|
|
|
| |
Hessian requests
Overview
Hessian is a binary web service protocol developed by Caucho Technology, Inc. It allows remote procedure calls to be executed between the client and server, using the standard Hessian RPC (Remote Procedure Call) communication or specific Frameworks such as Spring Remoting (Spring HTTP Invoker). The data exchange is carried out in binary and encapsulated in the HTTP protocol.
The Hessian module allows load testing web applications programmed in Java and using the standard Hessian RPC communication or specific Frameworks such as Spring Remoting (Hessian).
To be able to handle Hessian requests, you will need to purchase the optional Java Serialization module. This module is included in the demo version of NeoLoad.
- Warning: Hessian module supports only RPC communication over HTTP.
Dependent libraries
When recording Hessian requests, you will need to load the Java classes for the objects exchanged, as well as the client interfaces for the called services. See Hessian.
Recording
The following diagram shows how the Hessian module works during recording:

The binary data exchanged between the client and server passes through the recording proxy. The Hessian module comes into play as the data travels through the proxy, analyzing and decoding the requests. Once translated into XML, the requests are inserted in the project.
- Warning: Only requests with the Content-Type: x-application/hessian or application/x-hessian headers are recorded.
Runtime
The following diagram shows how the Hessian module works during a test run:
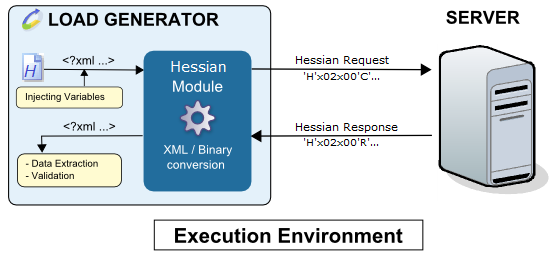
The XML request variables are evaluated and the module engine translates the XML to binary data. This data is then sent to the server. The binary response received is translated into XML, after which the validity checks and Variable Extractors in the played request are executed.