User session management concepts
A client/server session is a series of related communications between a single client and a server that take place over a period of time. With an established session, the server can identify the client associated with each request, and has the ability to remember—over numerous requests—a specific client.
Without an established session, the communication between a client and a server might be renegotiated for each subsequent request. Session state information improves performance by eliminating repeated closing and re-opening of client/server sessions. The client can log in once and make numerous requests without performing a separate login for each request.
The WebSEAL server has the ability to maintain session state with clients and to additionally extend this session information to junctioned back-end application servers.
WebSEAL uses a session identification key, called the WebSEAL session ID, to maintain session state between the client and WebSEAL. The WebSEAL session ID serves as an index to the client's session data stored in the WebSEAL session cache. See WebSEAL session cache structure and Session cache configuration overview.
A separate session identification key, called the user session ID, can be used to maintain session state between the client and a junctioned back-end application server. The user session ID uniquely identifies a specific session for an authenticated user and is stored as part of the user's credential information.
Back-end applications
can use user session IDs to track user sessions
and terminate sessions. See Enable user session ID management.
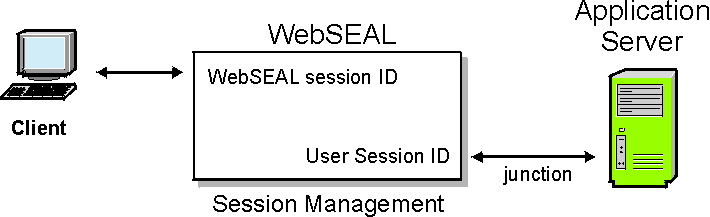
A single user that logs in multiple times (for example, from different machines) has multiple WebSEAL session IDs and a credential for each session. The user session ID is based on the WebSEAL session ID (there exists a one-to-one mapping between the two keys). Therefore, a user session ID exists for each WebSEAL session ID.
There are two configuration steps required to enable session management with the user session ID:
- Configure WebSEAL to store a unique user session ID for each authenticated client as an extended attribute in the credential of each client.
- Configure an extended attribute on a junction that can provide the value of this credential extended attribute (the user session ID) to a back-end application server in an HTTP header.
Parent topic: User session management for back-end servers