Connecting through another queue manager
The WebSphere MQ Explorer allows you to connect to a queue manager through an intermediate queue manager, to which the WebSphere MQ Explorer is already connected. In this case, the WebSphere MQ Explorer puts PCF command messages to the intermediate queue manager, specifying the following:
- The ObjectQMgrName parameter in the object descriptor (MQOD) as the name of the target queue manager. For more information on queue name resolution, see the WebSphere MQ Application Programming Guide.
- The UserIdentifier parameter in the message descriptor (MQMD) as the local userId.
If the connection is then used to connect to the target queue manager via an intermediate queue manager, the userId is flowed in the UserIdentifier parameter of the message descriptor (MQMD) again. In order for the MCA listener on the target queue manager to accept this message, either the MCAUSER attribute must be set, or the userId must already exist with put authority.
The command server on the target queue manager puts messages to the transmission queue specifying the userId in the UserIdentifier parameter in the message descriptor (MQMD). For this put to succeed the userId must already exist on the target queue manager with put authority.
The following example shows you how to connect a queue manager, through an intermediate queue manager, to the WebSphere MQ Explorer.
Establish a remote administration connection to a queue manager. Verify that the:
- Queue manager on the server is active and has a server-connection channel (SVRCONN) defined.
- Listener is active.
- Command server is active.
- SYSTEM.MQ EXPLORER.REPLY.MODEL queue has been created and that you have sufficient authority.
- Queue manager listeners, command servers, and sender channels are started.
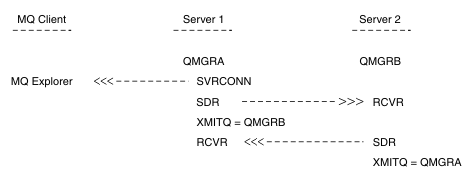
In this example:
- WebSphere MQ Explorer is connected to queue manager QMGRA (running on Server1) using a client connection.
- Queue manager QMGRB on Server2 can be now connected to WebSphere MQ Explorer through an intermediate queue manager (QMGRA)
- When connecting to QMGRB with WebSphere MQ Explorer, select QMGRA as the intermediate queue manager
In this situation, there is no direct connection to QMGRB from WebSphere MQ Explorer; the connection to QMGRB is through QMGRA.
Queue manager QMGRB on Server2 is connected to QMGRA on Server1 using sender-receiver channels. The channel between QMGRA and QMGRB must be set up in such a way that remote administration is possible; see Preparing channels and transmission queues for remote administration.
Parent topic:
Security
fa12130_
Home