Introduction and considerations
Unlike Oracle OPS/RAC, which uses a shared data architecture, IBM DB2 UDB Enterprise Extended Edition uses a share-nothing architecture. Because data access congestion is avoided for a share-nothing architecture, IBM DB2 UDB EEE performs and scales well for very large databases.
IBM DB2 UDB EEE is the high-end edition for supporting clustered servers. It supports parallel query processing in both Symmetric Multiple Processing (SMP) and Massively Parallel Processing (MPP) environments needed for large data warehouse and high-volume online transaction processing (OLTP) systems. The major difference that distinguishes DB2 UDB EEE from other DB2 editions is the concept of a database partition. In DB2 UDB EEE, a database is not restricted to a single physical machine; a whole cluster of servers hosts a single database. The data stored in the database can be partitioned across the servers that participate in the cluster. Each partition stores a portion of the data in the database. SQL query processing is performed in parallel by all partitions. Query predicates that cannot be answered locally at a single partition are resolved among database partitions. Each row stored in a database on IBM DB2 UDB EEE is assigned to a specific partition. This assignment is based on the value of the partitioning key, which must be a subset of the primary key and every unique constraint for the table. A partitioning key is defined for a table using the CREATE TABLE statement. For details, please refer to the IBM DB2 UDB EEE documentation, since we focus on the availability issues here.
Since the data is partitioned across many machines, no single failure of machines or data partitions will cause the complete failure of the data service.
We can also enhance availability using IBM DB2 UDB partition failover controlled by clustering software such as HACMP, MC/ServiceGuard, Sun Cluster, VERITAS Cluster, or MSCS, as shown in Figure 12-14. We have three partitions on three machines, and the fourth machine is used as a hot standby. If any of the three partitions fails, it will fail over to the hot standby machine.
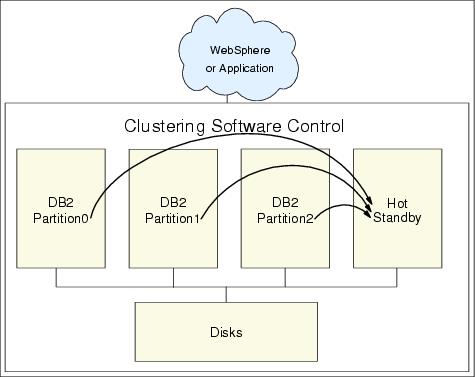
Figure 12-14 DB2 Parallel Server partition failover under control of cluster software
WebSphere is a trademark of the IBM Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.
IBM is a trademark of the IBM Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both.