Built-in redundancy
Syndication can be used to supply built-in redundancy to a group of Web Content Management servers.
Example 1: Automatic redundancy
In this example, a pair of Staging servers are used to syndicate between authoring and delivery servers. Syndication is enabled on both staging servers to each authoring and delivery server. This means that each staging server contains the same data. If one staging server goes down, data continues to be automatically syndicated from the authoring server to the delivery server via the remaining staging server.
This architecture is useful when you are continuously syndicating between authoring, staging and delivery servers. This automatic redundancy structure could also be applied to a set of authoring or delivery servers.

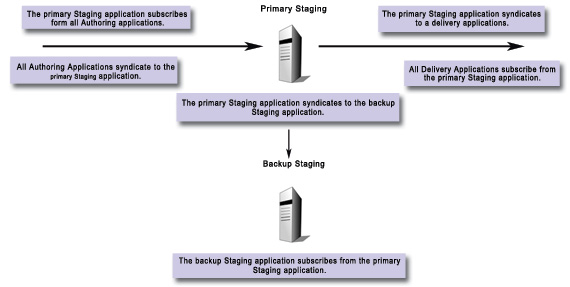
Example 2: Manual redundancy
In this example, a primary Staging server is used to syndicate to a Delivery server. This primary Staging server also syndicates to a backup server. If the primary Staging server goes down, you can manually switch to the backup Staging server by enabling syndication between the backup Staging server and any Authoring or Delivery servers.
This architecture is useful if you only manually "batch-syndicate" from a Staging server to a Delivery server. This manual redundancy structure could also be applied to a set of Authoring or Delivery servers.
Syndication is used as the transport layer that replicates data from one IBM Lotus Web Content Management server to another. Further information can be found in Syndication.