Foreign destinations and alias destinations
Foreign destinations and alias destinations are types of bus destination. A foreign destination represents a destination defined in another bus (a foreign bus). An alias destination maps to an alternative name for a bus destination defined either in the local bus or in a foreign bus.
Usually, we do not need to configure a foreign destination or an alias destination:
- For an application to send messages to a destination defined in the local bus, specified the bus name and the destination name in the JMS destination object (queue or topic).
It is possible to omit the bus name, because the default is the local bus name, but for a system with more than one bus, it is advisable to specify the bus name.
- For an application to send messages to a destination defined in a foreign bus, specified the bus name (that is, the foreign bus) and the destination name in the JMS destination object (queue or topic). You do not need to configure any destination objects in the local bus.
- Service integration uses the definition of the foreign bus configured on the local bus. This definition includes default values for the destination attributes, such as the default quality of service. These default values apply to all destinations in that foreign bus. For more information, see the topic about point-to-point messaging across multiple buses.
You use a foreign destination when we need to override messaging defaults, security settings, or both for an individual destination on a foreign bus. We define a foreign destination on the local bus. When an application that is connected to the local bus sends messages to the destination in the foreign bus, the attributes of the foreign destination override the destination default values. We can set properties and destination roles, but we cannot map to an alternative name for the destination.
You use an alias destination when use an alternative name for a bus destination. The bus destination can be on the local bus or on a foreign bus. You configure an alias destination on the local bus. When an application in the local bus uses the alias destination, the specified bus name and destination name are mapped to a new name. If we use an alias destination, we can also set properties, destination roles, or both.
When an application that is connected to a bus specifies a destination name and bus name in its JMS destination object (queue or topic) that match the identifier and bus of an alias destination defined in that bus, the destination that the application accesses is the same as if the application specified the target identifier and target bus from the alias destination. We can also use a alias destination defined in a foreign bus if we need to redirect messages that arrive over a foreign bus connection to differently named destinations or buses, and we cannot modify the configuration of the source bus.
Foreign destinations
A foreign destination represents a destination defined in another bus (a foreign bus). We can use a foreign destination for point-to-point messaging. You use a foreign destination if we need to override security settings, or messaging defaults, for an individual destination on a foreign bus. The foreign bus can be another service integration bus or a WebSphere MQ network (that is, one or more interconnected WebSphere MQ queue managers or queue-sharing groups).
To override messaging defaults of a destination on a foreign bus, you configure the properties (for example, the default priority) of the foreign destination. To override security settings and control which users and groups in the local bus have access to a destination in a foreign bus, you configure the destination roles of the foreign destination. These properties apply when an application that is connected to the local bus sends messages to the destination in the foreign bus.
When you define a foreign destination, use the actual names of the foreign bus and the destination on the foreign bus, so that the JMS destination object does not change.
When an application that is connected to the local bus sends messages to the destination in the foreign bus, service integration in the local bus uses the properties and destination roles of the foreign destination, rather than the default values from the definition of the foreign bus (on the local bus). Typically, you configure the properties of a foreign destination to match the properties configured for that destination in the foreign bus (where that destination is a local destination), but this is not essential.
We can also configure destination roles for the foreign destination. Service integration in the local bus uses these roles to control which users and groups in the local bus have access to the destination. It also complements any access controls that the foreign bus applies.
You do not use foreign destinations for publish-subscribe messaging. Instead, applications publish messages locally using a topic space destination in the local bus, and you configure a service integration bus link or a WebSphere MQ link. These links propagate the published messages into the foreign bus, or buses, where subscribers receive the messages. For a link to a service integration bus, configure topic space mappings, as described in Configure topic space mappings between service integration buses. For a link to a WebSphere MQ network, configure a publish/subscribe bridge, as described in Publish/subscribe messaging through a link.
Figure 1 shows a JMS application that sends messages from the local bus, Bus 1, to a destination in a foreign bus, Bus 2. Bus 1 has a foreign bus connection defined, which it uses to forward the message to the foreign bus. The foreign destination is not defined in the local bus. Bus 1 gets the destination defaults from the foreign bus connection.
