Plan to install WebSphere Application Client
Overview
In a traditional client server environment, the client requests a service and the server fulfills the request. Multiple clients use a single server. Clients can also access several different servers. This model persists for Java clients except that now these requests use a client run-time environment.
In this model, the client application requires a servlet to communicate with the enterprise bean, and the servlet must reside on the same machine as the WAS.
The Application Client for WebSphere Application Server, V6 consists of the following models:
- ActiveX application client
- Applet client
- J2EE application client
- Pluggable and thin application clients
The following graphic shows a topology for installing the Application Client and using client applications:
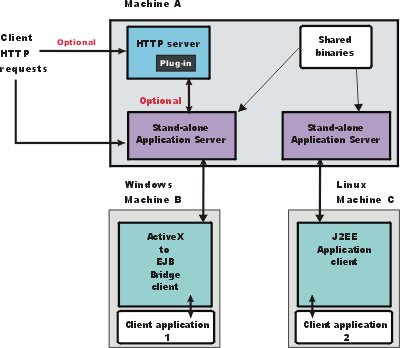
The example shows two types of application clients installed in a topology that uses client applications to access applications and data on Machine A:
- The ActiveX application client on Machine B is a Windows only client that uses the Java Native Interface (JNI) architecture to programmatically access the JVM API. The JVM code exists in the same process space as the ActiveX application...
- Visual Basic
- VBScript
- Active Server Pages (ASP)
...and remains attached to the process until that process terminates.
- The J2EE application client on Machine C is a Java application program that accesses...
- enterprise beans
- JDBC APIs
- JMS message queues
The application program must configure the execution environment of the J2EE application client and use the JNDI name space to access resources.
Use the following procedure as a example of installing the Application Client.
Procedure
- Install the WAS product from your product
CD on Machine A to establish the core product files.
- Use the Profile Management tool to create both stand-alone appserver profiles.
- Use the console of each appserver to deploy any user applications.
- Use the console of each appserver to create a Web server configuration for the Web server.
- Use the console of each appserver to regenerate each plugin-cfg.xml file in the local Web server configuration.
- Optional: Install the IBM HTTP Server from the product CD on Machine A.
- Optional: Use the Plug-ins installation wizard to install the plug-in for IBM HTTP Server on Machine A.
The wizard automatically configures the HTTP Server to communicate with the first appserver.
- Install the Application Client package from the product disc.
The diagram shows two different types of application clients on two different operating systems. Although this example shows two application clients, you do not have to install two application clients to have a working system. Each application client is fully functional and works independently of the other.
Optionally install the Application Client from your product CD on Machine B.
- Select the Custom installation type.
- Select the ActiveX to EJB Bridge feature.
- Select to add the Java run time to the system path.
- Select the Java run time as the default JRE, which adds the Java run time path to the beginning of the system path.
Optionally install the Application Client from your product CD on Machine C.
- Select the Custom install type.
- Select the J2EE application client feature.
- Select the Custom installation type.
Results
This topic can help you plan run-time environments for client applications.
What to do next
See Application Client for WAS for information about creating client applications.
Related information
Planning the installationApplication Client for WAS