Command Reference
weblogic.Server Command-Line Reference
The weblogic.Server class is the main class for a WebLogic Server instance. You start a server instance by invoking weblogic.Server in a Java command. You can invoke the class directly in a command prompt (shell), indirectly through scripts, or through the Node Manager.
Oracle recommends using java weblogic.Server primarily for initial development but not as a standard mechanism for starting production systems for the following reasons:
- java weblogic.Server will not function if you select a product directory outside of the BEA home directory.
- When executing java weblogic.Server, patches will not be recognized by the WebLogic Server run time.
This section describes the following:
- Required Environment and Syntax for weblogic.Server
- Default Behavior
- weblogic.Server Configuration Options
- Using the weblogic.Server Command Line to Start a Server Instance
- Using the weblogic.Server Command Line to Create a Domain
- Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line
For information about using scripts to start an instance of WebLogic Server, see Starting an Administration Server with a Startup Script and Starting Managed Servers With a Startup Script in Managing Server Startup and Shutdown.
For information about using the Node Manager to start an instance of WebLogic Server, see Using Node Manager to Control Servers in the Node Manager Administrator's Guide.
Required Environment and Syntax for weblogic.Server
This section describes the environment that set up before you can start a server instance. Then it describes the syntax for invoking weblogic.Server.
Environment
To set up your environment for the weblogic.Server command:
- Install and configure the WebLogic Server software, as described in the Installation Guide
- If desired, modify the CLASSPATH environment variable, as described in Modifying the Classpath.
- Include a Java Virtual Machine (JVM) in your PATH environment variable. You can use any JVM that is listed in the Supported Configurations page at
http://e-docs.bea.com/platform/suppconfigs/index.html.
If you do not include a JVM in the PATH environment variable, provide a pathname for the Java executable file that the JVM provides.
Modifying the Classpath
After installation, WebLogic Server's classpath is already set, but you may choose to modify it for a number of reasons such as adding a patch to WebLogic Server, updating the version of PointBase you are using, or adding support for Log4j logging.
To apply a patch to ALL of your WebLogic Server domains without the need to modify the classpath of a domain, give the patch JAR file the name, weblogic_sp.jar, and copy it into the WL_HOME/server/lib directory. The commEnv.cmd/sh script will automatically include a JAR named weblogic_sp on the classpath for you.
If you would rather not use the name weblogic_sp.jar for your patch file or you would just like to make sure a JAR file, such as one mentioned below, comes before weblogic.jar on the classpath:
- For ALL domains, edit the commEnv.cmd/sh script in WL_HOME/common/bin and prepend your JAR file to the WEBLOGIC_CLASSPATH environment variable.
- To apply a patch to a SPECIFIC WebLogic Server domain, edit the setDomainEnv.cmd/sh script in that domain's bin directory, and prepend the JAR file to the PRE_CLASSPATH environment variable.
If you use the trial version of PointBase, an all-Java database management system, include the following files on the classpath:
WL_HOME/common/eval/pointbase/lib/pbembedded51.jar and pbclient51.jar
If you use WebLogic Enterprise Connectivity, include the following files on the classpath:
WL_HOME/server/lib/wlepool.jar
WL_HOME/server/lib/wleorb.jar
If you use Log4j logging, include the following file on the classpath:
WL_HOME/server/lib/log4j.jar
The shell environment in which you run a server determines which character you use to separate path elements. On Windows, you typically use a semicolon (;). In a BASH shell, you typically use a colon (:).
Syntax
The syntax for invoking weblogic.Server is as follows:
java [options] weblogic.Server [-help]
The java weblogic.Server -help command returns a list of frequently used options.
Default Behavior
If you have set up the required environment described in Environment, when you enter the command java weblogic.Server with no options, WebLogic Server does the following:
- Looks in the domain_name/config directory for a file named config.xml.
- If config.xml exists in the domain_name/config directory, WebLogic Server does the following:
- If only one server instance is defined in config/config.xml, it starts that server instance.
For example, if you issue java weblogic.Server from WL_HOME\samples\domains\medrec, WebLogic Server starts the MedRec server.
- If there are multiple server instances defined in config/config.xml:
- If an Administration Server is defined, it looks for the server with that name.
