Administer WebSphere Commerce search
WebSphere Commerce search indexes are created separately based on a specific master catalog. After deploying the WebSphere Commerce search index, you can separately manage and rebuild each index to refresh its data. Performing a full re-indexing rebuilds the entire search index, while a delta re-indexing performs only incremental updates on the existing operational search index. Before deploying the index, consider the index-building scenarios, depending on the WebSphere Commerce search environment.
Index-building scenarios
WebSphere Commerce search consists of the following typical index-building scenarios:
The same operating system should be used across all search servers: that is, the source (master, staging) search server, target (slave, production) servers, and search server cluster.
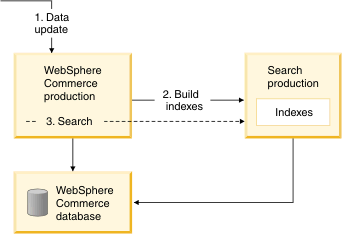
Small index size: WebSphere Commerce production server, without a dedicated index-building machine
In the small index size scenario, the WebSphere Commerce production server profile and search production server profile are on the same machine. All data and index-building operations are performed on the one existing production server. For example, consider the following flow:
- Update the WebSphere Commerce data in the WebSphere Commerce database.
- Build the search index.
- Execute searches against the updated search index.
Building the search index can be a timely process, and might therefore occasionally lead to inconsistencies between the database and search index. The runtime search performance is affected during index-building due to the added processing load on the machine.
The following diagram illustrates a typical WebSphere Commerce search deployment for a small index size:
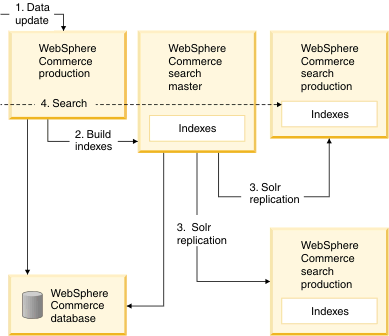
Small or medium index size: WebSphere Commerce production server, with dedicated index-building machine
In the small or medium index size scenario, there typically exists a dedicated index-building machine, known as the master, to build the index. The index is then replicated to other search engine machines, known as production. The runtime search performance is not affected during the index-building.
Building the search index can still be a timely process, and might therefore occasionally lead to inconsistencies between the database and search index. However, the runtime search performance is not affected during index-building due to the offset of the processing load to another machine.
The following diagram illustrates a typical WebSphere Commerce search deployment for a small or medium index size:
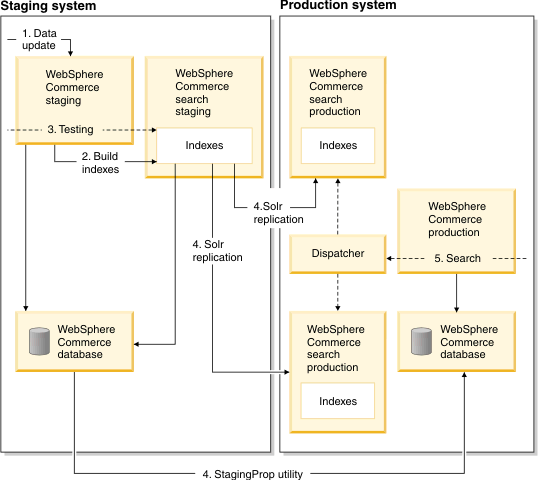
Recommended: Large index size: Staging and cluster search server
In the large index size scenario, the index-building is performed on the WebSphere Commerce staging database and search staging machine. Business users can test their new data in the staging database with the updated index. After successfully completing their tests, the data is propagated from the staging database to the production database, and the index is replicated from the search staging machine to the search production machines. This is the recommended approach, as this option imposes the least amount of risk to the production environment and provides a more flexible environment for making incremental changes.
The following diagram illustrates a typical WebSphere Commerce search deployment for a large index size:
Search administration flow
For a fully functioning WebSphere Commerce search implementation, understand and complete the search administration tasks involving deployment, management, and optionally replication.
 Deploy WebSphere Commerce search
Deploy WebSphere Commerce search
Deploying WebSphere Commerce search involves deploying the search server runtime in WebSphere Commerce and setting up the search index structure for a specific master catalog. Deploying the search runtime is typically performed only once, that is, during feature enablement. Setting up the index for specific master catalogs is run when introducing a new master catalog that you want indexed. Before deploying the search index, consider the available deployment options, depending on the WebSphere Commerce search environment. Manage WebSphere Commerce search: Populating and building the search index data
Manage WebSphere Commerce search: Populating and building the search index data
The tasks performed when managing search are those that are typically run on a regular basis, or on schedule. These tasks include preparing the WebSphere Commerce data for indexing using preprocessing, and indexing the data either partially through delta index updates or completely through full index builds. Replicating WebSphere Commerce search
Replicating WebSphere Commerce search
You can replicate the search index data on both the source machine and target machine to help improve reliability, fault-tolerance, and performance. Replicating WebSphere Commerce search maintains the search index data in more than one location, and involves copying designated changes for one location to another and synchronizing the data in both locations. Set up WebSphere Commerce search in a clustered environment
Set up WebSphere Commerce search in a clustered environment
Setting up WebSphere Commerce search in a clustered environment enables you to set up a cluster of WebSphere Commerce search, and manage multiple WebSphere Commerce search instances from one WebSphere Application Server console. Debug WebSphere Commerce search
Debug WebSphere Commerce search
You can debug WebSphere Commerce search by directly accessing Solr functionality using a Web browser, without using WebSphere Commerce runtime or utilities.
Related concepts
WebSphere Commerce search in starter stores
Related tasks
Work with search term associations to improve storefront search results
Related reference
WebSphere Commerce search tutorials