Database
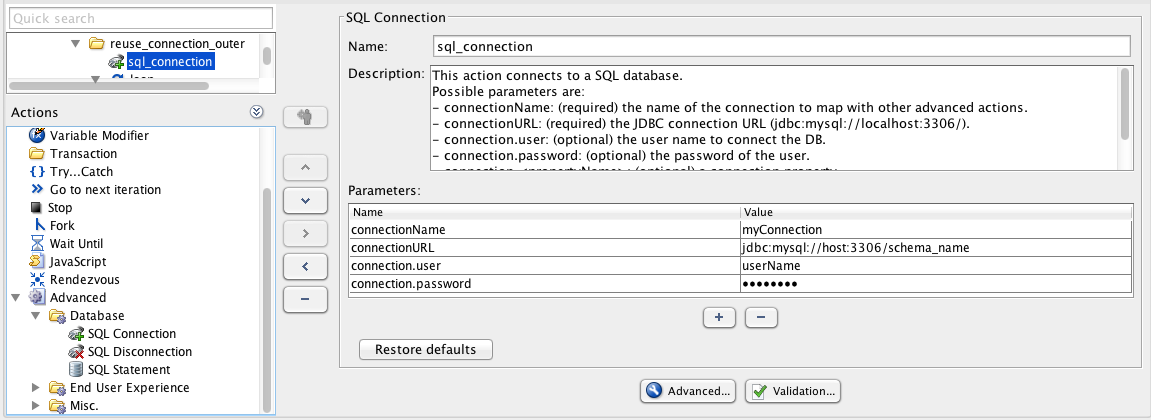
SQL Statement
The SQL Statement Advanced action executes SQL statements. It enables you to perform administrative tasks like cleaning a database after a test. It also allows you to get business-related metrics that you can monitor, for example the number of items in a work queue or the number of checkouts during the last minute.
The action produces an XML output that includes a status of the executed SQL statement as well as an optional section containing the results of the query. The query results are also stored in NeoLoad variables.
- Tip: Use the Advanced actions Store External Data Entry or Store External Data Entries to store and analyze the retrieved data in NeoLoad.
Information: In case of connection with Microsoft SQL Server 2005, you need to replace the Microsoft SQL Server 4.1 JDBC Driver with the Microsoft SQL Server 4.0 JDBC Driver by following this 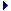 procedure.
procedure.
Parameters
- type: The type of SQL statement, possible values are QUERY and UPDATE.
- connectionName: The name of the connection to use.
- sqlStatement: The SQL statement to execute. Multi-line allowed.
- variableName (optional): The NeoLoad variable to put the value(s) in. More information in the Variables section below.
- includeQueryResults (optional): Default value is true. If set at false, the results are not included in the XML response. Should be "false" to optimize resource consumption when executing a query that returns multiple rows and retrieving the values from the variables.
- batchSize (optional): The batch number to keep in memory before performing a batch update.
When executing a query, be careful to specify the variable name, i.e "sqlEntries" and not "${sqlEntries}".
"columnName" is the column name as defined in the database. Invalid XML characters are removed, for example count(*) would be renamed to count.
The query result values will be retrieved in the following variables:
- variableName for value in first row, first column
- variableName_[columnName] for the first row
- variableName_[columnName]_[row] when several rows are expected
- Both variableName_[columnName]_count (recommended) and variableName_[columnName]_matchNr return the number of rows.
- variableName_[columnName]_rand returns a random value from the column specified
- variableName_[columnName] can be used as an input for the Store External Data Entries action in order to store all results values of a column in the Results data.
Examples
An example of removing all lines of a table:
- type: UPDATE
- connectionName: myConnection
- sqlStatement: DELETE FROM table_name
An example of getting number of rows:
- type: QUERY
- connectionName: myConnection
- sqlStatement: SELECT count(*) FROM table_name
- variableName: countTableName
In this example, since the query will return one row of one column, only the countTableName variable will be created.
