Attribute matchers
An attribute matcher compares the values of a specified attribute in the incoming device fingerprint with the existing device fingerprint of the user. Context-based access uses the information that is returned by the attribute matchers to calculate the risk score.
In some scenarios, multiple attributes or a set of composite attributes must be matched. For example, longitude, latitude, and accuracy are three attributes related to location. In a given scenario, two device fingerprints are considered a match if the distance between two location points is not greater than a specified threshold value. In this scenario, the comparison of only the longitude attribute does not provide accurate results. The matcher must do a more complex comparison or composite matching, where it matches multiple attributes from both fingerprints. The matcher returns one of the following results after it compares the attributes values in the registered device fingerprint and the incoming device fingerprint:
- Matched
- The decision the matcher returns if the attribute value in the registered device fingerprint and the incoming device fingerprint value are the same or considered equivalent.
- Mismatched
- The decision the matcher returns if the attribute value in the registered device fingerprint and the incoming device fingerprint value are not the same or considered equivalent.
- Indeterminate
- The decision the matcher returns if it cannot gather enough attribute information to determine a result. When the matcher returns Indeterminate as the result, the risk engine does not use the attribute in risk score calculations.
A mismatch increases the risk score based on the assigned weight of the attributes. The matcher might not be used in the risk calculation in the following situations:
- The incoming device fingerprint does not contain the required attributes.
- The historical data is not available for a matcher to make a match or mismatch decision.
Risk-based access provides ready-to-use attribute matchers that compare composite attributes or analyze a range of attribute values. We can configure one or more of the attribute matchers that are described in the following sections.
Exact match matcher
The exact_match matcher checks Whether the values of an attribute in a registered device and an incoming request exactly equal each other. Use this matcher if the more specialized matchers are not appropriate for the attribute.IP address matcher
The IP address matcher (ipaddr_matcher) compares the IP address of a request with:- A trusted list (inclusion list) of IP addresses
- An untrusted list (exclusion list) of IP addresses
- The historical IP addresses of the device
- The IP reputation of the device
The IP address matcher has the following properties:
- Trusted addresses
-
- IPV4 addresses
- IP and Netmask: Specifies the IP address and its netmask to include. Include X.X.X.X as a value to compare the incoming IP address with the IP address with which the device is registered.
- IPV6 addresses
- IP and Prefix: Specifies the IP address and its prefix to include. Include X:X:X:X:X:X:X:X as a value to compare the incoming IP address with the IP address with which the device is registered.
- Untrusted addresses
-
- IPV4 addresses
- IP and Netmask: Specifies the IP address and its netmask to exclude. Include X.X.X.X as a value to compare the incoming IP address with the IP address with which the device is registered.
- IPV6 addresses
- IP and Prefix: Specifies the IP address and its prefix to exclude. Include X:X:X:X:X:X:X:X as a value to compare the incoming IP address with the IP address with which the device is registered.
The IP address matcher returns one of the following decisions after it compares the incoming IP address with the IP address that belongs to the registered device:
- MISMATCHED
- The decision the matcher returns if either of the following conditions are true:
- The incoming IP address is in the list of untrusted IP addresses.
- The incoming IP address is not in the list of trusted IP addresses, and the IP address has a reputation other than Dynamic IPs.
- MATCHED
- The decision the matcher returns if the matcher finds the incoming IP address in the list of trusted IP addresses.
- INDETERMINATE
- The decision the matcher returns if the following conditions
are true:
- The IP address is not in the list of untrusted IP addresses.
- The IP address is not in the list of trusted IP addresses.
- The IP address qualifies for one of the following conditions:
- Does not have a reputation.
- Has a Dynamic IPs reputation.
PIP matcher
The policy information point (PIP) matcher (pip_matcher) uses the value of a single-valued attribute to determine one of the following results:
- Matched
- The value of the attribute is MATCHED.
- Mismatched
- The value of the attribute is MISMATCHED.
- Indeterminate
- The value of the attribute is INDETERMINATE.
The PIP matcher supports only single-valued attributes with String data types. Write and configure a JavaScript PIP with the following capabilities if you prefer to use the PIP matcher:
- The PIP determines attribute values.
- The PIP compares attribute values.
- The PIP returns match decisions based on the values of attributes that it compares.
