Tivoli Access Manager security for WebSphere Application Server
WebSphere Application Server provides embedded IBM Tivoli Access Manager client technology to secure the WAS-managed resources.
Benefits...
- Container-based authorization
- Centralized policy management
- Management of common identities, user profiles, and authorization mechanisms
- Single-point security management for resources using the TAM Web Portal Manager console.
- No requirements for coding or deployment changes to applications
- Management of users, groups, and roles using the WAS administrative console
WebSphere Application Server supports the Java Authorization Contract for Containers (JACC) specification, which sets contract requirements for Java EE containers and authorization providers. With this contract, authorization providers can perform access decisions for resources in Java EE application servers such as WebSphere Application Server. The TAM security utility embedded within WebSphere Application Server is JACC-compliant and is used to:
- Add security policy information when applications are deployed
- Authorize access to WebSphere Application Server-secured resources.
When applications are deployed, the embedded TAM client takes any policy and or user and role information stored within the application deployment descriptor or using annotations and stores it within the TAM Policy Server.
The TAM JACC provider is also called when a user requests access to a resource that is managed by WebSphere Application Server.
Figure 1. Embedded TAM client architecture
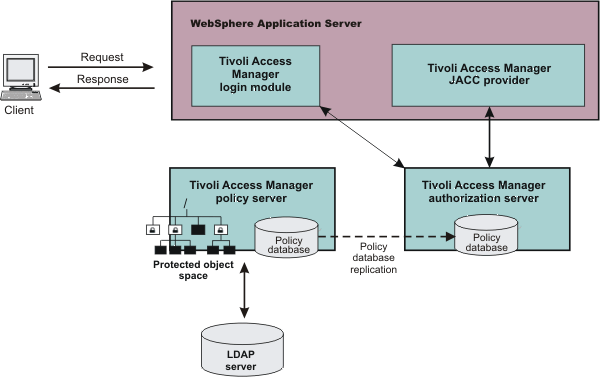
- Users accessing protected resources are authenticated using the TAM login module configured for use when the embedded TAM client is enabled.
- The WAS container uses information from the Java EE application deployment descriptor and annotations to determine the required role membership.
- WAS uses the embedded TAM client to request an authorization decision from the TAM authorization server. Additional context information, when present, is also passed to the authorization server. This context information is comprised of...
- cell name
- Java EE application name
- Java EE module name
If the TAM policy database has policies specified for any of the context information, the authorization server uses this information to make the authorization decision.
- The authorization server consults the permissions defined for the specified user within the TAM-protected object space. The protected object space is part of the policy database.
- The TAM authorization server returns the access decision to the embedded TAM client.
- WAS either grants or denies access to the protected method or resource, based on the decision returned from the TAM authorization server.
To learn more about TAM, see:
- IBM Tivoli Access Manager for e-business Installation Guide
- IBM Tivoli Access Manager for e-business Administration Guide
Example architecture showing WebSphere Application Servers secured by Tivoli Access Manager.
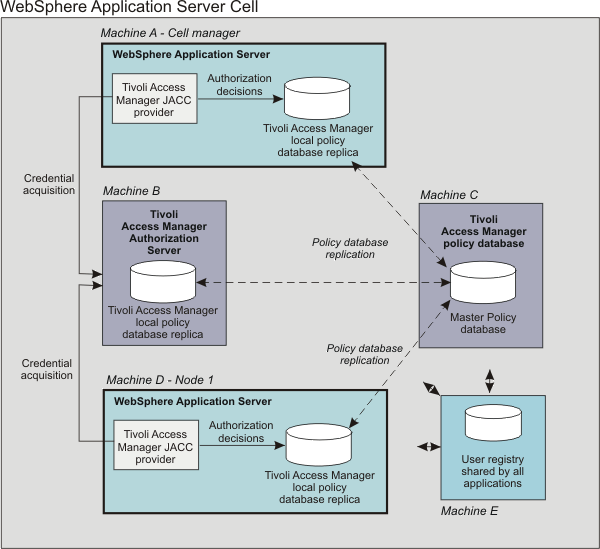
The participating WebSphere Application Servers use a local replica of the TAM policy database to make authorization decisions for incoming requests. The local policy databases are replicas of the master policy database. The master policy database is installed as part of the TAM installation. Having policy database replicas on each participating WAS node optimizes performance when making authorization decisions and provides failover capability.
Although the authorization server can also be installed on the same system as WAS, this configuration is not illustrated in the diagram.
All instances of TAM and WAS in the example architecture share the LDAP user registry on Machine E.
The LDAP registries that are supported by WAS are also supported by TAM.
It is possible to have separate WAS profiles on the same host configured for different TAM servers. Such an architecture requires that the profiles are configured for separate Java SE Runtime Environments (JRE 6) and therefore we need multiple JREs installed on the same host.
(iseries) Note: Even though all WAS profiles on the same host share a single JRE 6, we can configure separate WebSphere Application Server profiles on the same host for different TAM servers.
Related concepts
Related information: