Message-driven beans - automatic message retrieval
WebSphere Application Server supports the use of message-driven beans beans as asynchronous message consumers.
The following figure shows an incoming message being passed automatically to the onMessage() method of a message-driven bean that is deployed as a listener for the destination. The message-driven bean processes the message, in this case passing the message on to a business logic bean for business processing.
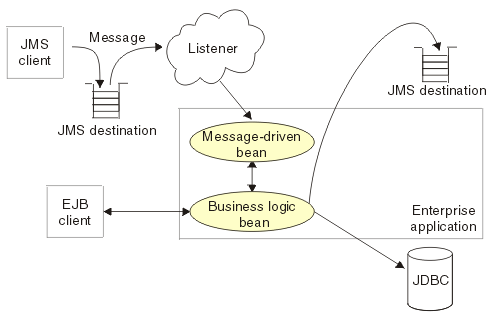
A client sends messages to the destination (or endpoint) for which the message-driven bean is deployed as the message listener. When a message arrives at the destination, the EJB container invokes the message-driven bean automatically without an application having to explicitly poll the destination. The message-driven bean implements some business logic to process incoming messages on the destination.
It can be helpful to separate the business logic of the application from the communication interfaces, such as the JMS request and response handling. To achieve this separation, we can design your message-driven bean to delegate the business processing of incoming messages to another enterprise bean. Separating message handling and business processing enables different users to access the same business logic in different ways, either through incoming messages or, for example, from a WebSphere J2EE client.
Message-driven beans can be configured as listeners on a Java EE Connector Architecture (JCA) 1.5 or 1.6 resource adapter or against a listener port. With a JCA 1.5 resource adapter, message-driven beans can handle generic message types, not just JMS messages. This makes message-driven beans suitable for handling generic requests inbound to WebSphere from enterprise information systems through the resource adapter. In the JCA 1.5 specification, such message-driven beans are commonly called message endpoints or just endpoints.
All message-driven beans must implement the MessageDrivenBean interface. For JMS messaging, a message-driven bean must also implement the message listener interface, javax.jms.MessageListener.
Messages arriving at a destination being processed by a message-driven bean have no client credentials associated with them; the messages are anonymous. Security depends on the role specified by the RunAs Identity for the message-driven bean as an EJB component. For more information about EJB security, see Secure enterprise bean applications.
For JMS messaging, message-driven beans can use a JMS provider that has a JCA 1.5 resource adapter, for example the default messaging provider that is part of WAS or the IBM MQ messaging provider. With a JCA 1.5 resource adapter, we deploy EJB 2.1 message-driven beans as JCA 1.5-compliant resources, to use a J2C activation specification. If the JMS provider does not have a JCA 1.5 resource adapter, for example the V5 default messaging provider, configure JMS message-driven beans against a listener port.
Subtopics
- Message-driven beans, activation specifications, and listener ports
- Message processing in ASF mode and non-ASF mode
- Message-driven beans - JCA components
- J2C activation specification configuration and use
- Message-driven beans - transaction support
- Message-driven beans - listener port components
- Message-driven beans - transaction handling with service integration bus
- Message-driven beans and tuning settings on z/OS