Figure 1. Point-to-point messaging between two buses with no foreign destination configured
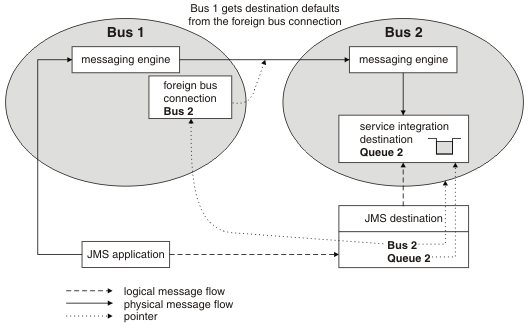
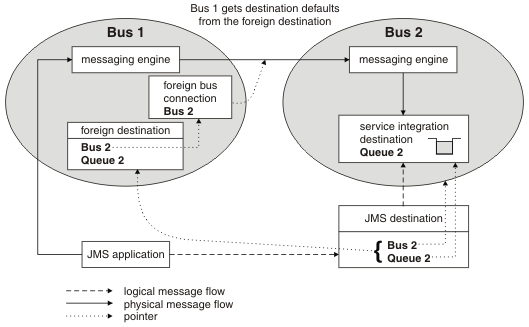
Figure 2 shows a JMS application that sends messages from the local bus, Bus 1, to a destination in a foreign bus, Bus 2. Bus 1 has a foreign bus connection defined, which it uses to forward the message to the foreign bus. Bus 1 includes a foreign destination definition. Bus 1 gets the destination defaults from the foreign destination.
Figure 2. Point-to-point messaging between two buses with a foreign destination configured on the local bus
Alias destinations
An alias destination maps an alternative name for a bus destination. We can use an alias destination for point-to-point messaging or publish/subscribe messaging. An alias destination maps a bus name and destination name (identifier) to a target where the bus name, or the destination name, or both, are different. An alias destination can map to a queue destination or a topic space destination. If required, alias destinations can be chained so that the target destination is itself an alias destination.
You use an alias destination when we need to make a destination available under an alternative name. For example:
- You need to interoperate with WebSphere MQ, but some service integration bus names or destination names do not comply with WebSphere MQ naming restrictions
(for example, the names are too long). We can define an alias destination that maps a WebSphere MQ-compliant
name to the service integration name.
For example, an application sends a message to a WebSphere MQ application and the reply-to destination name does not comply with the WebSphere MQ naming restrictions. We can define an alias that maps a compliant name to the actual reply-to destination name. The application then specifies the alias destination as the reply-to.
Another example is an application that sends a message through a WebSphere MQ foreign bus to a remote service integration foreign bus when the send-to destination name does not comply with the WebSphere MQ naming restrictions. We can define an alias in the remote bus that maps a compliant name to the actual send-to destination name. The application then specifies the alias destination as the send-to. The sending application to use the actual destination name, we can define an alias in the local bus that maps the actual destination name to the compliant name.
- If we move a destination from one bus to another (by deleting
it, then creating it on another bus), we can create an alias destination that redirects messages from the old destination to the new one. Create the alias destination in every bus where applications reference the destination, for example, the bus that the destination is moved from, and the bus that the destination is moved to.
However, it might be simpler to change the JMS destinations that are registered with JNDI to point to the new destination.
- We can assign an alias destination to a subset of the queue points of a partitioned queue destination, and therefore use the alias destination to restrict the queue points that the producing and consuming applications use.
When you use an alias destination, we can also set properties (for example, the default quality of service) for the alias destination. When an application uses the alias destination, these properties override the properties of the target destination. If we do not want to override a property, configure the alias destination to inherit the corresponding property from the target destination.
When you use an alias destination, we can also configure destination roles for the alias destination. When the application uses the alias destination, service integration in the local bus uses these roles to control which users and groups in the local bus have access to the target destination. If we do not want to override the security for the target destination, configure the alias destination to delegate the authorization check to the target destination.
Figure 3 shows a JMS application that sends messages from the local bus, Bus 1, to a destination in a foreign bus, Bus 2. Bus 1 has a foreign bus connection defined, which it uses to forward the message to the foreign bus. The JMS destination does not point to the target queue, but points to Bus X, Queue Y. Bus 1 includes an alias destination that maps Bus X, Queue Y to the target destination Bus 2, Queue 2. Bus 1 gets the destination defaults from the alias destination.
Figure 3. Point-to-point messaging between two buses with an alias destination configured on the local bus

Use an alias destination for a destination in a foreign bus
If an application uses an alias destination to access a destination defined in a foreign bus, we can configure the alias destination with the specific properties, destination roles, or both that the application requires. This means that you probably do not need to define a foreign destination as well.
Related concepts
Related tasks
Related information: