Routing client connection requests to IBM MQ queue manager servers by using security exits
In this scenario, we can dynamically route client connection requests, in a round-robin fashion, to a group of three IBM MQ queue manager servers. The queue manager on each server in the group must be identical.
Before starting
- Before you start to use this scenario, make sure that we have completed the prerequisite tasks listed in Getting started with IBM MQ Internet Pass-Thru.
- Install Java 8.0 JDK.
- Add the Java bin subdirectory to the PATH environment variable.
The sample exit used in this scenario is SampleRoutingExit.java. It is provided with MQIPT in the samples/exits subdirectory of the MQIPT installation directory.
The name and location of the compiled exit class file is defined with the MQIPT SecurityExitName and SecurityExitPath properties.
The list of queue manager and server names to be used is read from a configuration file, called SampleRoutingExit.conf. The exit expects the configuration file to exist in the same directory as the exit class file.
The first time the amqsputc command is run, the IBM MQ message is placed on the MQIPT.LOCAL.QUEUE queue on the first server. The second time it is run, the message is placed on the queue on the second server, and so on. Using this setup, it is not possible for the amqsgetc command to retrieve the message just placed on the queue, because the client connection request used by the amqsgetc command is passed to the next queue in the list. However, running the amqsputc command three times, followed by three amqsgetc commands, ensures that each message is retrieved in the same order.
Of course, by using another IBM MQ client, connecting directly to a queue manager (that is, not using the MQIPT in this sample), we can selectively retrieve messages from any of the queue managers.
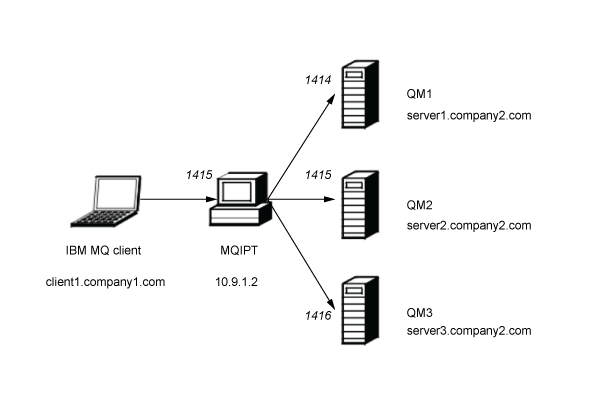
This diagram shows the connection flow from the IBM MQ client (called client1.company1.com on port 1415) through MQIPT to three IBM MQ servers (called server1.company2.com, server2.company2.com, and server3.company2.com).
Procedure
To route client connection requests sequentially to three different IBM MQ queue manager servers by using security exits, complete the following steps:
- Create three identical queue managers named MQIPT.QM1 on three separate servers. Each queue manager has a SVRCONN channel named MQIPT.CONN.CHANNEL and an empty local queue named MQIPT.LOCAL.QUEUE.
-
On the MQIPT server:
- Create a directory called exits in the MQIPT home directory by issuing the following command in a
command prompt:
md C:\mqiptHome\exits
-
In the C:\mqiptHome\exits directory (where
C:\mqiptHome is the directory where the mqipt.conf file is
located), create a sample configuration file, called SampleRoutingExit.conf
that contains the names of our three queue managers.
For example, the configuration file could contain the following entries:
server1.company2.com:1414 server2.company2.com:1415 server3.company2.com:1416
Ensure that there are no blank lines before the first entry in the file and that each entry is a valid server name. If we have used different server names, change these names to match your environment. - Open a command prompt and enter the following commands to compile the exit. You do not
have to do this if you have not changed the exit code as the compiled sample exit is supplied with
MQIPT.
C: cd \mqipt\samples\exits javac -classpath C:\mqipt\lib\com.ibm.mq.ipt.jar;. SampleRoutingExit.java
-
Enter the following command to copy the compiled exit class file
SampleRoutingExit.class to the C:\mqiptHome\exits
directory:
copy C:\mqipt\samples\exits\SampleRoutingExit.class C:\mqiptHome\exits
-
Edit mqipt.conf and add a route definition:
[route] ListenerPort=1415 Destination=server1.company2.com DestinationPort=1414 SecurityExit=true SecurityExitPath=C:\mqiptHome\exits SecurityExitName=SampleRoutingExit
Note that we do not have to set SecurityExitPath if you put SampleRoutingExit.conf in the default C:\mqiptHome\exits directory. -
Start MQIPT.
Open a command prompt and enter the following command:
C:\mqipt\bin\mqipt C:\mqiptHome -n ipt1
where C:\mqiptHome indicates the location of the MQIPT configuration file, mqipt.conf, and ipt1 is the name to be given to the instance of MQIPT. The following messages indicate that MQIPT has started successfully:5724-H72 (C) Copyright IBM Corp. 2000, 2020 All Rights Reserved MQCPI001 IBM MQ Internet Pass-Thru V9.2.0.0 starting MQCPI004 Reading configuration information from mqipt.conf MQCPI152 MQIPT name is ipt1 MQCPI021 Password checking has been enabled on the command port MQCPI011 The path C:\mqiptHome\logs will be used to store the log files MQCPI006 Route 1415 has started and will forward messages to : MQCPI034 ....server1.company2.com(1414) MQCPI035 ....using MQ protocol MQCPI079 ....using security exit C:\mqiptHome\exits\SampleRoutingExit MQCPI080 ......and timeout of 30 seconds MQCPI078 Route 1415 ready for connection requests
- Create a directory called exits in the MQIPT home directory by issuing the following command in a
command prompt:
- At a command prompt on the IBM MQ client
system, enter the following commands:
- Set the MQSERVER environment variable:
SET MQSERVER=MQIPT.CONN.CHANNEL/TCP/10.9.1.2(1415)
- Put three messages:
amqsputc MQIPT.LOCAL.QUEUE MQIPT.QM1 Hello world 1 amqsputc MQIPT.LOCAL.QUEUE MQIPT.QM1 Hello world 2 amqsputc MQIPT.LOCAL.QUEUE MQIPT.QM1 Hello world 3
Press Enter twice after typing each message string. - Get the messages:
amqsgetc MQIPT.LOCAL.QUEUE MQIPT.QM1 amqsgetc MQIPT.LOCAL.QUEUE MQIPT.QM1 amqsgetc MQIPT.LOCAL.QUEUE MQIPT.QM1
The messages, Hello world 1, Hello world 2, and Hello world 3 are returned.
- Set the MQSERVER environment variable:
Parent topic: Getting started with IBM MQ Internet Pass-Thru