Network Deployment configurations
In a typical Network Deployment cluster configuration, capacity and reliability can be increased by horizontal scaling, for example the usage of multiple physical nodes inside a cell and application clustering across these nodes (see Figure A-1). The Deployment Manager contains the master configuration repository and provides a centralized point of cell administration.
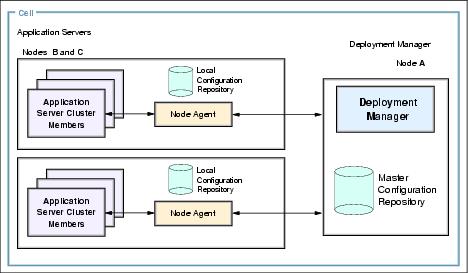
Figure A-1 A Network Deployment cell configuration
In the case of a Base node failure, the other cluster members transparently take over the load of the failed one, and after restoration, the node will continue to participate in sharing the workload again. If the Deployment Manager node fails, the appservers in the cell keep on working, but making configuration changes without the central administration view becomes inefficient and burdensome. You can choose to configure your system in a highly available cluster to minimize downtime, but this would require additional hard- and software and also add to the complexity of the system configuration. For an in-depth discussion of WAS system high availability and failover, refer to Part 4, High availability solutions in this book.
For an alternative implementation of Deployment Manager high availability without clustering, refer to the developerWorks article by Tom Alcott, which provides additionally hints and insights into system backup and restoration:
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/apps/transform.wss?URL=/developerworks/we bsphere/library/techarticles/0304_alcott/alcott.xml&xslURL=/developerworks/ websphere/xsl/document.xsl&format=one-column
WebSphere is a trademark of the IBM Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.
IBM is a trademark of the IBM Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.