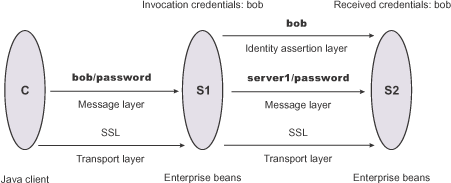

This example presents a pure Java client, C, that accesses a secure enterprise bean on server, S1, through user bob. The enterprise bean code on S1 accesses another enterprise bean on server, S2. This configuration uses identity assertion to propagate the identity of bob to the downstream server, S2. S2 trusts that bob already is authenticated by S1 because it trusts S1. To gain this trust, the identity of S1 also flows to S2 simultaneously and S2 validates the identity by checking the trustedPrincipalList list to verify that it is a valid server principal. S2 also authenticates S1. The following steps take you through the configuration of C, S1, and S2.
Configuring client, C
Client C requires message layer authentication with a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) transport. To accomplish this task:
All further configuration involves setting properties within this file.
In this case, SSL is supported but not required: com.ibm.CSI.performTransportAssocSSLTLSSupported=true, com.ibm.CSI.performTransportAssocSSLTLSRequired=false
In this case, client authentication is supported but not required: com.ibm.CSI.performClientAuthenticationRequired=false, com.ibm.CSI.performClientAuthenticationSupported=true
Configuring server, S1
In the administrative console, server S1 is configured for incoming requests to support message-layer client authentication and incoming connections to support SSL without client certificate authentication. Server S1 is configured for outgoing requests to support identity assertion.
Configuring server, S2
In the administrative console, server S2 is configured for incoming requests to support identity assertion and to accept SSL connections. Complete the following steps to configure incoming connections. Configuration for outgoing requests and connections are not relevant for this scenario.
Related reference
Scenario 2: Basic authentication, identity assertion, and client certificates
Scenario 3: Client certificate authentication and RunAs system
Scenario 4: TCP/IP transport using a virtual private network
Scenario 5: Interoperability with WebSphere Application Server Version 4.x
Example: Common Secure Interoperability Version 2 scenarios