|
15.3.1 Inspecting the Struts portlet projectNow that the Struts portlet has been created, let's take a look at what Rational Application Developer has generated for you.
<controller processorClass="com.ibm.portal.struts.portlet.WpRequestProcessor"> </controller>
<welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.html</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.htm</welcome-file> <welcome-file>default.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list> This list is not really necessary; as we will see, the Struts Portlet framework provides a mechanism to identify which page must be displayed first for each different mode and markup language.
For more information about other added elements, see the WebSphere Portal Infocenter. Example 15-1 Generated portlet preferences in portlet descriptor (portlet.xml)
<portlet-preferences>
<preference>
<name>com.ibm.struts.portal.page.view.html</name>
<value>index.jsp</value>
</preference>
<preference>
<name>com.ibm.struts.portal.page.edit.html</name>
<value>html/edit/index.jsp</value>
</preference>
</portlet-preferences>
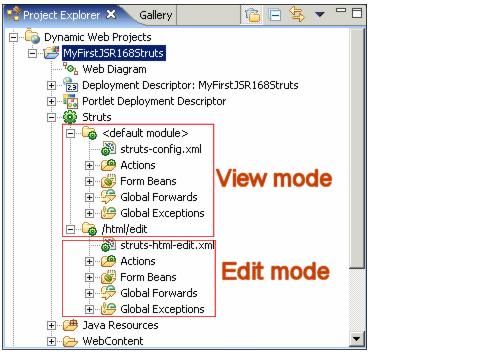
Figure 15-9 Generated Struts portlet |
 ibm.com/redbooks |