Security
Liberty security provides protection for web resources in accordance with the Servlet 3.0 specification and EJB resources in accordance with the ejbLite 3.1 specification. The Liberty security also provides protection for the JMX connections when we are using the REST connector.
The following diagram shows a typical security process involved when accessing a protected web resource. To make the security process work, configure the appropriate security features and the configurations required for the authentication and authorization. As the following image shows, the WebSecurity Collaborator uses authentication and authorization services to authenticate and authorize access to the web resource in the web container.
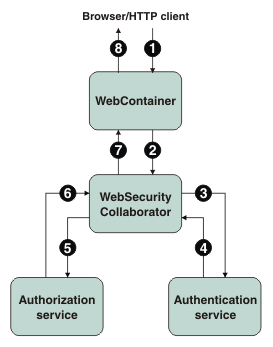
In the previous figure:
- An HTTP client requests a web resource in the WebContainer.
- The WebContainer delegates the security check to the WebSecurity Collaborator.
- The WebSecurity Collaborator prompts the user to enter credentials if absent, and uses the Authentication service to authenticate the user.
- The Authentication service authenticates, creates, and returns the subject if authenticated successfully. Otherwise, the Authentication service reports an exception for the authentication failure.
- The WebSecurity Collaborator uses the Authorization service to perform a user authorization check.
- The Authorization service returns the authorization result to the WebSecurity Collaborator.
- The WebSecurity Collaborator returns the result of the security check about whether the user is authorized.
- The WebContainer serves or rejects the requested resource.
Quick start
With the quickStartSecurity element, we can configure a single user security environment in Liberty.
See Quick overview of security for details of how the security workflow is when we use the quickStartSecurity element, and Getting started with security in Liberty for a sample task.
Authentication
Authentication confirms the identity of a user. The most common form of authentication is user name and password, such as through either basic authentication or form login for web applications. When a user is authenticated, the source of a request is represented as a Subject object at the run time. This process involves performing access control checks when a user accesses a resource, based on the authorization rules configured for the resource.
See Authentication for more concepts and Authenticating users in Liberty for detailed tasks.
Authorization
Authorization determines whether to grant a user access to resources within the system. The Java EE model uses subjects, resources, and roles to determine what can and cannot be allowed. This process involves checking the user credentials such as the user ID and password, certificates, and tokens, and creating a subject based on the authenticated user.
See Authorization for more concepts and Authorize access to resources in Liberty for detailed tasks.
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
SSL provides transport level security. See Enable SSL communication in Liberty
Single Sign-On (SSO)
SSO enables access to applications without the user being prompted to login multiple times. See Concept of SSO and Customizing SSO configuration using LTPA cookies in Liberty.
Web security-related properties
There are many configuration properties we can configure as part of web security, such as SSO and client certificate authentication, for the applications. See Customizing SSO configuration using LTPA cookies in Liberty and Web Service Security for available attributes and see Configure web security related properties in Liberty for some examples.
Security public APIs
Liberty contains public APIs used to implement security functions. The security public APIs in Liberty are a subset of the WebSphere Application Server traditional security public APIs. The main classes are WSSecurityHelper, WSSubject, and RegistryHelper. These classes contain a subset of the methods available in the WebSphere Application Server traditional versions. There is also a new class WebSecurityHelper.
See Liberty: Security public APIs.
The Java API documentation for each Liberty API is detailed in the Program interfaces (Javadoc) section of the online IBM documentation, and is also available as a separate .zip file in one of the javadoc subdirectories of the ${wlp.install.dir}/dev directory.
See Develop extensions to the Liberty security infrastructure for some examples.
Management security
Management security means we can manage Liberty using a remote JMX client. To secure remote connections using the REST connector, see Connecting to Liberty using JMX. We can also develop our own JMX client application as described in Develop a JMX Java client for Liberty.
z/OS security
The System Authorization Facility (SAF) on the z/OS platform is supported in Liberty for authentication and authorization.
See Enable z/OS authorized services on Liberty for z/OS and Configure SAF Authorization for detailed tasks.
Authentication aliases
Authentication data aliases provide the security support for database connectivity.
See Configure authentication aliases for Liberty.
Configuration examples and samples
There are several security configuration examples on the Open Liberty website for reference when configuring security for the applications on Liberty.
Security compatibility and differences
We can learn about the main differences in the security capability between the WebSphere Application Server traditional and Liberty.
See Configuration differences between the WebSphere Application Server traditional and Liberty: security.
Configure Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
After selecting the LDAP User Registry item to add to the server configuration, the LDAP User Registry Details panel will display a list for the supported LDAP server types. If we select a supported LDAP server type, the LDAP filters associated with the selected LDAP server type will not automatically pre-populated. Each of the supported LDAP server types has a default set of filters defined. After the LDAP User Registry item and server type has been added, the associated LDAP filters can be configured by selecting the LDAP User Registry configuration and adding the required LDAP filter:
- Active Directory LDAP filters
- Custom LDAP filters
- Domino LDAP filters
- eDirectory LDAP filters
- IBM Directory Server LDAP filters
- iPlanet LDAP filters
- Netscape LDAP filters
- SecureWay LDAP filters
Selecting any of the LDAP filters will display the default values for the filter types:
- user filter
- group filter
- user ID map
- group ID map
- group member ID map
If the default filters are used, the server.xml file is not updated with any filter information. If any of the filters are changed, only the changed filter types will be updated in the server.xml.
Note: If we do not specify or select a reference ID using the Browse button, the default filters associated with selected LDAP server type will be used.
Alternatively, we can add an LDAP filter to the server configuration. An ID must be specified to associate the reference to this particular filter configuration, in order to associate it with the LDAP User Registry configuration. If this method of configuring the LDAP filters is used, the reference ID will then be selected on the LDAP User Registry Details panel (located using the Browse button under the respective LDAP filter type).
If we are using Eclipse-based developer tools to configure LDAP, verify the configuration saved against the samples in wlp/templates/config/ldapRegistry.xml.
See Configure LDAP user registries in Liberty.
Troubleshooting
Use the troubleshooting information to solve security-related problems when we use Liberty.
See Troubleshooting security and Troubleshooting LDAP.
Tools
- Editing the Liberty configuration using developer tools.
- Configure TAI on Liberty using developer tools and Configure JAAS on Liberty using developer tools.
Security bulletins
To avoid preventable security issues, stay up to date on the most current maintenance options for the product.- Subscribe to My Notifications to receive notifications of security bulletins for WebSphere Application Server. These notifications include important product support alerts.
- Refer to the Update Strategy for fix packs. Take special note of the recommended update path.
- Refer to the security fixes for WebSphere Application Server Liberty, WebSphere Application Server traditional, IBM HTTP Server, and Java
See
- Quick overview of security
- Authentication
- Authorization
- Security on Liberty application client container
- Java 2 Security
- Liberty: Security public APIs
- Configuration differences between the WebSphere Application Server traditional and Liberty: security
- Limits to password encryption
Parent topic: Secure Liberty and its applications
Related information