Any queue manager can access messages
Any queue manager in the queue-sharing group can access a shared queue. This means that we can put a message on to a shared queue on one queue manager, and get the same message from the queue from a different queue manager. This provides a rapid mechanism for communication within a queue-sharing group that does not require channels to be active between queue managers.
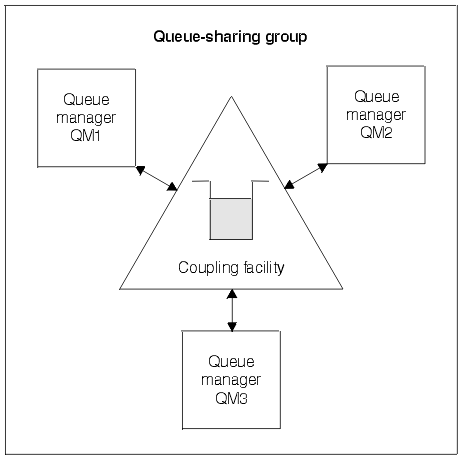
Large messages (>63KB) have a placeholder stored in the Coupling Facility (4K), and their message data stored in DB2. Figure 3 shows three queue managers and a Coupling Facility, forming a queue-sharing group. All three queue managers can access the shared queue in the Coupling Facility.
An application can connect to any of the queue managers within the queue-sharing group. Because all the queue managers in the queue-sharing group can access all the shared queues, the application does not depend on the availability of a specific queue manager; any queue manager in the queue-sharing group can service the queue.
This gives greater availability because all the other queue managers in the queue-sharing group can continue processing the queue if one of the queue managers has a problem.