Investigating why point-to-point messages are not arriving through a remote message point
There are a set of checks that we can carry out to investigate why point-to-point messages are not arriving at a destination on a service integration bus, when the messages are being routed through a remote message point. Follow the steps in Investigating why point-to-point messages are not arriving, which contains preliminary checks and investigative tasks that you should carry out before proceeding with this task.
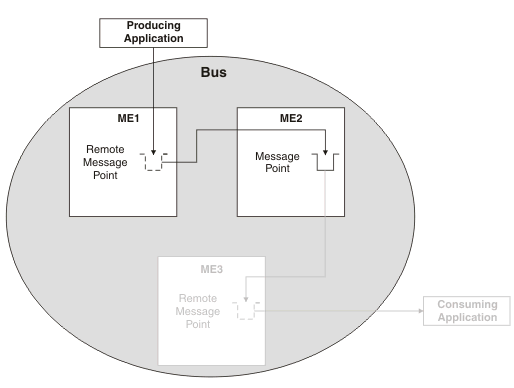
You should undertake this task as part of Investigating why point-to-point messages are not arriving. This task explains how to investigate the flow of messages in a point-to-point messaging scenario where the messages are being routed through a remote message point. In the following diagram, a bus contains three messaging engines, ME1, ME2 and ME3. The producing application is connected to ME1 and the consuming application is connected to ME3. The messages are produced to ME1 and are routed from ME1 to ME3 through ME2. This scenario is only concerned with ME1 and ME2. ME1 hosts a remote message point that represents the message point hosted by ME2. ME1 is the messaging engine that the producing application is attached to, and ME2 is the messaging engine that is hosting the queue point.
These messaging engines are referred to in the following steps.
Figure 1. Point-to-point message production by using a remote message point
- Display the properties for ME1 by clicking Service integration > Buses > bus_name > [Topology] Messaging engines > engine_name .
- On the Runtime tab for ME1, click [Remote message points] Remote queue points, then click the remote queue point that represents the queue point on ME2. Review the value of the Current outbound messages field.
- If the number of current outbound messages is greater than
zero, messages have been produced but they might not have been received
by ME2.
- Check that the two messaging engines can communicate with each other, see Service integration troubleshooting: Checking the communication between two messaging engines in a bus.
- Look for previous messages on the queue. If there are previous
messages, and some or all of them are for ME2, wait a few moments
and then refresh the view.
- If some of the messages have disappeared from the queue, the system is currently delivering messages but is backlogged. Wait until the backlog has been cleared, then inspect the queue point on ME2 to see if the test message has arrived.
- If none of the messages have disappeared from the queue, the transmission
of messages might be blocked by a message that is trapped in the Committing
state. Later messages must wait for this message to be delivered, otherwise the ordering of messages will be broken.
If a message is trapped in the Committing state, that message is contained in an unresolved transaction. A resource manager, such as a database, might have hung. Resolve the issue with the resource manager. If this fails, note the Transaction ID of the message and click Servers > Server Types > WebSphere application servers > server_name > Runtime > [Additional Properties] Transaction Service to display the general properties for the transaction service. Use the Review links to resolve the transaction whose Global ID matches the transaction ID of the message.
- Examine the state of the test message:
- If the status of the test message is "Pending send", the message is waiting to be sent. ME2 might not be accepting messages.
Complete the following checks:
- Check that the two messaging engines can communicate with each other, see Service integration troubleshooting: Checking the communication between two messaging engines in a bus.
- Check that the queue point on ME2 is not full: display the runtime
properties for the queue point and compare the Current
message depth to the High message threshold.
If the current message depth is equal to the high message threshold, the messaging engine will not accept new messages until the queued
messages have been consumed. Either restart the consumer and wait
until the backlog is cleared, or delete the messages.
You will not be able to recover the messages once they have been deleted.
- Check that configuration changes have been propagated. Ensure that ME2 is aware of the existence of the queue point by deploying the latest settings to the ME2 appserver.
- If the status of the test message is "Pending acknowledgement", the message has been sent but ME2 has either not received the message, or not processed the message. Check that there are no messages in the Committing state ahead of the test message in the transmit queue, then wait a few moments and examine the queue point again to see if the test message has arrived.If there are messages that are trapped in the Committing state, resolve this problem by referring to the following point.
- If the test message (or another message) is in the Committing state, the message is contained in an unresolved transaction. A resource manager, such as a database, might have hung. Resolve the issue with the resource manager. If this fails, note the Transaction ID of the message and click Servers > Server Types > WebSphere application servers > server_name > Runtime > [Additional Properties] Transaction Service to display the general properties for the transaction service. Use the Review links to resolve the transaction whose Global ID matches the transaction ID of the message.
- If the status of the test message is "Pending send", the message is waiting to be sent. ME2 might not be accepting messages.
Complete the following checks:
- If the number of completed outbound messages is greater
than zero, messages have been produced and processed by ME2, but the test message has not appeared. Rerun the producing application and
verify the number of completed outbound messages on ME1 increases
(we might see the active outbound message count increase before the completed outbound message count increases).
- If the counts do not increase, the message was not produced at ME1. Check that the producing application is connected to this messaging engine (see Determining which messaging engine an application is connected to).
- If the counts do increase, the message arrived at ME2, but was either consumed, sent to the exception destination, or expired. Check for the presence of consumers, and complete the preliminary checks again.
- If the number of current and completed messages are both zero, check that the producing application is producing messages to this destination, by performing the relevant preliminary checks again.
Next steps
If still having problems, contact the IBM customer service representative.Last updated Nov 10, 2010 8:23:07 PM CST