Creating Web services from an EJB
You can generate EJB Web services using either the Web Service wizard, or annotations. In this section, we create a JAX-WS Web service from an EJB session bean using annotations.

| Expand the EJB project RAD75WebServiceEJB and open the SimpleBankFacadeBean (in ejbModule/itso.rad75.bank.ejb.facade). |

| Add the @WebService annotation on the line above the @Stateless annotation (Example | 8-20). Press Ctrl+Shift+O to resolve the import. |
Example 18-20 Annotate a stateless session EJB

@WebService
@Stateless
public class SimpleBankFacadeBean implements SimpleBankFacadeBeanLocal {
......


| Wait for the RAD75WebServiceEAR application to publish on the server (or force a manual publish). Notice that a new Web service named RAD75WebServiceEJB is added in the Services views under JAX-WS. |

| An HTTP router module is required to allow transport of SOAP messages over the HTTP protocol. In the Services view, right-click the new RAD75WebServiceEJB and select Create Router Modules (EndpointEnabler) (Figure | 8-30). |
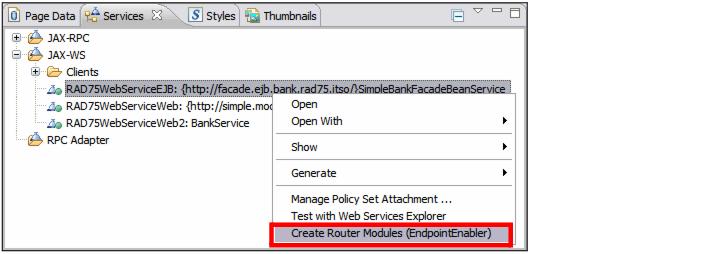
Figure 18-30 Create Router Module

| In the Create Router Project dialog, two EJB bindings are listed: HTTP and JMS. For this example, we use SOAP over HTTP. |

| Accept HTTP as the default EJB Web service binding (Figure | 8-31) and click Finish. |
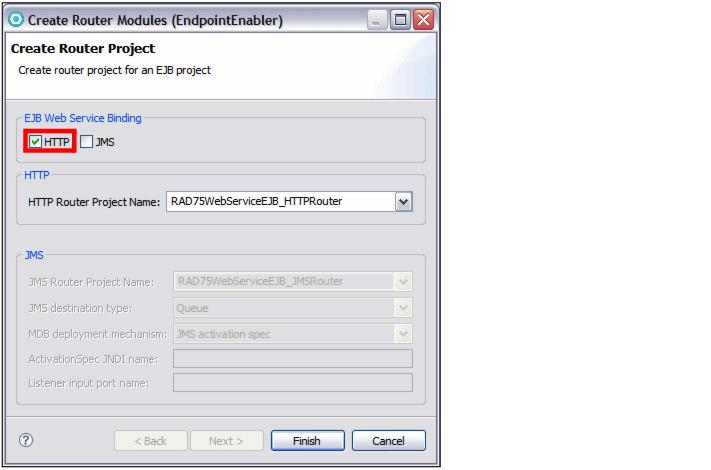
Figure 18-31 Create Router Project

| Open the deployment descriptor of the RAD75WebServiceEJB_HTTPRouter project and you can see the generated servlet. |

| In the Services view, right-click RAD75WebServiceEJB and select Test with Web Services Explorer. |

| Select the getAccountBalance operation, click Add, and type 001-999000777 as the account number. |

| Click Go and you can see the result of the Web service call: |
return (decimal): 12345.67
|
ibm.com/redbooks |