Network Deployment (Distributed operating systems), v8.0 > Administer applications and their environment > Manage applications through programming
Application management
Java EE applications and modules include an XML-based deployment descriptor that specifies various Java EE artifacts that pertain to applications or modules. The Java EE artifacts include EJB definitions, security role definitions, EJB references, resource references, and so on. These artifacts define various unresolved references that the application logic uses. The Java EE specification requires that these artifacts map to Java EE platform-specific information, such as that found in WAS, during deployment of Java EE applications.
The application assembly tools that WAS supports, as well as the application management support provided with the product, facilitate collection of certain WAS information. The collected information is used to resolve references that are defined in various deployment descriptors in a Java EE application. This information is stored in the application EAR file in conjunction with the deployment descriptors. The following diagram shows the structure of an EAR file that is populated with deployment information that is specific to WAS.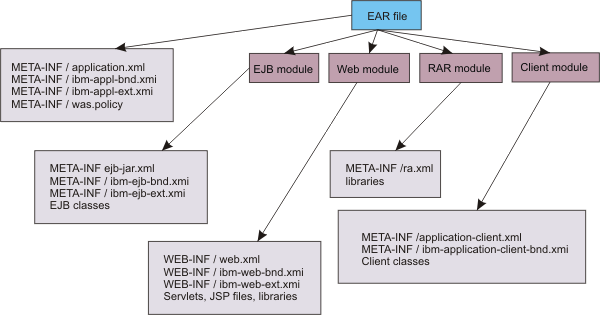
The application management architecture provides a set of classes with which deployers can collect WASdeployment information. This information is also referred to as binding information, and is stored in the application EAR file. The deployer can install the EAR file into aWASconfiguration by using the AppManagement interface.
The application management support in WAS provides functions such as installing and uninstalling applications, editing binding information for installed applications, updating the entire application or part of the application, exporting the application, and so on. The com.ibm.websphere.management.application.AppManagement interface, which is exposed as a JMX-based AppManagement MBean in WAS, provides this functionality. Code that runs on the server or in a stand-alone administrative client program can access the interface. Access to the application management functions is also possible in the absence of WAS. This mode, known as local mode, is particularly useful for installing Java EE applications as part of product installation. For WAS ND, the AppManagement MBean is present in the dmgr only, which facilitates centralized configuration and administration.
Application deployment in a WAS ND configuration
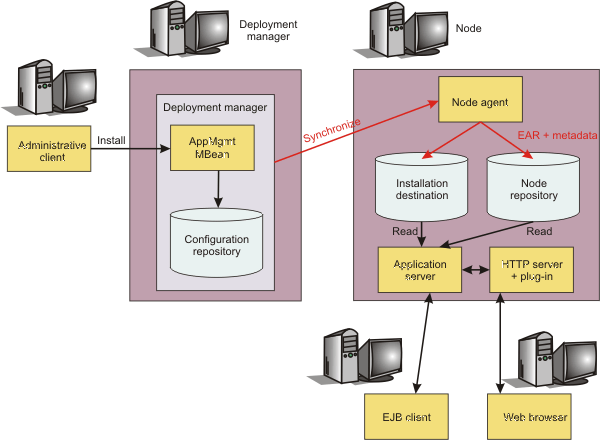
The following diagram explains application deployment for the WAS ND:
- The application EAR file that you install is stored in the master configuration repository of the dmgr, with the application metadata.
- The configuration synchronization operation replicates the application in the master repository into the repository of the target node.
- The application EAR file is extracted to the installation destination of the target node at the end of the synchronization operation.
- The WAS run time reads the application business logic such as EJB classes, servlets, and JSP from the installation destination while serving application client requests.
- WAS reads the application metadata, such as deployment descriptors and WAS bindings during application startup from the configuration repository or the installation destination only, depending on the option specified during application installation.
Use administrative programs (JMX)