Web Services Addressing: firewalls and intermediary nodes
Using the Web Services Addressing (WS-Addressing) support in WAS ND v9, we can create endpoint references that can be distributed across firewalls and intermediary nodes.
These endpoint references contain address information, based on the URL configured for the endpoint and any valid proxy configuration for the server that hosts the endpoint. Messages targeted at the endpoint reference from the client are routed to the endpoint through the appropriate intermediary node or nodes.
If we use the IBM proprietary API to create the endpoint reference, the topology of our system can also affect the type of endpoint reference that the WS-Addressing programming model generates. For example, if we use the method...
-
EndpointReferenceManager.createEndpointReference(QName serviceName, String endpointName)
...to create an endpoint reference in a cluster environment, the endpoint reference, by default, represents an endpoint that is workload-managed in the cluster in which the endpoint was created, in accordance with the appropriate topologies in the following sections. This behavior therefore provides a performance enhancement for the application.
If the requesting application component runs under a transaction or in an HTTP session, affinity constraints might apply to the workload-management of endpoints.
We can also use the IBM proprietary API to create an endpoint reference that represents a service that should not be workload-managed, for example because it maintains in-memory state. A service that uses a stateful session bean is one example of a service that relies on routing affinity to a specific server instance. To create an endpoint reference to such a service, use the method...
-
EndpointReferenceManager.createEndpointReference(QName serviceName, String endpointName, java.rmi.Remote statefulSessionBean)
If we enable high availability for stateful session beans, and create the endpoint reference using this method, the endpoint reference remains valid even if the stateful session bean is failed over, provided that the request originates from a WebSphere Application Server client at version 6.1 or later, or is routed by a Proxy Server for IBM WAS in the same administrative cell, as described in the following topology scenarios.
- Use the Direct connection topology for non-clustered configurations.
- Use the HTTP server, such as IBM HTTP Server, topology when endpoint references refer to services that:
- are deployed in a workload-managed cluster
- do not access any stateful information localized to a specific server
- Use the Proxy Server for IBM WAS topology, or the HTTP server with a Proxy Server for IBM WAS topology, when endpoint references refer to services that:
- are deployed in a workload-managed cluster
- optionally, access stateful information localized to a specific server
- optionally, can be failed over in a highly-available configuration
The HTTP server with a Proxy Server for IBM WAS topology is useful when the HTTP server itself has no integrated capability for affinity-based routing to WS-Addressing endpoints.
For endpoint references that refer to services that do not access stateful information localized to a specific server, all the following topology scenarios are suitable.
Direct connection
Use this topology for non-clustered configurations.
In this topology, there is no intermediary node. The client communicates directly with the server that hosts the target endpoint. In this topology, the WS-Addressing APIs automatically generate the appropriate endpoint reference address, based on the URL configured for the web service module. This scenario is illustrated in the following diagram.
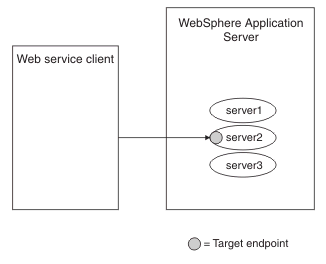
We can also use this topology when endpoint references created using the IBM proprietary API refer to services deployed in a workload-managed cluster. However, messages targeted at the endpoint reference are workload-managed only if the client targeting the endpoint reference is a WAS client, at v6.1 or later, that exists in the same administrative cell as the endpoint, as illustrated in the following diagram.
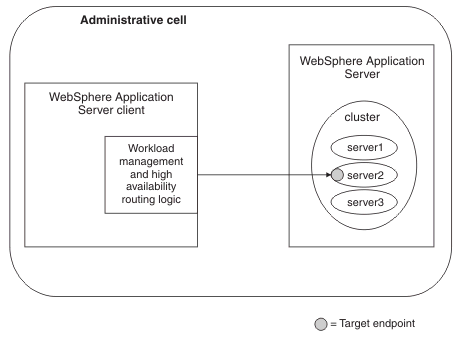
Endpoint references created using the standard JAX-WS API are not workload managed.
Proxy Server for IBM WAS
Use this topology when endpoint references refer to services deployed in a workload-managed cluster, optionally access stateful information localized to a specific server, and optionally can be failed over in a highly-available configuration.
In this topology, the WS-Addressing APIs automatically generate the appropriate endpoint reference address, based on the URL prefix of the Proxy Server for IBM WAS configured for the target web service module. Provide HTTP endpoint URL information, that is, configure the HTTP URL prefix for each deployment of each application. The client can exist outside the administrative cell containing the proxy server and target server. The client communicates with the proxy server, which dynamically routes the client requests to the appropriate server in the cluster.
