Horizontal scaling with high availability Apache Web server sample topology
Horizontal scaling refers to setting up multiple application server cluster members on two or more physical machines within a single WebSphere Application Server cell. In this variation on the basic horizontal scaling topology, the high availability Web server provides HTTP server failover support. This topology requires WebSphere Application Server Network Deployment.
This figure shows a sample horizontal scaling topology with a high availability Web server:
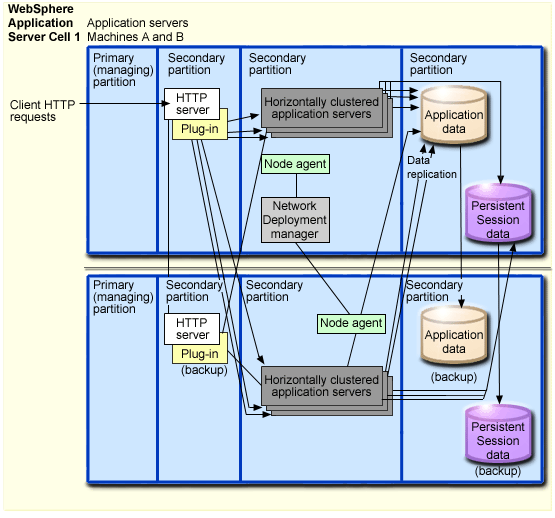
This sample topology includes these features:
- The use of two iSeries servers and LPAR provides process and data isolation, as well as hardware redundancy.
- Both Machine A and Machine B host a cluster member of each application server cluster.
- A partition on Machine A serves as the primary Web server for the application and distributes client requests to the application server cluster members on both machines.
- Machine B hosts the backup Web server.
- A single Network Deployment manager communicates with a node agent on each machine to manage the application servers.
- This topology also shows the application database and persistent session database. Each of these databases uses data replication to enhance availability and avoid creating a single point of failure. For more information on high availability databases, see High availability database.
Note: Although the high availability database is included in this sample topology, it is not required to implement the topology.
Advantages and disadvantages of horizontal scaling with high availability Apache Web server
In addition to the advantages and disadvantages of horizontal scaling, this topology provides the benefit of HTTP server failover support.