Authentication
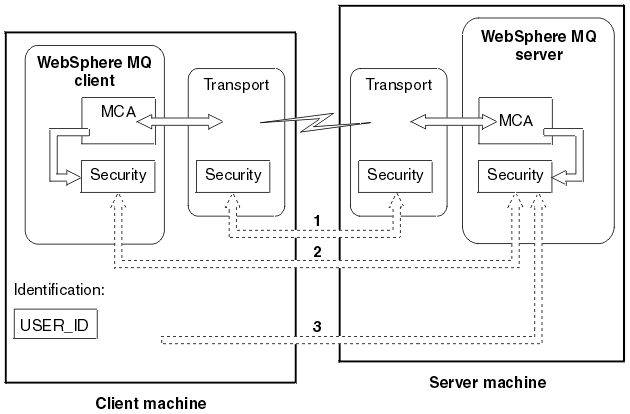
There are three levels of security to consider, as shown in the following diagram. MCA is a Message Channel Agent.
Figure 3. Security in a client-server connection
- Transport level
This is the same as for two WebSphere MQ queue managers (server to server) and is described in the WebSphere MQ Intercommunication manual.
- Channel security exits
The channel security exits for client to server communication can work in the same way as for server to server communication. A protocol independent pair of exits can be written to provide mutual authentication of both the client and the server. A full description is given in the WebSphere MQ Intercommunication manual.
- Identification passed to a channel security exit
In client to server communication, the channel security exits do not have to operate as a pair. The exit on the WebSphere MQ client side can be omitted. In this case the user ID is placed in the channel descriptor (MQCD) and the server-side security exit can alter it, if required. Windows clients also send additional information to assist identification.
- The user ID that is passed to the server is the currently logged-on user ID on the client. In addition, a client on Windows passes the security ID of the currently logged-on user.
The values of the user ID and, if available, the security ID, can be used by the server security exit to establish the identity of the WebSphere MQ client.
Home