Microsoft Windows
Definition
The Microsoft Windows monitor allows to check the operating system of Microsoft Windows servers: CPU, memory, disk, network, etc.
Microsoft monitors use a Windows API to list and query performance counters, namely the Performance Data Helper (PDH) library used by Perfmon which is a Windows tool. Therefore, the NeoLoad Microsoft monitors have the same characteristics and constraints as Perfmon:
- Monitoring is done without installing any additional component, which obviates the installation of a specific client on the machine to be monitored.
- The monitoring of Microsoft servers is only possible using Windows monitoring agents. Microsoft servers cannot be monitored with a Unix/Linux monitoring agent.
- The account used to start the monitoring agent (or NeoLoad for the built-in agent) must have the appropriate user rights. See Connect to a remote server.
When defining a counter, and depending on the type of counter, one or more instances may be also selected. One instance corresponds to a certain sub-division of the monitored object. For example, Processor/Processor Time % has several instances, one for each processor present in the monitored machine. Usually, an instance named _Total allows retrieving an average value across all available instances.
Connect to a remote server
To access a remote machine, the user running the monitoring agent (or NeoLoad for the built-in agent) must have the user rights required to remotely monitor a server. The authorizing rights are provided for administrators and members of the Performance Monitor Users Windows group on the server being monitored.
If the account being used does not have sufficient rights, launch the monitoring agent (or Controller in the case of the built-in monitoring agent) using the appropriate account by right-clicking on MonitoringAgent.exe and using the Run as option; alternatively, add the account to the Performance Monitor Users group.
- Warning: The Remote Registry service must be started on the remote monitored machine.
Firewall settings
TCP Port 445 and TCP Port 139 must be open on firewalls. For the Windows firewall, this can be done by adding an exception for "File and printer sharing".
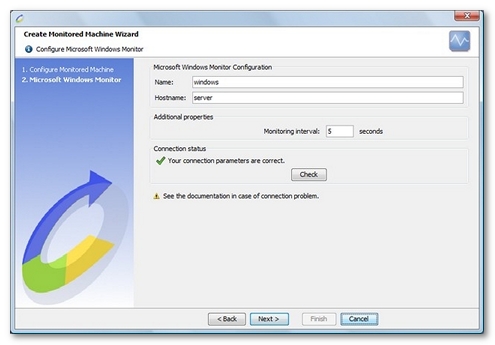
Create a Windows monitor
NeoLoad makes it possible to create a new monitor either using the monitored machine creation wizard, as described in Create and configure a monitored machine, or from an existing monitored machine, as described in Create and configure a monitor.
Available counters
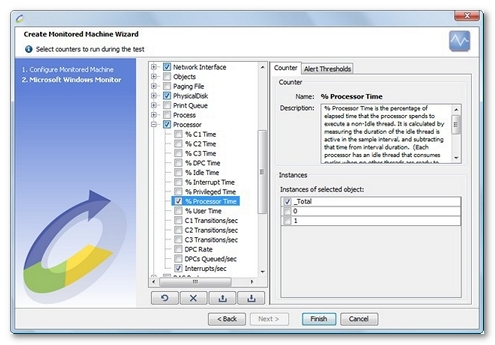
On a typical Windows server, the main, basic counters are as follows:
- Memory\Pages/sec. Detects the Pages/sec swap rate. The pages/sec rate is the speed at which the pages are read from or written to the disk when resolving hardware page faults. A hardware page fault occurs when a process has to access code on a physical disk because it cannot be accessed in the memory.
- Memory\Available Megabytes. Indicates how much physical memory remains after the working sets of running processes and the cache have been served. Should be greater than 10% of the physical memory.
- Processor\Processor Time \%. CPU activity in percentage.
- System\Processor Queue Length. This counter displays the number of threads waiting to be executed in the queue that is shared by all processors on the system. If this counter (divided by the number of processors) has a sustained value of five or more threads, there is a processor bottleneck.
- Physical disk\Disk Time \%. Percentage of elapsed time spent by the selected physical disk drive executing read or write requests. More than 55% for continuous periods indicates a bottleneck.
- Network Interface\Packets/s. Rate at which packets are sent and received on the network interface.