Java Management Extensions
This page gives an overview of Java Management Extensions (JMX) in general and how this standard applies to WAS.
Java Management Extensions overview
Java Management Extensions (JMX) is the Java standard for managing application resources. The management architecture that is defined by JMX is divided into three levels:- The bottom level is management instrumentation. Each manageable resource is described by an interface that specifies the attributes it has, the operations it supports, and the notifications it sends. This resource is a managed bean (MBean).
- The middle level is the management agent. Each managed process contains a JMX agent that includes an MBean server, which provides a registry and access point for MBeans. Management clients must use the MBean server to access the registered MBeans.
- The top level of the architecture is defined by JMX Remote API (JSR 160). JSR 160 uses Remote Method Invocation over Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (RMI-IIOP), but is not interoperable with the RMI connector. The RMI, SOAP/HTTP, and SOAP/HTTPS connectors were created before the JSR160 spec and are supported. The Inter-Process Communications (IPC) connector is also supported.
The top level of the architecture is the distributed services level, and its role is to facilitate remote access to JMX agents. This task is accomplished through connectors, which provide a protocol-independent, location-transparent, client-side interface to the MBean server (for example, a Remote Method Invocation (RMI) connector), or protocol adapters, which provide protocol-specific, server-side access to the MBean server (for example, an HTTP adapter).

Java Management Extensions in
Java Management Extensions (JMX) is at the core of Application Server administration capabilities. The appserver contains a JMX agent. All of the system components are defined as MBeans. The JMX agent in Application Server supports the following connectors: JSR160RMI, Remote Method Invocation/Internet Inter-ORB Protocol (RMI/IIOP), Simple Object Access Protocol/Hypertext Transfer Protocol (SOAP/HTTP), Simple Object Access Protocol/Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (SOAP/HTTPS), and IPC, which provides remote access to the server resources. All of the administration tools included with Application Server use these JMX facilities to accomplish their functions.
In a stand-alone Application Server installation, servers exist and are administered individually. An admin client connects directly to the appserver in this environment.
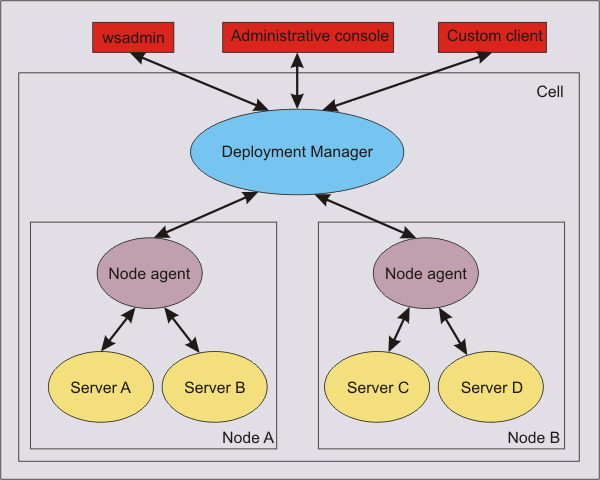
In an ND installation, a hierarchical topology groups application servers within nodes and groups nodes within a cell. Administrative servers exist at the node level (node agents) and at the cell level (the deployment manager), and act as aggregation points for the admin services in the subordinate servers.
MBeans in all servers on a node are visible through that node agent, and MBeans in all nodes are visible through the dmgr. Therefore, by connecting to the dmgr, we can invoke operations, can get and set attributes, and can receive notifications for any MBean in the cell. Application Server provides an AdminService class that reflects the standard JMX MBeanServer interface, and wraps the MBeanServer interface so that it takes part in implementing this distributed management functionality.
 Â Â Â
  Â