Horizontal scaling sample topology
Horizontal scaling refers to setting up multiple application server cluster members on two or more physical machines within a single WebSphere Application Server cell. In a horizontal scaling topology, an application can run on all of the machines and present a single system image to clients. This topology requires WebSphere Application Server Network Deployment.
In horizontal scaling, all of the machines host a cluster member for each application server cluster. For example, suppose you have two machines (myHost1 and myHost2) and two application server clusters (myCluster1 and myCluster2). Each cluster contains two cluster members, and each machine hosts one of the cluster members from each cluster.
- myCluster1 includes cluster members named mySvr1Cluster1 and mySvr2Cluster1.
- myCluster2 includes cluster members named mySvr1Cluster2 and mySvr2Cluster2.
- myHost1 hosts mySvr1Cluster1 and mySvr1Cluster2.
- myHost2 hosts mySvr2Cluster1 and mySvr2Cluster2.
This figure shows an example of a horizontal scaling topology:
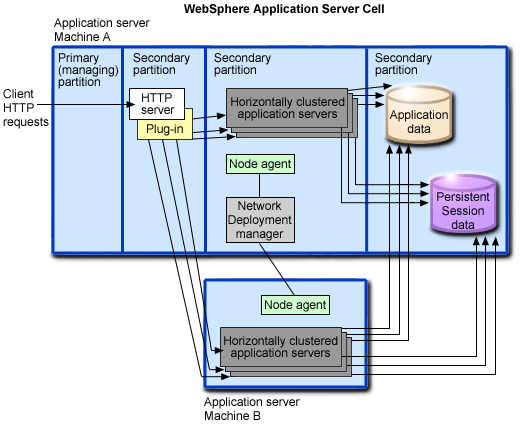
This sample topology includes these features:
- The use of two iSeries servers and LPAR provides process and data isolation, as well as hardware redundancy.
- Both Machine A and Machine B host a cluster member of each application server cluster.
- A partition on Machine A serves as the primary Web server for the application and distributes client requests to the application server cluster members on both machines. With the Web server in a separate partition, you can set up a firewall between the Web server and your application server. If you do not need the additional security of a firewall, it is not necessary to run the Web server in a separate partition.
- A single Network Deployment manager communicates with a node agent on each machine to manage the application servers.
You can include additional components to create more advanced horizontal scaling topologies. Two types of variations on the horizontal clustering topology are listed here:
- Horizontal scaling with Network Dispatcher
- Horizontal scaling with high availability Apache Web server
Advantages and disadvantages of horizontal scaling
Horizontal scaling provides these advantages:
- Increased throughput and failover support when compared to vertical scaling topologies.
- Improved availability, because application server process failure and hardware failure prevent significant interruptions to client service.
- Ability to optimize the distribution of client requests through mechanisms such as workload management or remote HTTP.
The primary disadvantage of a horizontal scaling topology is that it is more complex to administer and maintain than a vertical scaling topology or a single machine topology.