An overview of message-driven beans
WAS supports automatic asynchronous messaging with message-driven beans (a type of enterprise bean defined in the EJB 2.0 specification).
The support for message-driven beans is based on the message listener service, which comprises a listener manager that controls and monitors one or more listeners. Each listener monitors a JMS destination (a queue or topic) for incoming messages. When a message arrives on the destination, the listener passes the message to a new instance of a user-developed message-driven bean (an enterprise bean) for processing. The listener then looks for the next message without waiting for the bean to return.
Messages arriving at a destination being processed by a listener have no client credentials associated with them; the messages are anonymous. Security depends on the role specified by the RunAs Identity for the message-driven bean as an EJB component.
It is recommended that you develop a message-driven bean to delegate the business processing of incoming messages to another enterprise bean, to provide clear separation of message handling and business processing. This also enables the business processing to be invoked by either the arrival of incoming messages or, for example, from a WebSphere J2EE client.
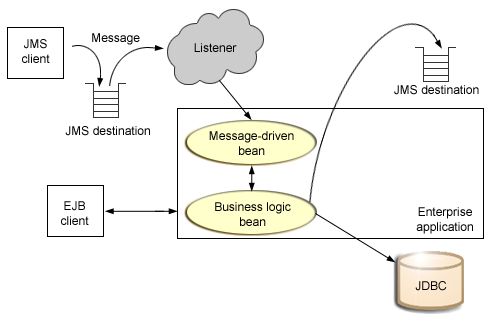
This figure shows an incoming message being passed by a JMS listener to a message-driven bean, which passes the message on to a business logic bean for business processing. This messaging is controlled by the listener manager.
For more overview information, see these topics:Message-driven beans - components
This topic describes the main components of WAS support for message-driven beans.Message-driven beans - transaction support
This topic describes the transaction support of message-driven beans.