Prepare the Windows machine
- Verify the operating system/service pack version
- Check the network setup
- Check access rights for the system logon user ID that is required during installation
- Manage the length of the PATH environment variable
- Disable any firewall products
- Launch Services
- Launch Task Manager
Verify the operating system/service pack version
We can check the operating system and service pack version by doing the following steps:
- Right-click on the My Computer icon
- Click Properties.
- Verify that an appropriate operating system/service pack combination is installed.
- If an appropriate operating system or service pack is not installed, refer to the Microsoft support site to download and install the required software.
Check for a configured, fully-qualified host name
WebSphere Portal requires the use of a fully-qualified host.name, which is typically the host.name of the server along with its fully-qualified domain name (FQDN). To verify....
ping yourserver.yourcompany.com
Check access rights for the system logon user ID that is specified for Windows service creation
Before installing WebSphere Portal, check that the system logon user ID to be used during installation has the following permissions and rights:
- The user ID must already exist prior to installation.
- The user ID must be a local Windows user ID that is in the Administrators group.
- The user ID must have specific security access rights if you intend to run WAS as a service.
To determine if a user account is a member of the Administrators group:
- Click...
Start | Programs | Administrative Tools | Computer Management | Local Users and Groups | Groups
- Open the Administrators group to see what members belong to it.
- Add users to the Administrators group as necessary.
A domain user ID with administrator privileges is not sufficient for installation.
Determine if a user ID has the appropriate access rights
If you install WAS during the installation, we can select to run WAS as a service, and then provide the system logon user ID and password. The user ID must have the following user rights:
Act as part of the operating system: Windows designates this user right as a privilege for the user account. Log on as a service: Windows designates this user right as a logon right for the user account.
Because a single user ID and password are used, the WebSphere Portal installation does not allow you to create separate user accounts for these services. User rights are maintained with the Local Security Policy tool.
To view or modify the user rights:
- Click...
Start | Programs | Administrative Tools | Local Security Policy | Local Policies | User Rights Assignment
- Locate and open Act as part of the operating system to determine if this user right is enabled. If it is enabled go to the next step. If it is not enabled, enable it.
- Locate and open Log on as a service to determine if the user right is enabled. If it is enabled, go to the next step. If it is not enabled, enable it.
- If you made any changes, log off and then log on to activate the changes. In some cases reboot the system.
If these changes are not made prior to starting the installation, rebooting will be required during the installation to update the user ID with the required privileges.
The Windows help system provides extensive information about the user rights and security options that are available. See the Windows help system for more information on setting user rights.
Manage the length of the Path environment variable
During installation and configuration values are added temporarily to the Path. As a result, you might see the following error during configuration:
The input line is too long. The syntax of the command is incorrect.This message might also appear in wpsinstalllog.txt.
This is because the Path environment variable is approaching the maximum length allowed by Windows. IBM recommends that you shorten the PATH and then attempt to configure again. The Path environment variable can be accessed by right-clicking My Computer and clicking Properties. Then click the Advanced tab and click Environment Variables.
Disable any firewall products
Before you start the WebSphere Portal installation program, disable any firewall products that are running on the machine where portal will be installed. If the installation program detects a firewall, a warning message displays.
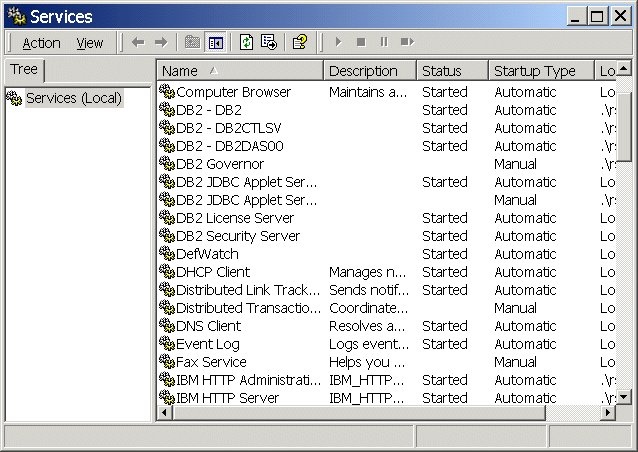
Launch Services
The Windows operating system includes an administrative tool called Services that enables you to stop, start, or check the status of a service. An example of a service is DB2 - DB2, which is the name of the main service provided by DB2.
At various times during the installation of WebSphere Portal, you might need to check the status of specific services or start and stop services. Note that some applications like DB2 have more than one service running, and if you have to start or stop these services, start or stop all of them.
To access Services:
- Click...
Start | Programs | Administrative Tools | Services
- To determine if a service has started, view the Status column. If there is no value in the Status column, then that service has not started.
- To start or stop a service, right-click on the service and then click Start or Stop.
Services are sometimes referred to as processes in the screens that are provided with some applications.
Launch Task Manager
Windows Task Manager provides real-time status information about the system, including the programs and processes that are running and the system resources, such as memory, that are being consumed. Because some parts of the WebSphere Portal installation are processor intensive, we can use Windows Task Manager to verify that the installation is continuing, even though progress indicators on the install panels might appear to have stalled.
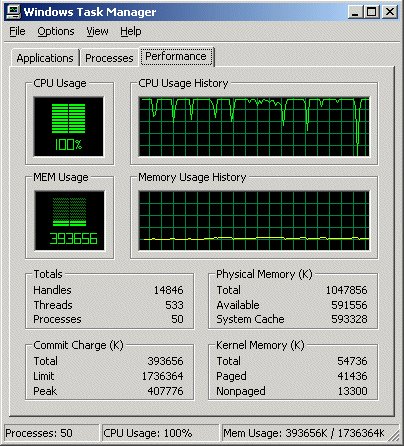
To open Windows Task Manager:
- Right-click an empty space on the taskbar.
- Click Task Manager.
- Click the Processes or Performance tab to view the progress.
Related information