeNumber where: - shortHostName is the short host name.
- NodeNumber is a sequential number starting at 01.
Use a unique name for the deployment manager. The name is used for administration within the deployment manager cell. Host name The long form of the DNS name
The host name must be addressable through your network. Use the actual DNS name or IP address of your machine to enable communication with your machine. See additional information about the host name that follows this table. Cell name shortHostNameCellCellNumber where: - shortHostName is the short host name.
- CellNumber is a sequential number starting at 01.
Use a unique name for the deployment manager cell. If you plan to migrate a V5 deployment manager cell to this V6 deployment manager, use the same cell name as the V5 deployment manager. A cell name must be unique in any circumstance in which the product is running on the same physical machine or cluster of machines, such as a sysplex. Additionally, a cell name must be unique in any circumstance in which network connectivity between entities is required either between the cells or from a client that must communicate with each of the cells. Cell names also must be unique if their name spaces are going to be federated. Otherwise, you might encounter symptoms such as a javax.naming.NameNotFoundException exception, in which case, create uniquely named cells.
All federated nodes become members of the deployment manager cell, which you name in this panel. Avoid using reserved folder names as field values. The use of reserved folder names can cause unpredictable results. The following words are reserved:
- cells
- nodes
- servers
- clusters
- applications
- deployments
On windows the number of characters in the profiles_directory_path\profile directory must be less than or equal to 80 characters.
The host name is the network name for the physical machine on which the node is installed. The host name must resolve to a physical network node on the server. When multiple network cards exist in the server, the host name or IP address must resolve to one of the network cards. Remote nodes use the host name to connect to and communicate with this node. Selecting a host name that other machines can reach within your network is extremely important. Do not use the generic identifier, localhost, for this value. Also, do not attempt to install WAS products on a machine with a host name that uses characters from the double-byte character set (DBCS). DBCS characters are not supported when used in the host name.
If you define coexisting nodes on the same computer with unique IP addresses, define each IP address in a DNS look-up table. Configuration files for stand-alone Application Servers do not provide domain name resolution for multiple IP addresses on a machine with a single network address. The value specified for the host name is used as the value of the hostName property in configuration documents for the stand-alone Application Server. Specify the host name value in one of the following formats:
- Fully qualified DNS host name string, such as...
xmachine.manhattan.ibm.com
- The default short DNS host name string, such as...
xmachine
- Numeric IP address, such as...
127.1.255.3
The fully qualified DNS host name has the advantages of being totally unambiguous and flexible. You have the flexibility of changing the actual IP address for the host system without having to change the Application Server configuration. This value for the host name is particularly useful if you plan to change the IP address frequently when using Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to assign IP addresses. A format disadvantage is a dependency on DNS. If DNS is not available, then connectivity is compromised.
The short host name is also dynamically resolvable. A short name format has the added ability of being redefined in the local hosts file so that the system can run the Application Server, even when disconnected from the network. Define the short name to 127.0.0.1 (local loopback) in the hosts file to run disconnected. A format disadvantage is a dependency on DNS for remote access. If DNS is not available, then connectivity is compromised.
A numeric IP address has the advantage of not requiring name resolution through DNS. A remote node can connect to the node that you name with a numeric IP address without DNS being available. A format disadvantage is that the numeric IP address is fixed. You must change the setting of the hostName property in Express configuration documents whenever you change the machine IP address. Therefore, do not use a numeric IP address if you use DHCP, or if you change IP addresses regularly. Another format disadvantage is that you cannot use the node if the host is disconnected from the network.
After displaying deployment manager characteristics, the wizard displays the Administrative security panel.
- shortHostName is the short host name.
-
Optionally enable administrative security; click Next.
You can enable administrative security now during profile creation, or later from the console. If you enable administrative security now, supply a user name and password to log onto the console.
After specifying security characteristics, the wizard displays the Port value assignment panel if you previously selected Advanced profile creation.
- If you selected Typical profile creation at the beginning of these steps, go to the step that displays the Profile summary panel.
- Verify that the ports specified for the deployment manager are unique and click Next.
If you chose not to deploy the administrative console, the console ports are grayed out on the Ports panel.
Port conflict resolution: Ports are recognized as being in use if
- They are assigned to a profile created under an installation performed by the current user.
- The port is currently in use.
Validation of ports occurs when you access the Port value assignment panel. Conflicts can still occur between the Port value assignment panel and the Profile Creation Complete panel because ports are not assigned until profile creation completes. If you suspect a port conflict, you can investigate the port conflict after the profile is created. Determine the ports used during profile creation by examining the
-
![[Linux]](../../linux.gif)
![[HP-UX]](../../hpux.gif)
![[Solaris]](../../solaris.gif)
![[AIX]](../../aixlogo.gif) profile_root/properties/portdef.props file
profile_root/properties/portdef.props file
-
![[Windows]](../../windows.gif) profile_root\properties\portdef.props file
profile_root\properties\portdef.props file
Included in this file are the keys and values used in setting the ports. If you discover ports conflicts, you can reassign ports manually. To reassign ports, run the updatePorts.ant file through the ws_ant script.
