Foreign buses
We can configure a service integration bus to connect to, and exchange messages with, other messaging networks. To do this, you configure a foreign bus connection, which represents either another service integration bus, or a WebSphere MQ queue manager or (for WebSphere MQ for z/OS ) queue-sharing group, that the existing service integration bus can exchange messages with. In this way, we can extend the network of buses that can exchange messages.
When an application connects to a service integration bus, that bus is its local bus. A foreign bus is any other bus that has a link to the local bus. When the foreign bus is a service integration bus, it can be in the same cell as the local bus, or in a different cell.
To exchange messages between two buses, you configure a foreign bus connection from the local bus to the second bus. The foreign bus connection is associated with the local bus, and identifies the second bus as a foreign bus.
If the second bus is another service integration bus, you then configure a foreign bus connection from the second bus to the first bus. The foreign bus connection is associated with the second bus, and identifies the first bus as a foreign bus relative to the second bus. If the second bus is in a different cell from the first bus, you use the console for the second cell to configure this foreign bus connection.
A foreign bus connection can be direct or indirect. For a direct foreign bus connection, messages route directly through a link between the local bus and the foreign bus. For an indirect foreign bus connection, messages route indirectly through one or more intermediate buses.
A foreign bus connection contains a routing definition, also known as a virtual link, which indicates the type of physical link:
- A service integration bus link specifies a link from a messaging engine in the local bus to a messaging engine in a foreign bus.
- A WebSphere MQ link specifies a link from a messaging engine in the local bus to a WebSphere MQ gateway queue manager. To the local bus, the linked WebSphere MQ network appears as a foreign bus.
In the following figure, for an application that is connected to Bus 1, messages that are routed to Bus 2 use a direct foreign bus connection. Messages that are routed to Bus 3 use an indirect foreign bus connection and use Bus 2 as an intermediate bus.
Figure 1. Linking service integration buses.
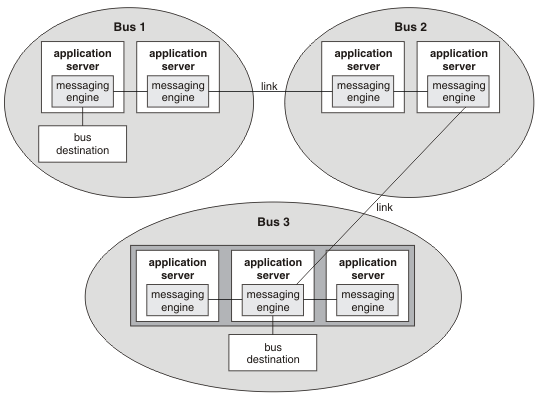
When you configure a foreign bus connection, the service integration bus link or WebSphere MQ link, as appropriate, is created automatically. If required, we can view or amend this link.
The following restrictions apply when you configure a foreign bus connection:
- The name of the foreign bus in the foreign bus connection must match the name of the existing service integration bus that it represents.
- For a direct foreign bus connection, the name of each bus must be unique.
- Specify the same user ID for both foreign bus connections on each side of a service integration bus link, for the following reasons. Consider two messaging engines, A and B, connected by a service integration bus link:
- Messaging engine A presents the user ID and its password to messaging engine B, so that messaging engine B can authenticate messaging engine A.
- Messaging engine A uses the user ID to authorize messaging engine B.
- Messaging engine A presents the user ID and its password to messaging engine B, so that messaging engine B can authenticate messaging engine A.
- After you configure a foreign bus connection, you must not change the name of the service integration bus that the foreign bus connection represents.
When you configure a bus, we can select the Configuration reload enabled option so that if the configuration properties of any foreign bus connections are changed later, the changes are updated automatically. The time when these changes take effect varies, depending on the properties that are changed:
- Foreign bus connection properties change immediately.
- WebSphere MQ link properties change on channel restart, except Description (immediately), and Initial State (on messaging engine restart).
- MQ sender channel properties change on channel restart, except
Initial State (on messaging engine restart or sender channel creation).
- MQ receiver channel properties on channel restart, except Initial
State (on messaging engine restart or receiver channel creation).
- Publish/subscribe broker profile (0 to n) properties change immediately.
- Service integration bus link properties change on link restart, except Description (immediately), and Initial State (on messaging engine restart or link creation).
We can define an explicit destination on a foreign bus that an application can send messages to. We can also configure default properties for use by messages sent to destinations on a foreign bus when there is no explicit foreign destination definition, and the application does not explicitly provide values for the properties. An application cannot receive messages from a foreign destination; it can only consume messages from a destination on the bus to which it is connected.
Messages flowing to or from a foreign bus that cannot be processed successfully are rerouted to the system exception destination of the messaging engine that owns the link to the foreign bus, possibly disrupting message order. Common reasons for rerouting messages to the exception destination are that the target destination is unknown by the foreign bus, or that the foreign bus has not granted the sending bus access to the target destination.
An application subscribing to a local topic space can receive messages published to a topic on a foreign bus. To allow publish/subscribe messaging between buses, you must map topic space names on a local bus to topic space names on a foreign bus.
A topic space mapping allows subscribers on the local topic space to receive messages published in the foreign topic space. For publications to flow from the local topic space to the foreign bus, an equivalent topic space mapping is required by the foreign bus.
You administer topic space mappings when creating a foreign bus connection, or through the routing properties for a foreign bus connection. Topic space names for the local bus are mapped to topic space names defined on the foreign bus. It is common for these two names to match. Note that mapping two topic spaces implies that the topics in them are the same.
Subtopics
- Message flow between service integration buses
An application connects to a bus, which is its local bus, and can exchange messages with other applications that connect to the same bus. To exchange messages with applications that connect to a different bus, that is, a foreign bus, we need a service integration bus link that connects the local bus to the foreign bus. - Message flow between a service integration bus and a WebSphere MQ network
An application connects to a bus, which is its local bus, and can exchange messages with other applications that connect to the same bus. To exchange messages with applications that connect to a WebSphere MQ network, we need a WebSphere MQ link that connects the local bus to a foreign bus that represents a WebSphere MQ network.
Related concepts
Related tasks
Related information: