Example: Developing a Web service from an EJB or JavaBeans implementation
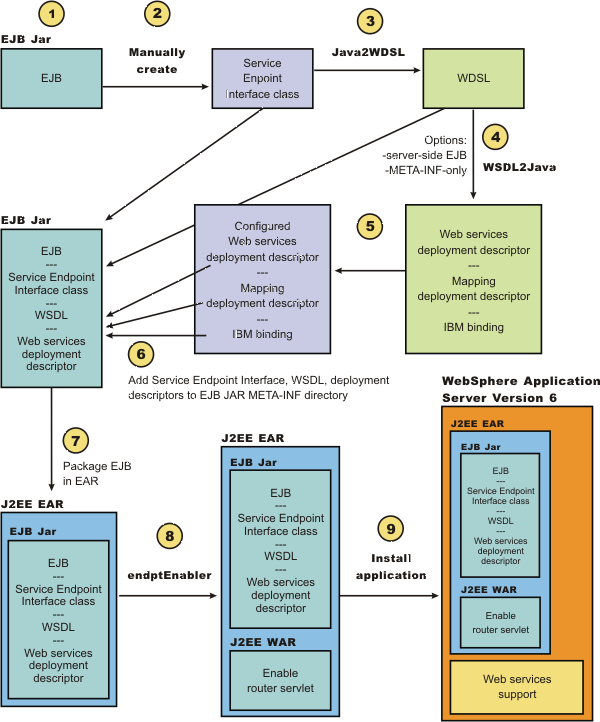
This example takes you through the steps to develop a Web service from an EJB or JavaBeans implementation. The development process is based on the Web Services for J2EE specification.
- Select the enterprise bean or JavaBeans implementation that you want to enable as a Web service.
The implementation must meet the following Web Services for J2EE specification requirements:
- It must have methods that can be mapped to a service endpoint interface. See step 2 for more information.
- It must be a stateless session EJB implementation or a JavaBeans implementation without client-specific state, because the implementation bean might be selected to process a request from any client. If a client-specific state is required, a client identifier must be passed as a parameter of the Web service operation.
The selected methods of an enterprise bean must not have a transaction attribute of mandatory, because no standard currently exists, for these Web services transactions.
A JavaBeans implementation in a Web container requires the following contents:
- A public default constructor
- Exposed public methods
- It must not save a client-specific state between method calls
- It must be a public, non-final, and non-abstract class
- It must not define a finalize method
- Develop a service endpoint interface.
Developing a Web service requires a service endpoint interface.
If you are using an EJB implementation, develop a service endpoint interface from an EJB remote interface.
If you are using a JavaBeans implementation, develop a service endpoint interface for a JavaBeans implementation.
- Develop a Web Services Description Language (WSDL) file.
- Develop deployment descriptor templates.
If you are using an EJB implementation, develop Web services deployment descriptor templates from an EJB implementation.
If you are using a JavaBeans implementation, develop Web services deployment descriptor templates for a JavaBeans implementation.
- Configure the deployment descriptors.
By setting the ejb-link or servlet-link values of the service-impl-bean elements one can link to the enterprise bean or JavaBeans implementation that implement the service.
Configure the webservices.xml deployment descriptor.
Configure the ibm-webservices-bnd.xmi deployment descriptor.
- Assemble an enterprise archive (EAR) file from a JAR file or assemble an EAR file from a WAR file.
- Enable the Web service-enabled
EAR file.
This step only applies if you are using an EJB implementation.
- Deploy the Web service application.
- Publish the WSDL file.
Related Tasks
Developing Web services applications