- If an Administration Server is not defined, it looks for a server configuration named myserver. If it finds such a server configuration, it starts the myserver instance.
- If it does not find a server named myserver, WebLogic Server exits the weblogic.Server process and generates an error message.
- If only one server instance is defined in config/config.xml, it starts that server instance.
- If there is no config.xml file in the current directory, WebLogic Server prompts you to create one. If you respond y, WebLogic Server does the following:
- Creates a server configuration named myserver, and persists the configuration in a file named config/config.xml.
Any options that you specify are persisted to the config.xml file. For example, if you specify -Dweblogic.ListenPort=8001, then WebLogic Server saves 8001 in the config.xml file. For any options that you do not specify, the server instance uses default values.
You can configure WebLogic Server to make backup copies of the configuration files. This facilitates recovery in cases where configuration changes need to be reversed or the unlikely case that configuration files become corrupted. For more information, see Configuration File Archiving in Understanding Domain Configuration.
- Uses the username and password that you supply to create a user with administrative privileges. It stores the definition of this user along with other basic, security-related data in domain_name/security files named DefaultAuthenticatorInit.ldift, DefaultRoleMapperInit.ldift, and SerializedSystemIni.dat.
WebLogic Server also encrypts and stores your username and password in a server_name/security/boot.properties file, which enables you to bypass the login prompt during subsequent instantiations of the server. For more information, see Boot Identity Files in Managing Server Startup and Shutdown.
- Creates two scripts, bin/startWebLogic.cmd and bin/startWebLogic.sh, that you can use to start subsequent instantiations of the server. You can use a text editor to modify startup options such as whether the server starts in production mode or development mode. The startWebLogic script contains comments that describe each option.
Note that the server starts as an Administration Server in a new domain. There are no other servers in this domain, nor are any of your deployments or third-party solutions included. You can add them as you would add them to any WebLogic domain.
- Creates a server configuration named myserver, and persists the configuration in a file named config/config.xml.
weblogic.Server Configuration Options
You can use weblogic.Server options to configure the attributes of a server instance. The following attributes are commonly used when starting a server instance:
WebLogic Server provides other startup options that enable you to temporarily override a server's saved configuration. For information about these startup options, see Options that Override a Server's Configuration.
Unless you are creating a new domain as described in Using the weblogic.Server Command Line to Create a Domain, all startup options apply to the current server instantiation; they do not modify the persisted values in an existing config.xml file. Use the Administration Console or WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) to modify the config.xml file. See Creating Domains Using WLST Offline in WebLogic Scripting Tool.
For information on verifying the WebLogic Server attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
JVM Parameters
The following table describes frequently used options that configure the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) in which the server instance runs. For a complete list of JVM options, see the documentation for your specific JVM. For a list of JVMs that can be used with WebLogic Server, see the Supported Configurations page at http://e-docs.bea.com/platform/suppconfigs/index.html.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -Xms and -Xmx | Specify the minimum and maximum values (in megabytes) for Java heap memory. For example, you might want to start the server with the default allocation of 256 megabytes of Java heap memory to the WebLogic Server. To do so, start the server using the java -Xms256m and -Xmx512m options. The values assigned to these parameters can dramatically affect the performance of your WebLogic Server and are provided here only as general defaults. In a production environment you should carefully consider the correct memory heap size to use for your applications and environment. |
| -classpath | The minimum content for this option is described under Modifying the Classpath. Instead of using this argument, you can use the CLASSPATH environment variable to specify the classpath. |
| -client
-server | Used by some JVMs to start a HotSpot virtual machine, which enhances performance. For a list of JVMs that can be used with WebLogic Server, see the Supported Configurations page at http://e-docs.bea.com/platform/suppconfigs/index.html. |
| -Dfile.encoding=Canonical Name weblogic.Server | To display special characters on Linux browsers, set the JVM's file.encoding system property to ISO8859_1. For example, java -Dfile.encoding=ISO8859_1 weblogic.Server. For a complete listing, see Sun's “ Supported Encodings” page for J2SE 1.6. |
Location of Configuration Data
All server instances must have access to configuration data. The following table provides options for indicating the location of this data.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -Dbea.home=bea_home | Location of the BEA home directory, which contains essential information. By default, weblogic.Server determines the location of the BEA home directory based on values in the classpath. |
| -Dweblogic.RootDirectory=path | Specifies the server's root directory. See A Server's Root Directory in Understanding Domain Configuration. By default, the root directory is the directory from which you issue the start command. |
| -Dweblogic.ConfigFile=
file_name |
This option was removed as of WebLogic Server 9.0. |
-Dweblogic.ConfigFile=myfile.xml If you do not specify this value, the default is config/config.xml in the server's root directory.
