Forms single sign-on process flow
Learn about the single sign-on process so that we understand how a client browser accesses a resource.
The following scenario assumes the user is authenticated in WebSEAL and the credential learning function is disabled. When the credential learning function is enabled, the flow is discussed in Forms single sign-on learning flow.
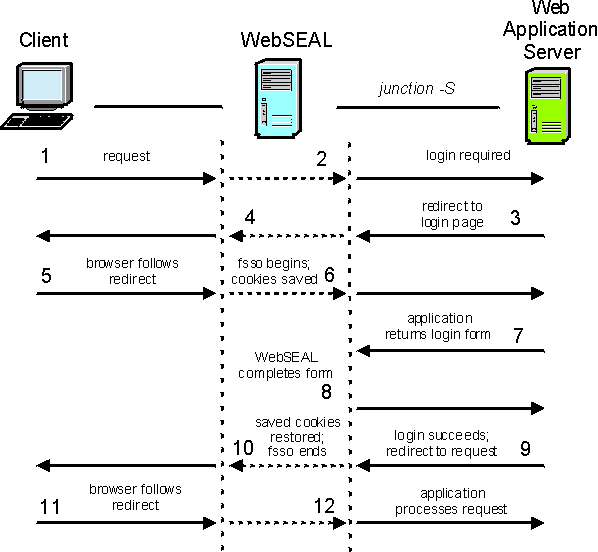
- Client browser requests the page:
- https://webseal/formsso/content.html
- WebSEAL passes the request to the junction.
- Because the back-end application requires the user to authenticate, a redirect to the application's login page (login.html) is sent back across the junction.
- WebSEAL passes the redirect to the browser.
- The browser follows the redirect and requests:
- https://webseal/formsso/login.html
Everything to this point in the process flow is standard WebSEAL function.
- WebSEAL is configured for forms single sign-on (-S option on the junction). WebSEAL recognizes the request as a request for a login page, which is based on information in the forms SSO configuration file. The request is passed to the junction. WebSEAL saves all cookies that are sent by the browser for use in step 8.
- The application returns the login page and application-specific cookies.
WebSEAL parses the HTML returned to identify the login form. When WebSEAL finds an HTML form, it compares the action URI in the form to the value of the login-form-action stanza entry in the custom configuration file. If there is a match, WebSEAL uses the form that it found. Otherwise, WebSEAL keeps searching for other forms. If no form in the page matches the action URI pattern from the configuration file, then WebSEAL stops forms single sign-on processing. WebSEAL then returns an error to the browser. WebSEAL parses the page to identify the request method, the action URI, and any other input fields in the form. WebSEAL then them for use in step 8.
- WebSEAL generates the authentication request (completes the login form) and sends it to the back-end application.
- The application authenticates the user with the authentication data that is supplied by WebSEAL in the form. The application returns a redirect to content.html.
- WebSEAL combines any cookies that are saved from the responses at step 7 and step 9, and returns these cookies with the redirect to the browser. If configured, login-success-pattern is used to inspect the response (even if credential learning is disabled). If the login is determined to be unsuccessful, the login page requested in step 5 is re-requested and returned to the user. This process completes the forms SSO-specific function.
- The browser follows the redirect and requests:
- https://webseal/formsso/content.html
- WebSEAL passes the request to the back-end application across the junction.
During this process, the browser makes three requests to WebSEAL. From the user's perspective, only a single request for https://webseal/formsso/content.html is made. The other requests occur automatically through HTTP redirects.
Parent topic: Forms single sign-on concepts