Use BorderLayout
The visual editor provides visual cues for helping you work with the Swing BorderLayout.
The BorderLayout manager lays out components into regions defined by compass directions. The class java.awt.BorderLayout implements LayoutManager2, and its constraint is a string that can be of the value "North", "South", "Center", "East", or "West".
Note: If you switch a container to BorderLayout and it has more than five components, only the first five components are added with constraints to the BorderLayout. The remaining components will be moved from the container to the free form area of the Design view.
BorderLayout positions each component at one of the compass constraints along the edge with its preferred width or height, and the "Center" component occupies all of the remaining space.
- To add a component on a BorderLayout:
- Select the Swing component from the palette that you want to add to the BorderLayout.
- Move your mouse cursor over the Design view.
- The BorderLayout will show five rectangular areas representing the five constraints of "North", "South", "Center", "East", or "West".
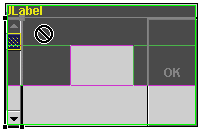
- If the region is already occupied by a component, the cursor will show
a circle with a line through it, meaning that you cannot drop the component
in that region.
- If the region is empty, the region will be highlighted and the cursor
will show a plus sign, indicating that you can drop the component.
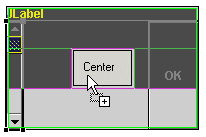
- Click the Design view in a valid region to add the component to the BorderLayout.
- To move components within a BorderLayout:
- In the Design view, select the component in the BorderLayout that you want to move to another region within the BorderLayout.
- Drag the component to another region and release your mouse button. The component will be moved to the new region. If the region was already occupied by another component, the components will switch places.
- To adjust the spacing for components within a BorderLayout, you
can set the following properties on the BorderLayout:
- Horizontal gap - sets the distance in pixels between the center component and the east and west components.
- Vertical gap - sets the distance in pixels between the center component and the north and south components.
The constraints value is used as the second argument to the method add(Component,Object) that adds the components to their parent container. For example, the code to initialize a JPanel might look like this:
private void initialize() {
this.setLayout(new java.awt.BorderLayout());
this.add(getJLabel(), java.awt.BorderLayout.NORTH);
this.add(getJScrollBar(), java.awt.BorderLayout.WEST);
this.add(getJButton(), java.awt.BorderLayout.EAST);
this.setSize(193, 124);
}
Note: Two additional constants are used to support relative positioning based on the container's ComponentOrientation: "before line begins" and "after line ends". For example, in a container where ComponenetOrientation is ComponentOrientation.LEFT_TO_RIGHT, "Before line begins" maps to "West", and "After line ends" maps to "East". Mixing the two types of constants is not recommended. Unusual results may show in the graph viewer and at run time, since the relative constants will take precedence.
Parent topic
Swing and AWT layout managers
Related concepts
Layout managers and containers
Related tasks
Using BoxLayoutUsing CardLayout
Using FlowLayout
Using GridLayout (AWT)
Using GridBag layout