For information on how a Managed Server retrieves its configuration data, see the -Dweblogic.management.server entry in Table 3-3.
The Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Example
The following example starts a Managed Server instance named SimpleManagedServer. Specifying a config.xml file is not valid because Managed Servers contact the Administration Server for their configuration data. Multiple instances of WebLogic Server can use the same root directory. However, if your server instances share a root directory, make sure that all relative filenames are unique. In this example, SimpleManagedServer shares its root directory with SimpleServer. The command itself is issued from the D:\ directory after running WL_HOME\server\bin\setWLSEnv.cmd:
D:\> java -Dweblogic.Name=SimpleManagedServer -Dweblogic.management.server=http://localhost:7001 -Dweblogic.RootDirectory=c:\my_domains\SimpleDomain weblogic.Server
Options that Override a Server's Configuration
In most cases, you do not use startup options to override the configuration that is saved in the domain's config.xml file. However, in some extraordinary cases you might need to do so.
| Caution: | When you use a startup option to override a configuration value, the server instance uses this value for the duration of its life cycle. Even if you use the Administration Console, the WebLogic Scripting Tool, or some other utility to change the value in the configuration, the value will remain overridden until you restart the server without using the override. |
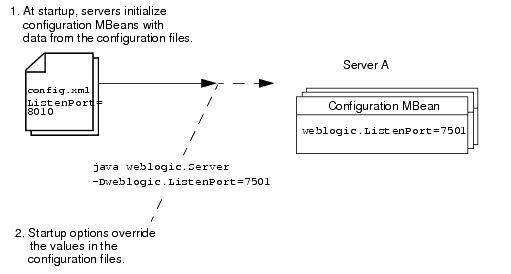
For example, in a production environment, your organization might have a policy against modifying the domain's config.xml file, but you need to shut down the Administration Server and restart it using a temporary listen port. In this case, when you use the weblogic.Server command to start the Administration Server, you can include the -Dweblogic.ListenPort=7501 startup option to change the listen port for the current server session. The server instance initializes its configuration MBeans from the config.xml file but substitutes 7501 as the value of its listen port. When you subsequently restart the server without passing the startup option, it will revert to using the value from the config.xml file, 8010. (See Figure 3-1.) Figure 3-1 Overriding config.xml Values
The following options temporarily override a server's configuration:
- Server Communication
- SSL
- Security
- Message Output and Logging
- Other Server Configuration Options
- Clusters
Server Communication
The following table describes the options for configuring how servers communicate.
portnumber
portnumber
discover={true | false}
This option was removed as of WebLogic Server 9.0. Determines whether an Administration Server recovers control of a domain after the server fails and is restarted. A true value causes an Administration Server to communicate with all known Managed Servers and inform them that the Administration Server is running. A false value prevents an Administration Server from communicating with any Managed Servers that are currently active in the domain.
| Caution: | Specify false for this option only in the development environment of a single server. Specifying false can cause server instances in the domain to have an inconsistent set of deployed modules. |
The Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
SSL
Each Weblogic Server instance uses an instance of weblogic.management.configuration.SSLMBean to represent its SSL configuration. All of the options in the following table that start with -Dweblogic.security.SSL modify the configuration of the server's SSLMBean. For example, the -Dweblogic.security.SSL.ignoreHostnameVerification option sets the value of the SSLMBean's ignoreHostnameVerification attribute.
The following table describes the options for configuring a server to communicate using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL).
HostnameVerifier=
hostnameverifierimplmentation
To start a server instance so that it uses a FIPS-compliant (FIPS 140-2) crypto module in its SSL implementation, also ensure that jsafeFIPS.jar is added to the PRE_CLASSPATH variable in the server start script (for example, startWebLogic.cmd/sh).
sessionCache.ttl=
sessionCacheTimeToLive
- The minimum value is 1
- The maximum value is Integer.MAX_VALUE
- The default value is 90000
pkpassword=pkpassword
trustedCAKeyStore=path
The Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Setting Additional SSL Attributes
To set additional SSL attributes from the startup command, do the following:
- To determine which SSL attributes can be configured from startup options, view the WebLogic Server Javadoc for the SSLMBean and ServerMBean. The Javadoc also indicates valid values for each attribute.
