WebSphere MQ messaging provider activation specifications
Activation specifications are used to configure inbound message delivery to message-driven beans (MDBs) running inside WebSphere Application Server. They supersede message listener ports, which are now a stabilized function.
Activation specifications and message-driven beans
Activation specifications are the standardized way to manage and configure the relationship between an MDB running in WebSphere Application Server and a destination withinWebSphere MQ. They combine the configuration of connectivity, the Java Message Service (JMS) destination and the runtime characteristics of the MDB, within a single object.
Message-driven beans are a special class of Enterprise Java Bean (EJB). They enable JEE (JEE) applications to process messages asynchronously, with WebSphere Application Server managing the transactionality and concurrency of the application.
The following figure shows how an activation specification can be used to link a WebSphere MQ queue manager destination to an MDB running within WebSphere Application Server. The process of delivering a message from a client to an MDB via an WebSphere MQ messaging provider activation specification occurs in this way:
Figure 1. WebSphere MQ messaging provider activation specification in action
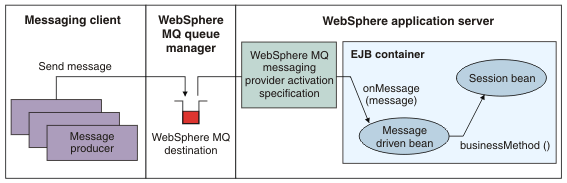
- A messaging client, either running in a stand-alone process or within an application server environment, sends a message using JMS
(or any other messaging API, such as MQI) to a WebSphere MQ queue or topic defined in a WebSphere MQ queue manager.
- A WebSphere MQ activation specification is configured to listen on that destination for messages. When the new message is detected, it is removed from the destination (potentially
under an XA transaction).
- The message is then passed to an MDB that has been configured to use the activation specification through its onMessage method.
- The MDB uses the information in the message to perform the relevant business logic.
Activation specifications compared with listener ports
Versions of WAS earlier than Version 7.0, use listener ports to define the association between a connection factory, a destination, and an MDB.
Activation specifications supersede the use of listener ports, which became a stabilized feature in WAS v7 (for more information, see Stabilized features). There are several advantages to using activation specifications over listener ports:
- Activation specifications are simple to configure, because they only require two objects: the activation specification and a message destination. Listener ports require three objects: a connection factory, a message destination, and the message listener port itself.
- Activation specifications are not limited to the server scope.
They can be defined at any administrative scope in WebSphere Application Server. Message listener
ports must be configured at the server scope. This means that each server in a node requires its own listener port. For example, if a node is made up of three servers, three separate listener ports must be configured. Activation specifications can be configured at the node scope, so in the example only one activation specification would
be needed.
- Activation specifications are part of the JEE Connector Architecture 1.5 and 1.6 standards specification (JCA 1.5 and 1.6). Listener port support in WebSphere Application Server makes use of the application server facilities interfaces defined in the JMS specification, but is not part of any specification itself.
It is still possible to use message listener ports to deliver messages to an MDB using the WebSphere MQ messaging provider. There are certain scenarios in which the use of listener ports is still preferable to using activation specifications. This usually is the case with configurations in which some of the servers are running on versions of WAS earlier than WAS v7. It is possible to configure both message listener ports (which make use of WebSphere MQ messaging provider resources) and WebSphere MQ messaging provider activation specifications at the same time. For more information, see Message-driven beans, activation specifications, and listener ports.
To assist in migrating listener ports to activation specifications, the WAS console provides a Convert listener port to activation specification wizard on the Message listener port collection panel. This allows us to convert existing listener ports into activation specifications. However, this function only creates a new activation specification with the same configuration used by the listener port. It does not modify application deployments to use the newly created activation specification.
Related concepts
Related tasks