Service test details
In the test editor, the test element is the first element in the test suite. The settings in the test element apply to the entire test.
Common options
- Datapools
- This lists details about each datapool that the test uses: the name of the datapool, the columns that are used, and the location in the test where the datapool column is referenced. Click the location to navigate there.
- Add datapool
- This adds a reference to a datapool you want a test to use. Clicking this option is the same as clicking Add > Datapool with the test selected.
- Remove
- This removes the selected datapool. This option is not available if the datapool is in use.
SSL configuration
Define an SSL configuration for certificate authentication between the client and the server. SSL configurations can be used by any message request in the test. If you use multiple SSL configurations in the test, specify the configuration in each message request.
The default SSL configuration always trusts servers, which is equivalent to no authentication.
- SSL configuration
- Select an existing SSL configuration or create one. You can use the toolbar push buttons to create a New SSL configuration and to Rename or Delete existing SSL configurations. You can also Copy and Paste SSL configurations to and from the SSL editor and the test editor.
- Server Authentication
-
- Always trust server
- Select if no authentication is required or to ignore server certificates so that all servers are trusted. If you are using single authentication and to accept trusted servers only, then disable this option and specify a truststore containing the trusted server certificates.
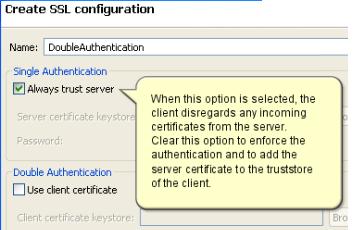
- Client truststore
- When you are using single authentication, the client truststore contains the certificates of all trusted servers. Click Browse to specify a KS, JKS, or JCEKS file containing valid certificates of the trusted servers.
- Password
- If the client truststore file is encrypted, set the password required to access the file.
- Mutual Authentication
- This section describes how the server trusts the client in addition to server authentication.
- Use client-side certificate
- If you are using double authentication, select this option to specify a keystore containing the client certificate. This certificate allows the server to authenticate the client.
- Client certificate keystore
- Click Browse to specify a KS, JKS, or JCEKS file containing a valid certificate that authenticates the client.
- Password
- If the client truststore file is encrypted, set the password required to access the file.
Protocol Configuration (HTTP)
The HTTP configuration page of the test element specifies the information that your server libraries require to execute the HTTP send and receive functions.
An HTTP configuration can be used by any message call in the test. If you are using multiple protocol configurations in the test, specify the configuration for each message call.
- Use HTTP Keep Alive
- Keep the HTTP connection open after the request. This option is not available if you are using IBM Rational AppScan.

- Use SSL
- Use an SSL configuration. Click Configure SSL to create an SSL configuration or select an existing configuration.
- Platform Authentication
- Type of authentication required to access the service. Select None if no authentication is required.
- Basic HTTP authentication
- Specify the User Name and Password that are used for basic authentication.
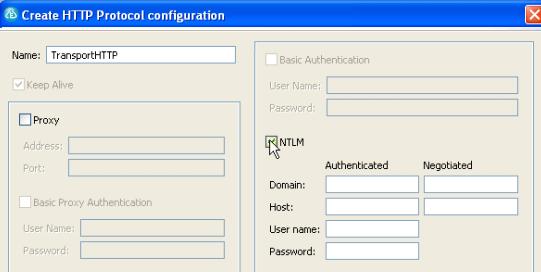
- NTLM authentication
- Use the Microsoft NT LAN Manager (NTLM) authentication protocol. NTLM uses challenge-response authentication. This view lists what is negotiated (supported by the client and requested of the server) and what is authenticated (the client reply to the challenge from the server).
- Kerberos authentication
- Use the Kerberos authentication protocol between the client and server.
- Connect through proxy server
- If the HTTP connection needs to go through a proxy server or a corporate firewall, specify the Address and Port of the proxy server. If the proxy requires authentication, select either Basic proxy authentication or NTLM proxy authentication.
- Proxy authentication
- Type of authentication required to access the proxy. Select None if no authentication is required.
- Basic proxy authentication
- The User Name and Password that are used for basic authentication.
- NTLM proxy authentication
- Use the Microsoft NT LAN Manager (NTLM) authentication protocol. NTLM uses challenge-response authentication. This view lists what is negotiated (supported by the client and requested of the server) and what is authenticated (the client reply to the challenge from the server).
- Custom class
- Select this option if the communication protocol requires complex, low-level processing with a custom Java code to transform incoming or outgoing messages. Click Browse to select a Java class that uses the corresponding API. This option is not available in IBM Rational AppScan.
Protocol Configuration (JMS)
The JMS configuration page of the test element specifies the information that your server libraries require to execute the JMS send and reception.