Each attribute that SSLMBean and ServerMBean expose as a setter method can be set by a startup option.
- To set attributes in the SSLMBean, add the following option to the start command:
-Dweblogic.ssl.attribute-name=valuewhere attribute-name is the name of the MBean's setter method without the set prefix.
- To set attributes in the ServerMBean, add the following option to the start command:
-Dweblogic.server.attribute-name=valuewhere attribute-name is the name of the MBean's setter method without the set prefix.
For example, the SSLMBean exposes its Enabled attribute with the following setter method:
setEnabled()
To enable SSL for a server instance named MedRecServer, use the following command when you start MedRecServer:
java -Dweblogic.Name=MedRecServer
-Dweblogic.ssl.Enabled=true weblogic.Server
The Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Security
The following table describes the options for configuring general security parameters.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -Dweblogic.management.
username=username | Specifies the username under which the server instance will run. The username must belong to a role that has permission to start a server. For information on roles and permissions, see Users, Groups, an Security Roles in Securing WebLogic Resources. This option prevents a server instance from using any boot identity file and overrides other startup options that cause a server to use boot identity files. For more information, see Boot Identity Files in Managing Server Startup and Shutdown. |
| -Dweblogic.management.
password=password | Specifies the user password.
This option prevents a server instance from using any boot identity file and overrides other startup options that cause a server to use boot identity files. For more information, see
Boot Identity Files in Managing Server Startup and Shutdown.
If you supply the password, but no username, you will be prompted for both the username and the password. |
StoreBootIdentity=true
BootIdentityFile=filename
-Dweblogic.system.BootIdentityFile=
WL_HOME\mydomain\servers\myserver\security\boot.properties If you do not specify a filename, a server instance or the weblogic.Admin SHUTDOWN and FORCESHUTDOWN commands use the boot.properties file in the server's root directory. If there is no boot identity file:
- When starting a server, the server instance prompts you to enter a username and password.
- When using the weblogic.Admin SHUTDOWN and FORCESHUTDOWN commands, use the -username and -password arguments to provide user credentials.
The weblogic.Admin utility is deprecated in WebLogic Server 9.0. Oracle recommends that you use the WebLogic Scripting Tool (WLST) for equivalent functionality such as SHUTDOWN and FORCESHUTDOWN. For more information on using these commands, see “Life Cycle Commands” in the WLST Command and Variable Reference.
RemoveBootIdentity=true
UserName=name
filename
fullyDelegateAuthorization=true
anonymousAdminLookupEnabled=true
identityAssertionTTL=seconds
<insert the location of your policy file here> -Djavax.security.jacc.PolicyConfigurationFactory.provider=
weblogic.security.jacc.simpleprovider.PolicyConfigurationFactoryImpl -Djavax.security.jacc.policy.provider=
weblogic.security.jacc.simpleprovider.SimpleJACCPolicy -Dweblogic.security.jacc.RoleMapperFactory.provider=
weblogic.security.jacc.simpleprovider.RoleMapperFactoryImpl
maxSize=<max bytes>
changeLogThreshold=<number of entries>
The Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Message Output and Logging
The following table describes options for configuring a server instance's message output.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -Dweblogic.Stdout="filename" | Redirects the server and JVM's standard output stream to a file. You can specify a pathname that is fully qualified or relative to the WebLogic Server root directory. For more information, see Redirect JVM output in the Administration Console Online Help. |
| -Dweblogic.Stderr="filename" | Redirects the server and JVM's standard error stream to a file. You can specify a pathname that is fully qualified or relative to the WebLogic Server root directory. For more information, see Redirecting JVM output in Configuring Log Files and Filtering Log Messages. |
| -Dweblogic.
AdministrationMBeanAuditingEnabled= {true | false} | Determines whether the Administration Server emits configuration auditing log messages when a user changes the configuration or invokes management operations on any resource within a domain. By default, the Administration Server does not emit configuration auditing messages. See “ Enable configuration auditing” in the Administration Console Online Help. |
The Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Setting Logging Attributes
Each Weblogic Server instance uses an instance of weblogic.management.configuration.LogMBean to represent the configuration of its logging services.
To set values for LogMBean attributes from the startup command, do the following:
- To determine which log attributes can be configured from startup options, view the WebLogic Server Javadoc for the LogMBean. The Javadoc also indicates valid values for each attribute.
Each attribute that the LogMBean exposes as a setter method can be set by a startup option.
- Add the following option to the start command:
-Dweblogic.log.attribute-name=valuewhere attribute-name is the name of the MBean's setter method without the set prefix.
The LogMBean exposes its FileName attribute with the following setter method:
setFileName()
To specify the name of the MedRecServer instance's local log file, use the following command when you start MedRecServer:
java -Dweblogic.Name=MedRecServer
-Dweblogic.log.FileName="C:\logfiles\myServer.log"
weblogic.Server
The Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Other Server Configuration Options
The following table describes options for configuring additional attributes of a server instance.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -Dweblogic.Name=
servername | Name of the server instance that you want to start. The specified value must refer to the name of a server that has been defined in the domain's config.xml file. |
| -Dweblogic.ProductionModeEnabled=
{true | false} | This attribute is deprecated in WebLogic Server 9.0.
Determines whether a server starts in production mode.
A true value prevents a WebLogic Server from automatically deploying and updating applications that are in the domain_name/autodeploy directory.
If you do not specify this option, the assumed value is false.
To enable production mode, you can use WLST to set DomainMBean.isProductionModeEnabled to true, or use the Administration Console. See
Change to production mode in the Administration Console Online Help.
It is recommended that you enable production mode via the Administration Console or in config.xml. You should only enable production mode from the command line on the Administration Server. |
It is important to note that when ProductionModeEnabled is set from the command line on the Administration Server, this value is propogated to all managed servers.
startupMode=STARTUPMODE
- STANDBY starts a server and places it in the STANDBY state. See
STANDBY state in Managing Server Startup and Shutdown.
To use this startup argument, the domain must be configured to use the domain-wide administration port.
For information about administration ports, see “ Administration Port and Administrative Channel” in Configuring WebLogic Server Environments and Configure the domain-wide administration port in the Administration Console Online Help.
- ADMIN starts a server and places it in the ADMIN state. See ADMIN state in Managing Server Startup and Shutdown.
maxentityrefs=numerical-value
The Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line.
Clusters
The following table describes options for configuring additional attributes of a cluster.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -Dweblogic.cluster.
multicastAddress | Determines the Multicast Address that clustered servers use to send and receive cluster-related communications. By default, a clustered server refers to the Multicast Address that is defined in the config.xml file. Use this option to override the value in config.xml.
The Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line. For information on verifying the attribute values that you set, see Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line. |
Using the weblogic.Server Command Line to Start a Server Instance
A simple way to start a server instance is as follows:
- In a command shell, set up the required environment variables by running the following script:
WL_HOME\server\bin\setWLSEnv.cmd (on Windows)
WL_HOME/server/bin/setWLSEnv.sh (on UNIX)where WL_HOME is the directory in which you installed the WebLogic Server software.
- In the command shell, change to the root of the domain directory, usually BEA_HOME\user_projects\domains\DOMAIN_NAME. For example, change to the WL_HOME\samples\domains\medrec directory.
- To start an Administration Server, enter the following command:
java weblogic.ServerThe password you use must be a string of at least 8 case-sensitive characters. The space character is not supported. For more information, see “ Configure an Administrator Username and Password” in Creating WebLogic Domains Using the Configuration Wizard.
- If the domain's Administration Server is already running, and if you have already defined a Managed Server in the config.xml file, you can start a Managed Server as follows:
java -Dweblogic.Name=managed-server-name
-Dweblogic.management.server=url-for-Administration-Server
weblogic.ServerFor example, if you create a Managed Server named MedRecManagedServer in the MedRec domain, you can enter the following command:
java -Dweblogic.Name=MedRecManagedServer
-Dweblogic.management.server=localhost:7011
weblogic.Server
Using the weblogic.Server Command Line to Create a Domain
You can use weblogic.Server to create a domain that contains a single server instance. You cannot use weblogic.Server to add Managed Server instances to a domain, nor can you use weblogic.Server to modify an existing domain.