![[Windows]](../../windows.gif)
![[Linux]](../../linux.gif) The wizard displays the Windows service definition panel if you are installing on a Windows platform and the installing ID has the administrative group privilege, or the Linux service definition panel if you are installing on a supported
Linux platform and the ID that runs the Profile Management tool is the root user.
The wizard displays the Windows service definition panel if you are installing on a Windows platform and the installing ID has the administrative group privilege, or the Linux service definition panel if you are installing on a supported
Linux platform and the ID that runs the Profile Management tool is the root user.
- They are assigned to a profile created under an installation performed by the current user.
- Choose whether to run the dmgr process as a Windows service on a Windows platform or as a Linux Service on a Linux platform, then click Next.
The Windows service definition panel displays for the Windows platform only if the ID that installs the Windows service has the administrator group privilege. However, you can run the WASService.exe command to create the Windows service as long as the installer ID belongs to the administrator group. See Automatically restarting server processes for more information.
![[Windows]](../../windows.gif) WAS attempts to start Windows services for dmgr processes that are started by a startManager command.
For example, if you configure a deployment manager as a Windows service and issue the startManager command, the wasservice command attempts to start the defined service.
WAS attempts to start Windows services for dmgr processes that are started by a startManager command.
For example, if you configure a deployment manager as a Windows service and issue the startManager command, the wasservice command attempts to start the defined service.
If you chose to install a local system service, you do not have to specify your user ID or password. If you create a specified user type of service, specify the user ID and the password for the user who runs the service. The user must have Log on as a service authority for the service to run properly.
If the user does not have Log on as a service authority, the Profile Management tool automatically adds the authority.
To perform this installation task, the user ID must not have spaces in its name. In addition to belonging to the administrator group, the ID must also have the advanced user right Log on as a service. The Installation wizard grants the user ID the advanced user right if it does not already have it, if the user ID belongs to the administrator group.
You can also create other Windows services after the installation is complete, to start other server processes. See Automatically restarting server processes for more information.
You can remove the Windows service that is added during profile creation during profile deletion.
IPv6 considerations
Profiles created to run as a Windows service fail to start when using IPv6 if the service is configured to run as Local System. Create a user-specific environment variable to enable IPv6. Since this environment variable is a user variable instead of a Local System variable, only a Windows service that runs as that specific user can access this environment variable. By default, when a new profile is created and configured to run as a Windows service, the service is set to run as Local System. When the Windows service for the dmgr process tries to run, the service is unable to access the user environment variable that specifies IPv6, and thus tries to start as IPv4. The server does not start correctly in this case. To resolve the problem, when creating the profile, specify that the Windows service for the dmgr process runs as the same user ID under which the environment variable that specifies IPv6 is defined, instead of as Local System.
Default Windows service information
![[Windows]](../../windows.gif) The defaults for the Windows service definition panel are as follows:
The defaults for the Windows service definition panel are as follows:
- The default is to run as a Windows service.
- The service process is selected to run as a system account.
- The user account is the current user name. User name requirements are the requirements that the Windows operating system imposes for a user ID.
- The startup type is automatic. The values for the startup type are those values that the Windows operating system imposes.
![[Linux]](../../linux.gif) The
Linux service definition panel displays if the current operating system is a supported version of Linux and the current user has the appropriate permissions.
The
Linux service definition panel displays if the current operating system is a supported version of Linux and the current user has the appropriate permissions.
WAS attempts to start Linux services for appserver processes that are started by a startServer command. For example, if you configure an appserver as a Linux service and issue the startServer command, the wasservice command attempts to start the defined service.
By default, WAS is not selected to run as a Linux service.
To create the service, the user that runs the Profile Management tool must be the root user. If you run the Profile Management tool with a non-root user ID, the Linux service definition panel does not display, and no service is created.
You must specify a user name under which the service runs.
To delete a Linux service, the user must be the root user or have proper privileges for deleting the service. Otherwise, a removal script is created that the root user can run to delete the service on the user's behalf.
The wizard displays the Profile Creation Summary panel.
- The default is to run as a Windows service.
-
Click Create to create the deployment manager or click Back to change the characteristics of the deployment manager.
The Profile creation progress panel, which shows the configuration commands running, is displayed.
When the profile creation completes, the wizard displays the Profile Creation Complete panel.
- Optionally, select Create another profile; click Finish to exit.
- Optionally, select Launch the
First steps console, Create another profile, or both; click Finish to exit.
With the First steps console, you can create additional profiles and start the appserver. Use the Create another profile option to create additional profiles.
Results
You created a deployment manager profile. The node within the profile has a deployment manager named dmgr.
Refer to the description of the manageprofiles command to learn about creating a profile using a command instead of a wizard.
What to do next
Create an appserver profile and add the node into the cell. Then you are ready to deploy an application.
Deploy an application to get started.
See Fast paths for WAS to get started deploying applications.
Related tasks
manageprofiles command
Creating profiles through the graphical user interface
Related Reference
Profiles: file system requirements