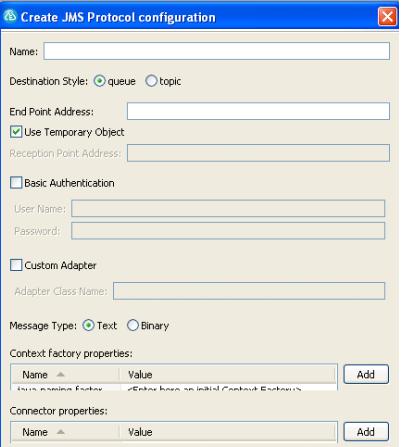
A JMS configuration can be used by any message call in the test. If you are using multiple protocol configurations within the test, specify the configuration in each message call.
| Destination style | Select either Topic or Queue. |
| End-point address | Address of the destination. |
| Use temporary object | Send the JMS destination as a temporary object. For a JMS queue, a temporary JMS queue is sent in the message.
|
| Basic authentication | The User Name and Password that are used for basic authentication. |
| Custom adapter class name | Set up a custom JNDI vendor adapter for this configuration. To use a custom adapter, you must write a Java class that extends the Axis class and methods. Specify the name of your custom adapter class in Adapter class name. |
| Text message | Specify whether the message is a text or a byte message. |
| Context factory properties | Edit the properties for a context factory. Click Add to add string properties to the context factory configuration. |
| Connector properties | Edit the properties for a connector. Click Add to add string properties to the connector configuration. The product supports the following connectors:
|
Protocol Configuration (WebSphere MQ)
The WebSphere MQ configuration page of the test element specifies the information that your server libraries require to execute the WebSphere MQ transport send and receive functions.
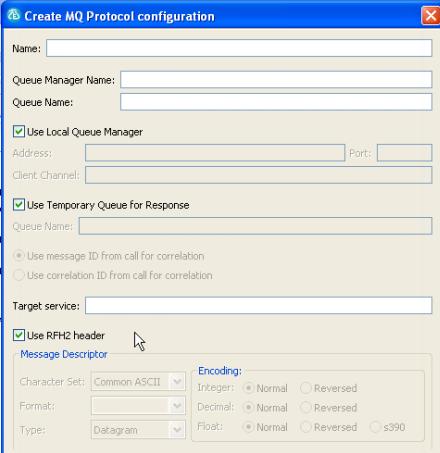
An MQ configuration can be used by any message call in the test. If you are using multiple protocol configurations in the test, specify the configuration for each message call.
- Queue Manager
- Use this area to specify queue manager options for the service.
- Queue manager name
- Specify the name of the queue manager to which to send the request.
- Use local queue manager
- Use a local queue manager.
If you disable this option, specify the following information:
- Queue manager address
- Specify the IP address or host name of the remote WebSphere MQ server.
- Queue manager port
- Specify the listener port of the remote WebSphere MQ server.
- Client channel
- Specify the server-connection mode channel of the remote queue manager.
- Queues
- Use this area to specify the send queue options for the service.
- Send queue name
- Specify the name of the queue that the queue manager manages.
- Use temporary queue for response
- Specifies whether the WebSphere MQ server creates a temporary queue. If selected, the temporary
queue is created for the sole purpose of receiving specific messages,
and then deleted.
- Receive queue name
- If Use temporary queue is cleared, this option specifies the queue manager specified on the Queue manager name line. The specified queue manager must manage this queue. You can specify multiple queue names by using a semicolon (;) as a separator.
- Use RFH2 header
- Select whether to use the transport for SOAP over MQ feature provided by WebSphere MQ. This feature uses a predetermined MQ message format (RFH2); therefore, when selected, other Message Descriptor options are disabled.
- SSL connection
- Use an SSL configuration if a Client Channel setting refers to a secure channel. Click Open SSL Editor to create an SSL configuration or Change to change the SSL configuration associated
with the current test.
If the WSDL that you use to create the message request uses a supported JMS URI to point to the WebSphere MQ server, then the SSL configuration is created automatically. If the test generator is unable to create the SSL configuration, create a new one manually.
If the WSDL is generated with the WebSphere MQ service (amqwdeployWMService), you must edit the WSDL to change the transport binding from HTTP to JMS to prevent the test generator from producing an HTTP configuration.
- Cipher suite
- Specify the cipher suite used in the channel configuration.
- Message Descriptor
- Configure the fields of the request. You can replace a subset of an MQ message descriptor with a custom format for use with other server types, specifically when using an XML message request. Refer to WebSphere MQ documentation for details about message descriptors.
- Use the Message Properties table to specify the following MQ message properties:
- JMSXDeliveryCount
- JMSXGroupSeq
- JMS_IBM_Report_Exception
- JMS_IBM_Report_Expiration
- JMS_IBM_Report_COA
- JMS_IBM_Report_COD
- JMS_IBM_Report_PAN
- JMS_IBM_Report_NAN
- JMS_IBM_Report_Pass_Msg_ID
- JMS_IBM_Report_Pass_Correl_ID
- JMS_IBM_Report_Discard_Msg
- JMS_IBM_MsgType
- JMS_IBM_Feedback
- JMS_IBM_PutApplType
- JMS_IBM_Encoding
- JMS_IBM_Last_Msg_In_Group
For more information about these properties, refer to the IBM WebSphere MQ documentation.
- Target service
- When using Microsoft .NET framework with the SOAP over MQ feature of WebSphere MQ, specify the name of the target service for the WSDL.
Related:
Web service test editor overview
Add elements to a service test
Compare service test response contents
Related reference:
Service call details
XML call details
Binary call details
Text call details
Service message return details
Service verification point details
Service callback details
Service timeout details
Service parallel details
Service receive details
Service test editor preferences
Error 404 - Not Found
The document you are looking for may have been removed or re-named. Please contact the web site owner for further assistance.