Trust associations
Trust association enables the integration of IBM WebSphere Application Server security and third-party security servers, which act as reverse proxies, providing front-end authentication, with WAS appliying its own authorization policy onto the credentials passed by the proxy server. The reverse proxy server passes an HTTP request that includes the authenticated user's credentials. WAS application security recognizes and processes these HTTP requests, and uses the credentials to authorize the request, providing fine-grained access control.
WAS and the proxy server engage in a contract in which:
- WAS gives its full trust to the proxy server
- Proxy server applies its authentication policies on every web request dispatched to WebSphere
- WAS provides authorization
Trust is validated by the interceptors using methods agreed upon by the proxy server and the interceptor.

Out of the box WAS supports the following trust association interceptor (TAI) interfaces:
- com.ibm.ws.security.web.TAMTrustAssociationInterceptorPlus
- Implements the new WAS interface, WAS v5.1.1 and later. The interface supports WebSEAL v5.1, but does not support WebSEAL v4.1. For an explanation of security attribute propagation, see Security attribute propagation.
- com.ibm.ws.security.spnego.TrustAssociationInterceptorImpl
- New to this release. SPNEGO has replaced SPNEGO TAI as the web authenticator for WAS.
Running in trust association mode does not prohibit WAS from accepting requests that did not pass through the proxy server. In this case, no interceptor is needed for validating trust.
We can create our own custom interceptors, for example a SAML Web Inbound TAI
WebSEAL Integration
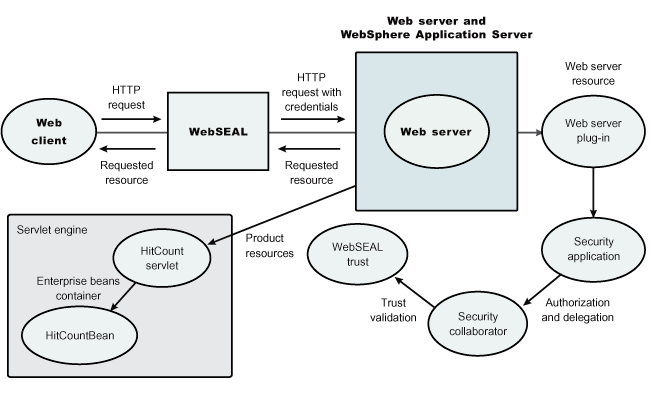
The integration of WebSEAL and WAS security is achieved by placing the WebSEAL server at the front-end as a reverse proxy server. From a WebSEAL management perspective, a junction is created with WebSEAL on one end, and the product web server on the other end. A junction is a logical connection created to establish a path from the WebSEAL server to another server. In this setup, a request for web resources stored in a protected domain of the product is submitted to the WebSEAL server where it is authenticated against the WebSEAL security realm. If the requesting user has access to the junction, the request is transmitted to the WAS HTTP server through the junction, and then to the application server. Meanwhile, WAS validates every request that comes through the junction to ensure that the source is a trusted party. This process is referenced as validating the trust and it is performed by a WebSEAL product-designated interceptor. If the validation is successful, WAS authorizes the request by checking whether the client user has the required permissions to access the web resource. If so, the web resource is delivered to the WebSEAL server through the web server, which then gives the resource to the client user.
The WebSEAL server and iv-creds
The Access Manager Policy Director delegates web requests to its web component, the WebSEAL server, which performs authentication of the requesting user using the LDAP directory of the access manager. The WebSEAL server plays the role of a client to WebSphere when channeling the request. The WebSEAL server needs its own user ID and password to identify itself to WebSphere. This identity must be valid in the security realm of WAS. The WebSEAL server replaces the basic authentication information in the HTTP request with its own user ID and password. In addition, WAS must determine the credentials of the requesting client so that the application server has an identity to use as a basis for its authorization decisions. This information is transmitted through the HTTP request by creating a header called iv-creds, with the Security Access Manager user credentials as its value.
|
WebSEAL can also map the original user ID to another user ID, such as when global single sign-on (GSO) is used.
HTTP server
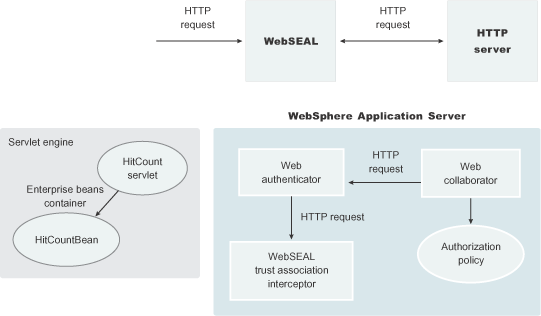
The junction created in the WebSEAL server must get to the HTTP server that serves as the product front end. However, the HTTP server is shielded from knowing that trust association is used. As far as it is concerned, the WebSEAL product is just another HTTP client, and as part of its normal routines, it sends the HTTP request to WebSphere. We can use an SSL or non-SSL junction. Use SSL to protect the requests that flow within the junction.
|
Web collaborator
When trust association is enabled, the web collaborator manages the interceptors that are configured in the system. The web collaborator loads and initializes these interceptors when servers are restarted. When a request is passed to WebSphere by the Web server, the web collaborator eventually receives the request for a security check. Two actions must take place:
- The request must be authenticated.
- The request must be authorized.
The web authenticator is called to authenticate the request by passing the HTTP request. If successful, a good credential record is returned by the authenticator, which the web collaborator uses to base its authorization for the requested resource. If the authorization succeeds, the web collaborator indicates to WebSphere that the security check has succeeded and that the requested resource can be served.
Web authenticator
The web authenticator is asked by the web collaborator to authenticate a given HTTP request. Knowing that trust association is enabled, the task of the web authenticator is to find the appropriate trust association interceptor to direct the request for processing. The web authenticator queries every available interceptor. If no target interceptor is found, the web authenticator processes the request as though trust association is not enabled.
WAS Version 4 through WAS v6.x support the com.ibm.websphere.security.TrustAssociationInterceptor.java interface. WAS v7.0.x and later supports the com.ibm.ws.security.spnego.TrustAssociationInterceptorImpl interface.
Trust association interceptor interface
The TAI interface uses reverse proxy security servers such as WebSEAL as the exposed entry points. WebSEAL performs authentication and coarse-grained authorization, and communicates with WebSpere Application Server, using the TAI. WAS can then enforce further fine-grained access control.
When a web server, such as an IBM HTTP Server, uses a TAI to communicate with WAS, sometimes it is essential for the TAI to know whether a request came through a web server or came directly to WebSphere Application Server. Therefore the WAS Web container uses three HttpServletRequest attributes to provide the TAI with the certificate information for a request:
| com.ibm.websphere.ssl.direct_connection_peer_certificates | X509Certificate[] object of the certificate for a direct peer. |
| com.ibm.websphere.ssl.direct_connection_cipher_suite | String object of a direct cipher suite. |
| com.ibm.websphere.webcontainer.is_direct_connection | Boolean object that indicates whether the connection was made through a web server, or was made directly to WebSphere. |
See the topic Web container request attributes for more information about these attributes.