Redundant server topology for EJB failover support
As shown in Figure 9-3, horizontal and vertical scaling is used to have appserver redundancy to tolerate possible process and machine failures.
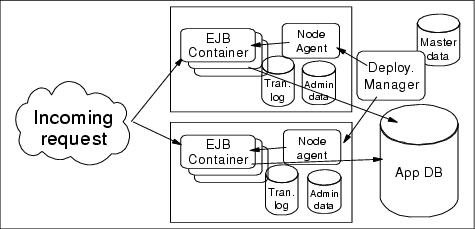
Figure 9-3 WebSphere EJB container failover
We discuss how to fail over two-phase transactions and recover tranlog in 9.5, Enhancing WebSphere HA using clustering software and how to fail over a database in Chapter 12, WebSphere data management high availability.
The mechanisms for routing workload managed EJB requests to multiple cluster members are handled on the client side of the application. In WebSphere V5.0, this functionality is supplied by a workload management plug-in to the client ORB and the routing table in LSD hosted in the Node Agent. The WLM failover support for EJBs is to maintain the routing table and to modify the client ORB to redirect traffic in case of a server failure.
There are the following possible failures:
WebSphere is a trademark of the IBM Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.
IBM is a trademark of the IBM Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.