WebSphere eXtreme Scale Administration Guide > Configure WebSphere eXtreme Scale
|
| |
Loaders
With an eXtreme Scale Loader plug-in, an eXtreme Scale map can behave as a memory cache for data that is typically kept in a persistent store on either the same system or another system. Typically, a database or file system is used as the persistent store. A remote Java™ virtual machine (JVM) can also be used as the source of data, allowing hub-based caches to be built using eXtreme Scale. A loader has the logic for reading and writing data to and from a persistent store.
Overview
Loaders are backing map plug-ins that are invoked when changes are made to the backing map or when the backing map is unable to satisfy a data request (a cache miss). See Cache scenarios for an overview on how eXtreme Scale can interact with a loader.
Figure 1. Loader
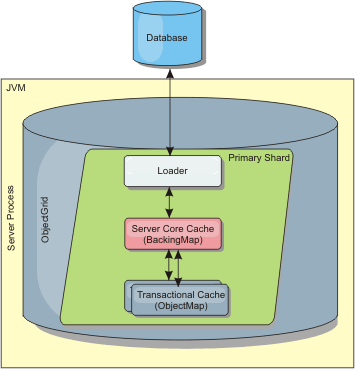
Two built-in loaders can greatly simplify integration with relational database back ends. The JPA loaders utilize the Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) capabilities of both the OpenJPA and Hibernate implementations of the Java Persistence API (JPA) specification. See JPA loaders for more information.
Use a loader
To add a Loader into the BackingMap configuration, you can use programmatic configuration or XML configuration. A loader has the following relationship with a backing map.
- A backing map can have only one loader.
- A client backing map (near cache) cannot have a loader.
- A loader definition can be applied to multiple backing maps, but each backing map has its own loader instance.
For more information, see Write a Loader.
XML configuration approach to plug in a Loader
An application-provided Loader can be plugged in by using an XML file. The following example demonstrates how to plug in the "MyLoader" loader into the "map1" backing map. You must specify the className for your loader, the database name and connection details, and the isolation level properties. You can use the same XML structure if you are only using a preloader by specifying the preloader classname instead of a complete loader classname.
Loader configuration with XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<objectGridConfig xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://ibm.com/ws/objectgrid/config ../objectGrid.xsd"
xmlns="http://ibm.com/ws/objectgrid/config">
<objectGrids>
<objectGrid name="grid">
<backingMap name="map1" pluginCollectionRef="map1" lockStrategy="OPTIMISTIC" />
</objectGrid>
</objectGrids>
<backingMapPluginCollections>
<backingMapPluginCollection id="map1">
<bean id="Loader" className="com.myapplication.MyLoader">
<property name="dataBaseName"
type="java.lang.String"
value="testdb"
description="database name" />
<property name="isolationLevel"
type="java.lang.String"
value="read committed"
description="iso level" />
</bean>
</backingMapPluginCollection>
</backingMapPluginCollections>
</objectGridConfig>
Programmatically plug in a Loader
You can only use a programmatic configuration with local, in-memory grids. The following snippet of code demonstrates how to plug an application-provided Loader into the backing map for map1 using the ObjectGrid API:
Programmatic configuration of a Loader
import com.ibm.websphere.objectgrid.ObjectGridManagerFactory;
import com.ibm.websphere.objectgrid.ObjectGridManager;
import com.ibm.websphere.objectgrid.ObjectGrid;
import com.ibm.websphere.objectgrid.BackingMap;
ObjectGridManager ogManager = ObjectGridManagerFactory.getObjectGridManager();
ObjectGrid og = ogManager.createObjectGrid( "grid" );
BackingMap bm = og.defineMap( "map1" );
MyLoader loader = new MyLoader();
loader.setDataBaseName("testdb");
loader.setIsolationLevel("read committed");
bm.setLoader( loader );
This snippet assumes that the MyLoader class is the application-provided class that implements the com.ibm.websphere.objectgrid.plugins.Loader interface. Because the association of a Loader with a backing map cannot be changed after ObjectGrid is initialized, the code must be run before invoking the initialize method of the ObjectGrid interface that is being called. An IllegalStateException exception occurs on a setLoader method call if it is called after initialization has occurred.
The application-provided Loader can have set properties. In the example, the MyLoader loader is used to read and write data from a table in a relational database. The loader must specify the name of the database and the SQL isolation level. The MyLoader loader has the setDataBaseName and setIsolationLevel methods that allow the application to set these two Loader properties.
- Loader configuration
Implementing a loader requires configuration for several attributes. - Write-behind caching support
You can use write-behind caching to reduce the overhead that occurs when updating a back-end database. Write-behind caching queues updates to the Loader plug-in. - Configure JPA loaders
A Java Persistence API (JPA) Loader is a plug-in implementation that uses JPA to interact with the database. - Configure a JPA time-based data updater
You can configure a time-based database update using XML for a local or distributed eXtreme Scale configuration. You can also configure a local configuration programmatically.
Parent topic
Configure WebSphere eXtreme ScaleRelated tasks
Configure a JPA time-based data updater
Related reference
Write-behind dumper class sample code