WebSphere MQ custom properties
WebSphere Application Server supports the use of custom properties to define WebSphere MQ properties. This is useful because it enables WebSphere Application Server to work with later versions of WebSphere MQ that might have properties that are not available in the WAS console.
For WAS v7 or later, the custom properties defined are validated by the WebSphere MQ resource adapter contained in WebSphere Application Server. In earlier releases, this was done within WebSphere Application Server itself, and then by the WebSphere MQ client jar files. If we have defined a property that is not valid for WebSphere MQ, the WebSphere MQ resource adapter creates an exception, which is caught by WebSphere Application Server, and logged in the Systemout.log and SystemErr.log files. Examples of error messages are given at the end of this topic.
When a later version of WebSphere MQ is available that is supported by the WAS installation, new WebSphere MQ properties might be created that are not known to WebSphere Application Server. We can configure these as custom properties through WebSphere Application Server so that they are recognized by the WebSphere MQ resource adapter. We can also configure WebSphere Application Server to point to the WebSphere MQ resource adapter in the external JMS provider, as described in Configure the WebSphere MQ messaging provider with native libraries information.
For information on valid values for WebSphere MQ properties, refer to the Use Java and System Administration sections of the WebSphere MQ information center.
This topic references one or more of the application server log files. As a recommended alternative, we can configure the server to use the High Performance Extensible Logging (HPEL) log and trace infrastructure instead of using SystemOut.log , SystemErr.log, trace.log, and activity.log files on distributed and IBM i systems. We can also use HPEL in conjunction with the native z/OS logging facilities. If we are using HPEL, we can access all of the log and trace information using the LogViewer command-line tool from the server profile bin directory. See the information about using HPEL to troubleshoot applications for more information on using HPEL.
The following scenarios illustrate how different cell configurations might be affected.
Mixed node scenario
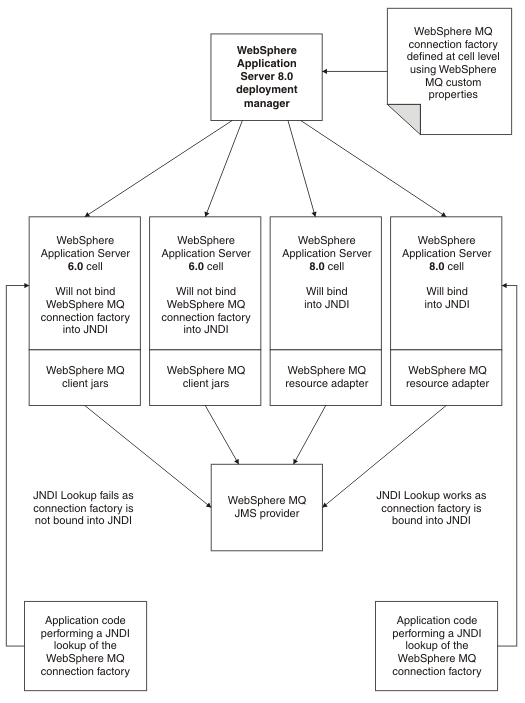
In this mixed node scenario, a cell consists of a WAS, v8.5 deployment manager, two WebSphere Application Server, Version 6 nodes, and two WebSphere Application Server, v8.5 nodes. If a WebSphere MQ connection factory is defined at cell level and has custom properties defined that exploit the new fields available in WebSphere MQ, then the connection factory is only bound into the WAS cells that are at v8.5 level. The WebSphere Application Server, Version 6 nodes do not know about the new WebSphere MQ properties and do not bind into the JNDI. The enhancements made to WebSphere Application Server, v8.5 allow validation of the properties to be deferred to the WebSphere MQ resource adapter.Figure 1. Mixed node scenario
WebSphere MQ Version 7 or later scenario
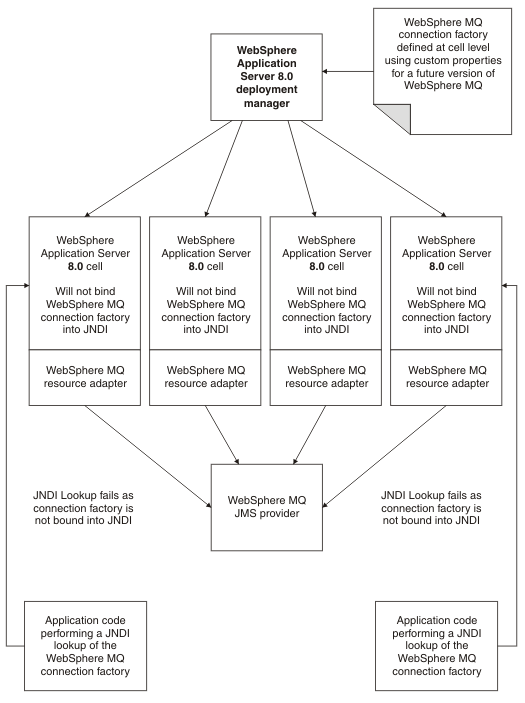
In this scenario a cell consists of WAS, v8.5 deployment manager and nodes. The WebSphere MQ messaging provider is running at a level later than Version 6. WebSphere Application Server is using the default WebSphere MQ resource adapter shipped with WebSphere Application Server v8.5. In this scenario the WebSphere MQ resource adapter is not aware of the new WebSphere MQ properties so the validation fails and the connection factory does not bind into the JNDI.Figure 2. Future version of WebSphere MQ scenario
Correctly configured scenario
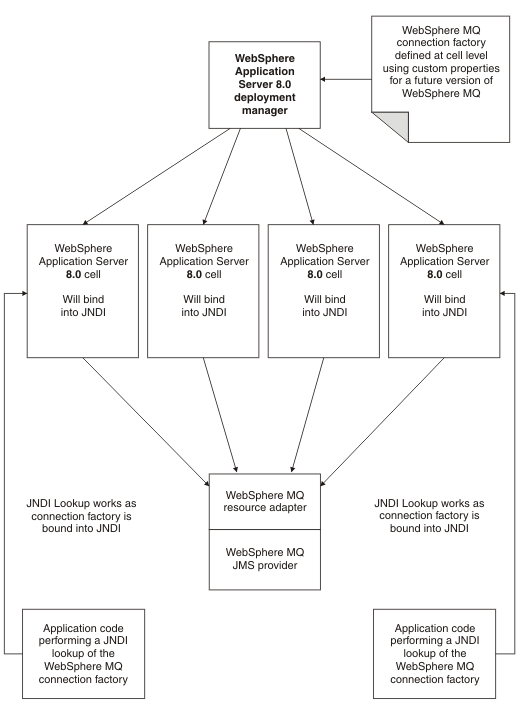
In this scenario, which is similar to the previous one, a cell consists of WAS, v8.5 deployment manager and nodes. The WebSphere MQ messaging provider is running at a level later than Version 6. To successfully use the new WebSphere MQ properties it is necessary to configure the WAS to point to the WebSphere MQ resource adapter associated with the later version of WebSphere MQ.Figure 3. Correctly configured scenario
Error message example
The exception created by the resource adapter contains error messages similar to the following example:[09/02/06 15:40:06:377 GMT] 0000000a ContainerImpl E WSVR0501E: Error creating component null [class com.ibm.ws.runtime.component.ApplicationServerImpl] com.ibm.ws.exception.RuntimeWarning: com.ibm.ws.runtime.component.binder. ResourceBindingException: invalid configuration passed to resource binding logic. REASON: Failed to create connection factory: Error raised constructing AdminObject, error code: XAQCF PropertyName : XAQCF PropertyNamewhere PropertyName is the name of the invalid property.
Related tasks