An example of SELECT with a custom driver:
- type: QUERY
- connectionName: myConnection
- sqlStatement: SELECT * FROM records WHERE date='2014-11-11'
- variableName: records
- driverClassName: com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2Driver
In this example, the following multi-valued variables will be created : records_id and records_date records_id_1 gives access to the id of the first row, records_id_count and records_id_matchNr give access to the number of rows, records_date_rand gives access to the date of a random row.
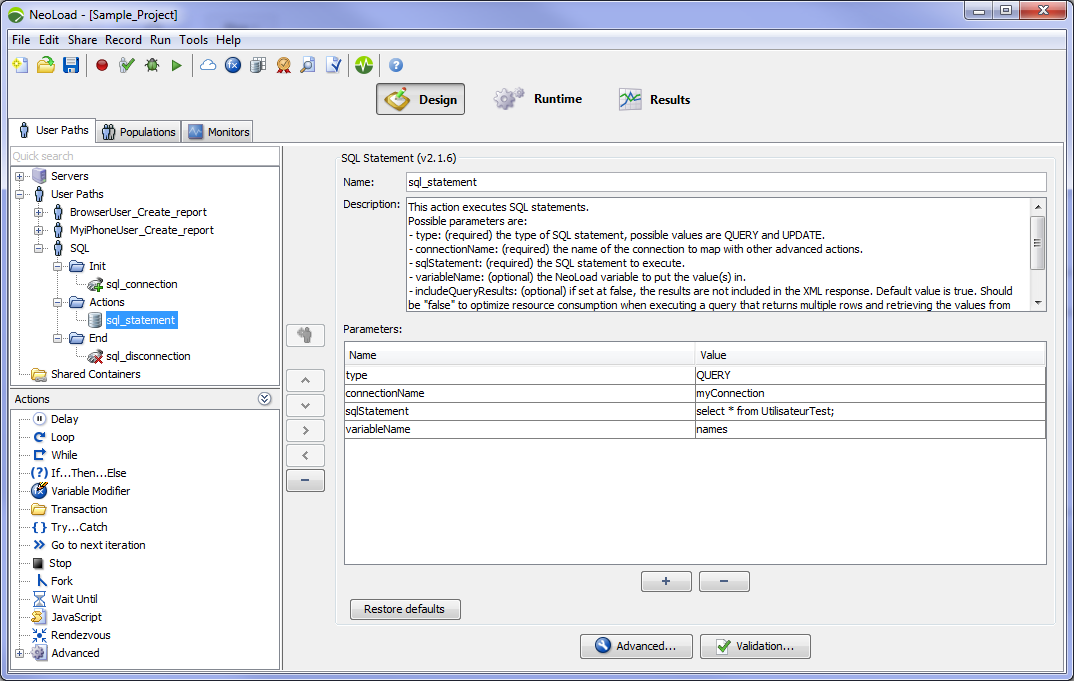
SQL Connection
The SQL Connection Advanced action creates a database connection.
Parameters
- connectionName: The name of the connection to open.
- connectionURL: The JDBC connection URL (jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/).
- connection.user (optional): The user name to connect the database.
- connection.password (optional): The password of the user.
- connection.<propertyName> (optional): Any property that can be used to customize your connection.
Examples
An example of creating a connection to a MySQL database:
- connectionURL: jdbc:mysql://host:3306/mysql
- connection.user: my_user_name
- connection.password: my_password
An example of creating a connection to a DB2 database:
- connectionURL: jdbc:db2://host:50000/db
- connection.user: my_user_name
- connection.password: my_password
- driverClassName: com.ibm.db2.jcc.DB2Driver
SQL Disconnection
The SQL Disconnection Advanced action closes a previously opened database connection.
Parameters
- connectionName: The name of the connection to close.
Example
An example of closing the connection "myConnection".
- connectionName: myConnection