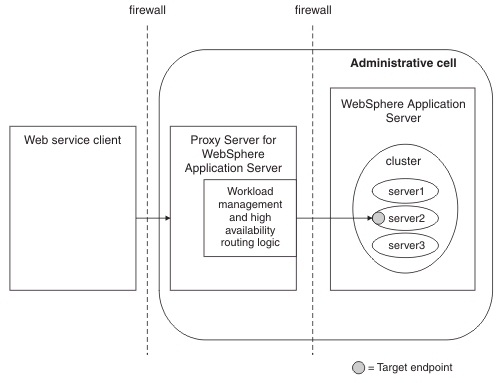
If the proxy that is addressed by the endpoint reference is a Proxy Server for IBM WAS, at v6.1 or later, that exists in the same administrative cell as the endpoint, messages targeted at a workload-managed endpoint reference are workload-managed, based on the cluster. For endpoint references created using the IBM proprietary API, the following behavior also applies:
- If the endpoint reference represents a stateful session bean, requests targeted at the endpoint reference retain affinity to the server and the instance of that stateful session bean.
- If the endpoint reference represents a highly available stateful session bean, the endpoint reference remains valid if the stateful session bean is failed over to another server.
Endpoint references created using the standard JAX-WS API do not have server affinity or high availability.
(ZOS) If the proxy that is addressed by the endpoint reference is a Proxy Server for IBM WAS, at v6.1 or later, that exists in the same administrative cell as the endpoint, messages targeted at a workload-managed endpoint reference are workload-managed, based on the cluster.
HTTP server, such as IBM HTTP Server
Use this topology when endpoint references refer to services deployed in a workload-managed cluster, and that do not access any stateful information localized to a specific server.
In this topology, the IBM WS-Addressing API automatically generates the appropriate endpoint reference address based on the URL prefix of the HTTP server configured for the target web service module. Provide HTTP endpoint URL information, that is, configure the HTTP URL prefix for each deployment of each application. The client communicates with the HTTP server, which then routes the client requests to a specific server based on the HTTP server configuration.
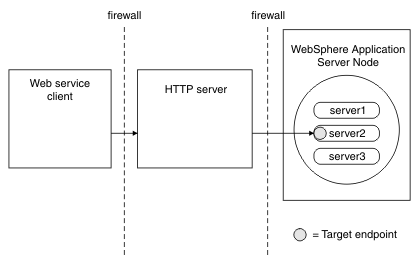
Do not deploy an endpoint reference that represents a stateful session bean in this topology, because the HTTP server will not retain affinity to that stateful session bean, and will spread its requests across the available servers.
To maintain stateful session bean affinity and high availability of endpoint references created using the IBM proprietary API, use a Proxy Server for IBM WAS in addition to the HTTP server, as described in the following topology.
HTTP server with a Proxy Server for IBM WAS
Use this topology when endpoint references refer to services deployed in a workload-managed cluster, optionally access stateful information localized to a specific server, and optionally, can be failed over in a highly-available configuration. The topology is similar to the Proxy Server for IBM WAS topology, but supports the use of any HTTP server as the external reverse proxy.
In this topology, the WS-Addressing API automatically generates the appropriate endpoint reference address based on the URL prefix of the HTTP server configured for the target web service module. Provide HTTP endpoint URL information, that is, configure the HTTP URL prefix for each deployment of each application.
The client communicates with the HTTP server, which we configure, by routing requests from a plug-in to a proxy server, to forward the client requests to a Proxy Server for IBM WAS. The proxy then dynamically routes the requests to the appropriate server.
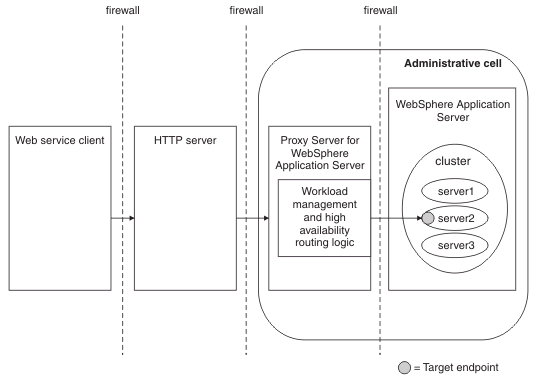
If the proxy addressed by the endpoint reference is Proxy Server for IBM WAS, at v6.1 or later, and exists in the same administrative cell as the endpoint, messages targeted at a workload-managed endpoint reference are workload-managed, based on the cluster. For endpoint references created using the IBM proprietary API, the following behavior also applies:
- If the endpoint reference represents a stateful session bean, requests targeted at the endpoint reference retain affinity to the server and the instance of that stateful session bean.
- If the endpoint reference represents a highly available stateful session bean, the endpoint reference remains valid if the stateful session bean is failed over to another server.
Endpoint references created using the standard JAX-WS API do not have server affinity or high availability.
(ZOS) If the proxy that is addressed by the endpoint reference is Proxy Server for IBM WAS, at v6.1 or later, and exists in the same administrative cell as the endpoint, messages targeted at a workload-managed endpoint reference are workload-managed, based on the cluster.
Related: