Develop > Business logic layer
WebSphere Commerce search
WebSphere Commerce search provides enhanced search functionality in starter stores by providing enriched search engine capabilities such as automatic search term suggestions and spelling correction, while influencing store search results using search term associations, and search-based merchandising rules.
WebSphere Commerce search provides the following key business benefits:
- It is built on the top of open architecture.
- It contains a rich set of search functionality for shoppers in starter stores.
- It provides integrated search management tooling for business users in the Management Center.
- It lowers the total cost of deployment and ownership, since its functionality is included as a feature of WebSphere Commerce.
WebSphere Commerce search runs as a search server for the starter store that helps deliver targeted search results, while enabling customers to find products more effectively. It provides advanced administering features such as dynamic clustering, database integration, rich document handling, distributed search and index replication.
The following diagram illustrates WebSphere Commerce search:
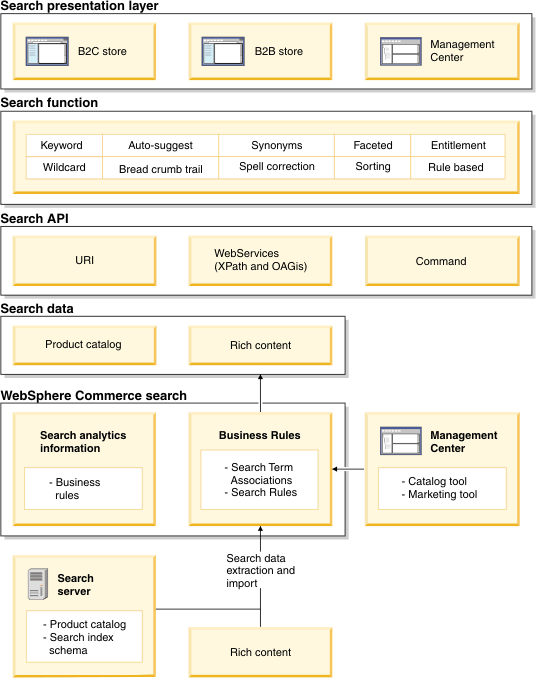
Where:
- WebSphere Commerce search works with the search index to provide search results consisting of structured and unstructured content, and external data.
- Structured content is obtained from the store's product catalog using a product catalog adapter.
- Unstructured content is obtained as a document and file adapter and crawler.
- External content such as product ratings from BazaarVoice is obtained using an external data adapter and crawler.
- All content is merged and presented in starter store pages.
Understand WebSphere Commerce search
WebSphere Commerce search is based around the search index, where an index is represented by a large flat table containing searchable fields optimized for search performance. The search index must be built before it can be used for any searches. The search index is built with one or more Documents, with Documents containing Fields. A Field consists of a name, its content, and metadata that tells WebSphere Commerce search how to handle the content. Typically, Fields can contain boolean values, numbers, or strings. A field is flexible, enabling you to define the own type. Fields contain two important attributes: indexed and stored. If a field is indexed, it is searchable, sortable, and facetable. If an index is stored, its value is retrievable during a search.
WebSphere Commerce search uses a schema represented similar to a database schema. The search schema defines the structure of the search index. Typically the search configurations are performed in the search schema configuration file. This configuration file contains information about which fields the documents can contain, and how those fields should be processed when adding documents to the index, or when querying those fields.
The schema contains three main sections:
- Data Types
- Enables you to define a list of field type declarations to use in the schema.
- Fields
- Contains a list of the individual field declarations to use in the documents.
- Miscellaneous
- Contains miscellaneous information.
WebSphere Commerce search uses HTTP requests to initiate indexing and searching. These requests are typically wrapped using utilities provided with WebSphere Commerce search. During the indexing process, WebSphere Commerce search takes input Documents as XML and builds an index using the information, and uses each Field in the input Document to build a searchable column. Once the index is built, it can be queried using search commands. These search queries are HTTP requests, where if a match is found, it returns XML data as the search results.
Use WebSphere Commerce search to influence starter store search results
The following search tooling and features are available by default to influence search results in the starter store:
- Search term associations
- The Product Manager is responsible for creating and managing search term associations. Search term associations include synonyms and search term replacements, and linking search terms with landing pages.
When customers search the storefront:
- Synonyms increase the scope of search results by adding additional search terms to the customer's search submission.
- Replacement terms modify potential search results by changing the search terms from the customer's search submission.
- Landing pages promote certain products or activities in the store by directing to specific store pages based on the customer's search submission.
- Synonyms increase the scope of search results by adding additional search terms to the customer's search submission.
- See Work with search term associations to improve storefront search results for more information.
- Search-based merchandising rules
- Search rules are managed by Marketing Managers. They are used when customers search the storefront to deliver customized search results and ordering.
For example, the following search rules can be created using the Search Rule Builder:
- When a customer searches the store, change the relative order of the search result by favouring catalog entries that belong to a specific brand or category, or sort catalog entries by price.
- When a customer searches the store, promote specific catalog entries to the top of the search result.
- When a customer searches the store, sort catalog entries by their manufacturer name.
- When a customer searches the store, change the relative order of the search result by favouring catalog entries that belong to a specific brand or category, or sort catalog entries by price.
- See Work with search rules for more information.
- Starter stores integration
- You can deliver powerful search-based catalog browsing flows by enabling WebSphere Commerce search in starter stores. Starter store enhancements for the storefront are provided such as automatic search term suggestions, spelling correction, and search result highlighting.
- See WebSphere Commerce search in starter stores for more information.
Limitations
The following limitations exist in WebSphere Commerce search-enabled starter stores:
- Coremetrics is not supported by default, therefore analytics cannot be used to influence store behavior.
- If considering integrating with third party search solution functionality, consider the scope of the customization points listed in Integrate WebSphere Commerce search with third-party search engines.
 WebSphere Commerce search interactions
WebSphere Commerce search interactions
WebSphere Commerce search includes several key interaction areas, including the Presentation layer, WebSphere Commerce server, and the search engine. Work with the WebSphere Commerce search configuration file
Work with the WebSphere Commerce search configuration file
The wc-search.xml file is the configuration file for WebSphere Commerce search. It contains properties that can control certain search features, and can be extended to meet the business requirements. Index synchronization and delta updates in WebSphere Commerce search
Index synchronization and delta updates in WebSphere Commerce search
The WebSphere Commerce search index can typically fall out of synchronization with the latest production data over time. To maintain accuracy of the search result data, re-indexing must be performed at a certain time during normal business operation. There are three forms of search re-indexing, and depending on the business requirements, there are costs and benefits associated with each of the following options: Full re-indexing, delta re-indexing, and emergency updates. Structured content and the index schema in WebSphere Commerce
Structured content and the index schema in WebSphere Commerce
Structured content includes items in the product catalog and delivers search results based on items that are sold in the store. Unstructured content in WebSphere Commerce
Unstructured content in WebSphere Commerce
Unstructured content includes documents that do not adhere to a specific data model, such as product attachments contained in various formats. For example, content such as user manuals and warranty information are considered unstructured content, as its elements, construction, and organization are typically unknown and can vary depending on its file type. WebSphere Commerce search index data structure definition
WebSphere Commerce search index data structure definition
The WebSphere Commerce search index process involves a search index schema, and is built from temporary tables.
Related concepts
Administer WebSphere Commerce search
WebSphere Commerce search in starter stores
Related tasks
Work with search term associations to improve storefront search results
Related reference
WebSphere Commerce search tutorials