As described in Default Behavior, if weblogic.Server is unable to find a config.xml file, it offers to create the file. Any command option that you specify and that corresponds to an attribute that is persisted in the config.xml file will be persisted. For example, the -Dweblogic.Name and -Dweblogic.Domain options specify the name of a server configuration and the name of a domain. If weblogic.Server is unable to find a config.xml file, both of these values are persisted in config.xml. However, the -Dweblogic.system.BootIdentityFile option, which specifies a file that contains user credentials for starting a server instance, is not an attribute that the config.xml file persists.
To create and instantiate a simple example domain and server, do the following:
- In a command shell, set up the required environment variables by running the following script:
WL_HOME\server\bin\setWLSEnv.cmd (on Windows)
WL_HOME/server/bin/setWLSEnv.sh (on UNIX)where WL_HOME is the directory in which you installed the WebLogic Server software.
- In the command shell, create an empty directory.
- In the empty directory, enter the following command:
java -Dweblogic.Domain=SimpleDomain -Dweblogic.Name=SimpleServer
-Dweblogic.management.username=weblogic -Dweblogic.management.password=weblogic -Dweblogic.ListenPort=7001
weblogic.Server
After you enter this command, WebLogic Server asks if you want to create a new config.xml file. If you enter y, it then instantiates a domain named SimpleDomain. The domain's Administration Server is configured as follows:
- The name of the Administration Server is SimpleServer.
- The domain's security realm defines one administrative user, weblogic, with a password of weblogic.
- For the listen address of the Administration Server, you can use localhost, the IP address of the host computer, or the DNS name of the host computer. For more information about setting the listen address, see Configure the listen addresses in the Administration Console Online Help.
- The Administration Server listens on port 7001.
Entering the weblogic.Server command as described in this section creates the following files:
- config.xml
- DefaultAuthenticatorInit.ldift, DefaultRoleMapperInit.ldift, and SerializedSystemIni.dat, which store basic security-related data.
- boot.properties file, which contains the username and password in an encrypted format. This file enables you to bypass the prompt for username and password when you start the server. For more information, see Boot Identity Files in Managing Server Startup and Shutdown.
- startWebLogic.cmd and startWebLogic.sh, that you can use to start subsequent instantiations of the server.
Invoking weblogic.Server in an empty directory results in implicit domain creation which uses the same configuration process as WLST offline and the Configuration Wizard and thus ensures that you always see uniform domains. As a result, implicitly creating a domain in an empty directory using weblogic.Server may take around 15 seconds.
Verifying Attribute Values That Are Set on the Command Line
The Administration Console does not display values that you set on the command line because the startup options set attribute values for the server's local configuration MBean. To see the values that are in a server's local configuration MBean, use WLST as follows:
- Follow “
Main Steps for Using WLST” which includes “
Setting Up Your Environment” and “
Invoking WLST” in WebLogic Scripting Tool.
>java weblogic.WLST
- Start a WebLogic Server instance (see
Starting and Stopping Servers) and connect WLST to the server using the connect command. For detailed information about the connect command, see “
connect” in the WLST Command and Variable Reference.
wls:/(offline)> connect('username','password','t3s://localhost:7002')
Connecting to weblogic server instance running at t3s://localhost:7002 as username weblogic ...wls:/mydomain/serverConfig>
- For example, to determine the multicast address that a cluster member is using, connect WLST to that server instance and enter the following commands:
wls:/mydomain/serverConfig> cd('Clusters/cluster_name')
wls:/mydomain/serverConfig/Clusters/mycluster> cmo.getMulticastAddress()'239.192.0.0'
- To determine the severity level of messages that the server instance prints to standard out, connect WLST to that server instance and enter the following commands:
wls:/mydomain/serverConfig> cd('Servers/server_name/Log/server_name')
wls:/mydomain/serverConfig/Servers/myserver/Log/myserver>cmo.getStdoutSeverity()'Notice'
For more information on using WLST, see
WebLogic Scripting Tool. For more information about configuration MBeans, see
Understanding WebLogic Server MBeans in Developing Custom Management Utilities with JMX.