Neoload handles WebSocket
The way NeoLoad can map the WebSocket request and response is to define how to extract a mapping ID from the WebSocket channel response and specify the mapping ID on each WebSocket request. During the recording, NeoLoad will associate requests and responses when the mapping IDs are equal.
Having a communication based on the request/response pattern eases the usage of variable extractor/injection workflow and provides response times for business transactions.
Example
The example below illustrates a drawing editor allowing to create shapes. A shape is identified by a unique ID provided by the server and can either be moved or deleted.
We send this operation on WebSocket described as follows:
|
Action |
Execution type |
Request |
Response |
|
Create a new shape |
Synchronous |
Create(shape) |
Created(shape, id) |
|
Delete an existing shape thanks to the ID of the shape given by the server during creation. |
Synchronous |
Delete(id) |
Deleted(id) |
The sequence diagram belows represents a scenario showing how to create a diamond and delete it.
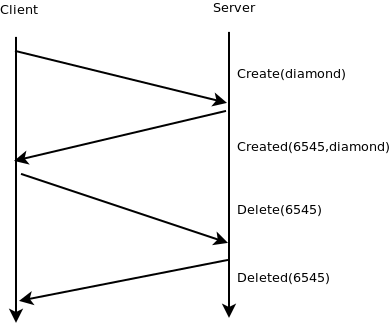
In this example, we need to:
- know the creation time, namely the time elapsed between the request Create(diamond) and the response Created(6545,diamond)
- wait that the diamond is created before deleting it
WebSocket channel
WebSocket channel provides a way to specify the XPath or regular expression to extract the mapping ID from the WebSocket responses. The expressions will be applied on all messages received on the channel in order to extract a mapping ID. If a mapping ID matches the one of a synchronous WebSocket request, then it is considered as the response of this request. A WebSocket channel can define only one way to extract the mapping ID from the response, so the XPath or regular expression has to be generic enough to handle all responses.
For more information about WebSocket channel, see Creating a WebSocket Channel.
In the example of a drawing editor, the response ID extraction is configured as shown below:
Regular expression: ^Created\([^,]*,([a-z]*),\)
Value template: $1$
WebSocket request
By default, all recorded WebSocket requests are asynchronous. The request execution does not wait for any response. Since no response can be linked to this request, there is no way to get response time on this action, nor specify a variable extractor.

If the WebSocket request can be mapped to a response, then it is possible to change the mode of this request from asynchronous to synchronous. A mapping ID has to be specified. It is a string that represents the link with a future WebSocket response. The next message received on the WebSocket channel that contains the same mapping ID will be considered as the response of this request.

In the drawing editor example, the mapping ID is "diamond".
For more information about WebSocket request, see Recording a WebSocket Request.
Configure messages mapping
See Configuring messages mapping for more information.
In the drawing editor example, we can recognize the protocol with the regular expressions:
- for the request: Create\(([^,])\) and $1$ as value template
- for the response: Created\([0-9]*,([^,]*),
Post-recording wizard
At the end of the recording, a wizard asks the user to search for framework parameters. If the Use Framework rules option is enabled, NeoLoad can search for WebSocket messages mapping in the recorded requests and configure the User Path. When XPath or regular expressions from a framework match the mapping identifier from a request and a response, NeoLoad brings the below modification to the User Path:
- the mapping identifier extracted from the WebSocket request is assigned to the Mapping ID field (the request is asynchronous by default but it can be switched to synchronous manually in order to have variable extractors, validations and response times)
- the WebSocket response becomes the response of the WebSocket request
- the response matcher (defined by the WebSocket push framework) that has been used is assigned to the WebSocket channel. If the WebSocket channel already defines a response matcher, then new ones are ignored.
- Advanced: WebSocket requests that cannot be matched to a WebSocket response remain as WebSocket asynchronous requests and they don't have neither mapping ID nor response pre-filling.
- Advanced: All WebSocket responses remain on the WebSocket channel, even if they match a request in WebSocket round-trip message.
The Post-recording wizard can be started on demand on the User Path already recorded with the option Search for dynamic parameter on a User Path.