Create a new display format
To create a new display format:- Run the following command:
select * from language
This command returns the language IDs in use by currently available display formats. Choose the next available ID_VALUE. - Run the following command:
insert into language (LANGUAGE_ID, ENCODING, LOCALENAME, LANGUAGE, COUNTRY) values (ID_Value, ENCODING_VALUE, 'x', 'y', 'z')
Where:- ID_VALUE
- The value you selected in step 2.
- LANGUAGE_ID (Required)
- An identifier to uniquely identify the display format.
- ENCODING_VALUE (Required)
- The character encoding value that the browser should use to display the page for this language. This should be the same encoding value used in your property files. ENCODESTATEMENT = text/html; charset=[ENCODING_VALUE]. A list of encoding values supported by the Sun JDK is available from the Sun Java site at www.java.sun.com.
- LOCALENAME (Required)
- A java locale used to represent a political, geographical, or cultural region that has a distinct language and customs for formatting. The localename is the two-letter ISO 639 language code, followed by the two-letter ISO 3166 country code, separated by an underscore.
- LANGUAGE (Optional)
- The name of the language.
- COUNTRY (Optional)
- The country or region for the display format.
- VARIANT (Optional)
- The variant column is an extra column that allows you to describe a subgroup within a particular culture, such as teen, technical, other any other classification.
- Add an entry to the LANGUAGEDS table. For an example, refer to Example of creating a new display format.
- Add an entry to the LANGPAIR table. For an example, refer to Example of creating a new display format.
- Add the language to the store. The WebSphere Commerce instance must support this new language or you will also need to add the language to the WebSphere Commerce instance in Configuration Manager. Refer to the SupportedLanguages element in the WebSphere Commerce configuration file.
You may need to add multiple entries to the LANGUAGEDS and LANGPAIR tables, one for every language that your store supports.
Example of creating a new display format
The following example shows how you could create a display format to view the ConsumerDirect starter store pages in Thai.
- Translate the storetext_locale.properties file to Thai.
- Ensure that the encoding statement in the properties file references a character set that target browsers will support. For Thai the encode statement is as follows: ENCODESTATEMENT = text/html; charset=MS874
- Save the file as storetext_th_TH.properties
- Open a database command window and run the following command
select * from language
This command returns the language IDs in use by currently available display formats. Choose the next available ID_VALUE. In this example, the ID_VALUE is for Thai is 3. - Run the following command
insert into language (LANGUAGE_ID, ENCODING, LOCALENAME, LANGUAGE, COUNTRY, MIMECHARSET) values (ID_Value, ENCODING_VALUE, 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z')
Using the following valuesinsert into language (LANGUAGE_ID, ENCODING, LOCALENAME, LANGUAGE, COUNTRY) values ('3', 'MS874', 'th_TH', 'Thai', 'Thailand',) - Add an entry to the LANGUAGEDS table with the following values
language_id=-1, description=<new_language_displayname_in_English>, language_id_desc= new_language_id
For example: "language_id=-1, description=French, language_id_desc=2Use the following values:
language_id= new_language_id, description= new_language_displayname_in_the_new_language;, language_id_desc= new_language_id
For example: "language_id=3, description=Fran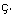 ais, language_id_desc=3.
ais, language_id_desc=3.
See, step 2 for more information about the values.
- Create an alternative language for Thai used if the data requested in
Thai does not exist. This is useful if not all the data in the database is
translated into the new language. To create an alternative language run the
following command
insert into langpair(LANGUAGE_ID, LANGUAGE_ID_ALT, SEQUENCE, STOREENT_ID) values (ID_Value, ID_Value_ALT, 'x', 'y')
Using the following valuesinsert into langpair(LANGUAGE_ID, LANGUAGE_ID_ALT, SEQUENCE , STOREENT_ID) values ('3','-1', '1' '12345')where- LANGUAGE_ID
- The requested language
- LANGUAGE_ID_ALT
- is the alternative language
- SEQUENCE
- When the requested Language is supported as specified in the STORELANG table, but information is not available in that Language, each alternative Language is tried in ascending order of SEQUENCE. A store may override the SEQUENCE specified for its StoreGroup.
- STOREENT_ID
- The StoreEntity this relationship belongs to The alternative Language
relationships for a Store include the alternative Language relationships for its StoreGroup.
The preceding insert statement will assign English (language id = -1) as the first alternative language to try for store with id '12345' in the event that no Thai data is found.
- Convert any properties file from native to ascii: Copy the storetext_th_TH.properties
file to a temporary directory (for example, /tmp). Run the following command
JDK_dir/bin/native2ascii -encoding TIS620 /tmp/storetext_th_TH.properties /tmp/storetext_th_TH_new.properties
Where JDK_dir is the path to your JDKCopy the storetext_th_TH_new.properties file from the temporary directory to WC_eardir/Stores.war/WEB-INF/classes/ storeDir/storetext_th_TH.properties.
Related concepts
Supporting globalization
Programming models for globalized stores
Cultural considerations
Localized store assets
Globalized store design
Related tasks
Use resource bundles in store pages
Create a globalized store
Related reference
Globalization tips
massload utility (Server environment)