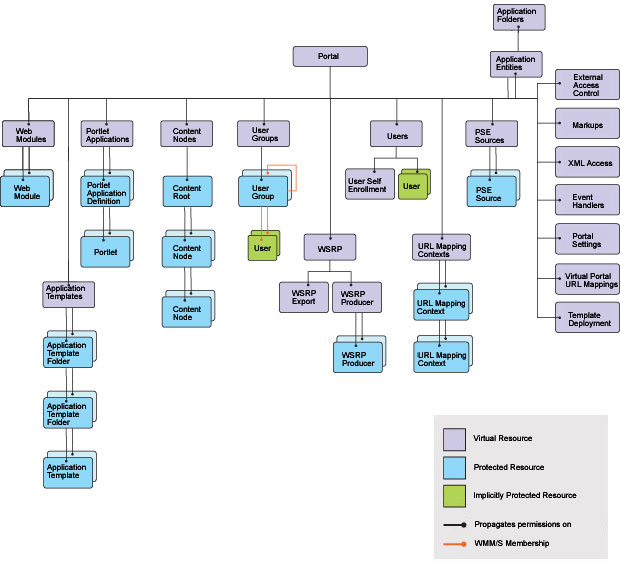
Resources
Resources propagate their access control configuration to child resources.
For example, if a user has the Editor role on the Market News Page, then by default that user also has the Editor role on all pages that are children of the Market News Page.
Resource instances are specific resources, such as a single portlet or page. Each resource instance belongs to only one resource type. For example, the resource instance Market News Page would belong to the Content Nodes resource type.
Virtual resources...
For example, the WEBMODULES virtual resource is the root node of all Web modules instances. Role assignments on WEBMODULES propagate to all individual Web module resources.
Resource data is stored in one of four different database domains.
| JCR domain | JCR nodes. |
| Customization domain | User customization resources. |
| Community domain | Resources related to collaborative applications. |
| Release domain | All remaining resources. |
Resources can be administered in the following ways:
Resources in this domain are not shown in the administration portlets
No role assignments are possible in this domain, so resources in this domain are also not shown in the administration portlets
Role inheritance never crosses domain boundaries, thus limiting the inheritance scope. Therefore, a role assignment for a user on the Content Nodes virtual resource in the release domain will only grant access to Content Nodes resources (pages) in the release domain.
Next are illustrations of the available resources tree, first for the release domain, and second for the JCR domain.

The following illustration shows the hierarchy of resources in the JCR domain. These resources are related to...
Resource permission inheritance applies to this hierarchy as well as to the release domain. Permission granted on the JCR content root node are propagated to all children in the hierarchy.
To reduce this propagation of permissions to children in the hierarchy use...

A different user interface is provided to administer access control for each type of resource in the JCR domain. The following list shows the path to take within WebSphere Portal to reach the access control portlet for each resource stored in the JCR domain:
Administration | WebSphere Portal | Access | Resource Permissions | Resource Permissions portlet
Administration | WebSphere Portal | Access | User and Group Permissions | User and Group Permissions portlet
You can assign roles on virtual resources and on resource instances. Assigning roles on virtual resources reduces the time needed to administer access control because all child resources inherit roles that are assigned to the parent resource by default. Assigning roles to specific resource instances offers more granular access control. You might need to assign roles to specific resource instances to override role blocks that block inheritance.
The following table describes virtual resources.
| Virtual Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| Application Templates | Root node of application template folders and objects for composite applications. |
| Application Entries | Root node of all application entity objects for composite applications. |
| Application Folders | Root node of all application folder objects for composite applications. |
| Content Nodes | Root node of all pages, labels, and external URLs. Pages contain the content that determines the portal navigation hierarchy.
If a new top-level page is created, it is automatically a child resource of the Pages virtual resource. If a new page is created beneath an existing page the new page is automatically child of the existing page. Pages inherit access control configuration from their parent page unless role blocks are used. |
| Designer Deploy Service | Protect the ability to execute the automatic deployment feature of IBM Workplace Designer. |
| Event Handlers | Protect management of Event Handlers.
No child resources. |
| External Access Control | Protect modifying access control configuration for resources that are controlled externally by a security manager such as Tivoli Access Manager. Also protect the ability to externalize or internalize a resource. This virtual resource has no child resources. |
| Markups | Protect the ability to control markups for the portal. This virtual resource has no child resources. |
| Portal | This is the root node of all resources in the release domain. Roles on this resource affect all other resources in the release domain by default through inheritance unless role blocks are used. Resources in other domains like Templates and Policies are not affected through role mappings on this resource. |
| Portal Settings | Protect portal settings that can be modified through the Portal Settings portlet or the xmlaccess. This virtual resource has no child resources. |
| Portlet Applications | Root node of all installed portlet applications.
Portlet applications are the parent containers for portlets. If a new Web module is installed, the portlet applications that are contained within that Web module are automatically child resources of the Portlet Applications virtual resource. Portlets that are contained within a portlet application appear as child nodes of that portlet application. Thus a two-layer hierarchy consisting of portlet applications and the corresponding portlets exists beneath the Portlet Applications virtual resource. Portlets inherit access control configuration from their parent portlet applications unless role blocks are used. |
| PSE Sources | Root node of all search collections. If a new search collection is created, it is automatically a child of this virtual resource.
Roles on this resource affect all defined search collections unless role blocks are used. |
| Template Deployment | Protect the deployment of arbitrary composite application templates into portal. This virtual resource has no child resources. |
| URL Mapping Contexts | Root node of all URL mapping contexts.
URL mapping contexts are user-defined definitions of URL spaces that map to portal content. If a new top-level URL mapping context is created, it is automatically a child resource of the URL Mapping Contexts virtual resource. If a new URL mapping context is created beneath an existing context, the new context is automatically a child of the existing context. URL mapping contexts inherit access control configuration from their parent context unless role blocks are used. |
| User Groups | Root node of all user groups.
Each user group in the portal inherits its access control configuration from the User Groups virtual resource. It is not possible to create role blocks on individual user groups. |
| User Self Enrollment | Protect the Selfcare and User Enrollment facilities (sign up and Edit My Profile). This virtual resource has no child resources. |
| Users | This virtual resource has no child resources. The Users virtual resource protects sensitive operations that deal with user management.
For example, in order to add a user to a user group, have the role...
Users are implicitly protected resources. Users cannot be protected individually, but only through their group membership. As a result, it is not possible to have a role assignment on a specific user. Roles must be on user groups instead. So, you can edit Mary's user profile if you have a role assignment on some user group to which Mary belongs. |
| Virtual Portal URL Mappings | Protect the ability to modify a URL Mapping linked to a virtual portal. |
| Web Modules | Root node of all Web modules.
Web modules are portlet WAR files that are installed on WAS. Web modules can contain multiple portlet applications. If a new Web module is installed, it is automatically a child of the Web Modules virtual resource. Roles on this resource affect all child resources (all installed Web modules) unless role blocks are used. |
| WSRP | This is the parent resource of the virtual resources WSRP Export and WSRP Producers.
By default, roles on the WSRP resource affect the other two virtual WSRP resources and all WSRP resource instances via inheritance. As long as there are no role blocks in between, users who have role assignments on the WSRP resource have access rights on all WSRP resources. |
| WSRP Export | Controls the ability of a user to provide and withdraw portlets as a WSRP Service. |
| WSRP Producers | This is the root node of all registered Producer instances.
Each Producer that is registered in the portal inherits its access control configuration from the WSRP Producers virtual resource unless role blocks are used. |
| XML configuration interface | Protect the ability to execute xmlaccess scripts.
No child resources. |