Location matcher
The location matcher (location_matcher) checks Whether the location of a device is within a specific distance from the previous known locations of the device. Configure the location matcher properties to specify the accuracy range and how to compare the location information.Limitation: The retrieval of location attributes depends on the web browser and the settings the user specifies in the web browser. The web browser must support the Geolocation API. An error might occur in some web browsers if a user tries to access a protected resource from a device with a wired internet connection.The location-based analysis processes all three location attributes (longitude, latitude, and accuracy) collectively when it determines the match for the location. Though weights are assigned to all three attributes, the weight for only the longitude attribute is considered. The weights assigned to the supporting latitude and accuracy attributes are ignored. The location matcher has two properties:
- Comparison
- Indicates how we want the attribute matcher to calculate the accuracy range of the location coordinates.
The following figure illustrates the closest points, midpoints, and farthest points of the accuracy ranges of two locations. In this figure, the circle represents the accuracy range and the center of the circle represents the location.
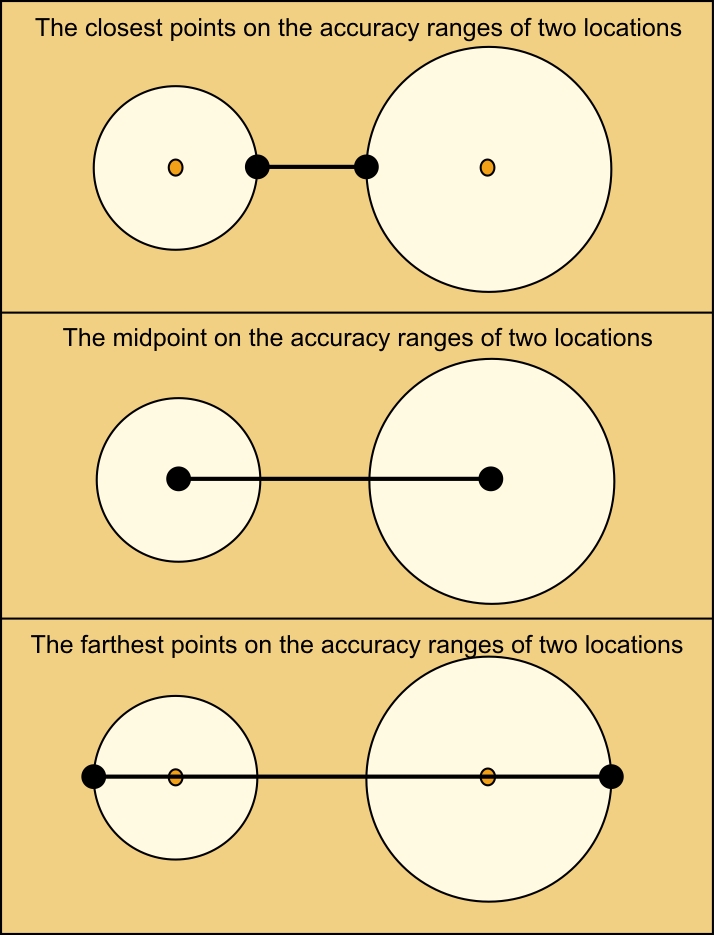
Set the Comparison property to one of the following values:
- Specify the value as closest to calculate the distance between the closest points on the accuracy range of two locations. This calculation is the most restrictive calculation.
- Specify the value as midpoint to calculate the distance between the midpoints of the circles without considering accuracy.
- Specify the value as farthest to calculate the distance between the farthest points on the accuracy ranges of the two locations. This calculation is the least restrictive calculation.
- Distance
- The maximum distance between the new location and the historic locations. The unit of the numeric value is in kilometers. The default value is 40.
Login time matcher
The login time matcher (login_time_matcher) compares and analyzes the historical login time data of the user with the current login time of the user. We must configure the attributes and properties required for login time analysis. The login time matcher primarily detects the logins per session. The first of the several access times that are captured within the session is considered the login time of the user. The result of the analysis determines the probability of a fraudulent user.The login time matcher has one property:
- Threshold
- The probability that a user might log in at a particular time. Valid values are 0 to 1. The default value is .3. This default value indicates the probability the user logs in approximately within an hour of the previous login times. If we set a lower value, the odds of the matcher returning true are higher and the risk score is lower. If we set a higher value, the odds of the matcher returning true are lower and risk score is higher. For example, if we set a value of 0.5, the matcher almost always returns false. The login time analysis collects data for eight login times before it provides input for risk score calculation.
- IP reputation
The IP reputation policy information point (PIP) uses the IP reputation database to determine the reputation of the IP address of a request. Based on the IP address reputation, we can write a policy to grant or prohibit access to the requesting IP address. The IP reputation PIP is pre-configured with Advanced Access Control. - Modify attribute matchers
Attribute matchers match incoming attributes to attributes in a device fingerprint. The predefined matchers are set to default values. We can modify those values to customize the risk calculations for your policies.
Parent topic: Advanced Access Control administration
Related concepts
Related tasks