Administrative topic objects
Use an administrative topic object, we can assign specific, non-default attributes to topics.
Figure 1 shows how a high-level topic of Sport divided into separate topics covering different sports can be visualized as a topic tree: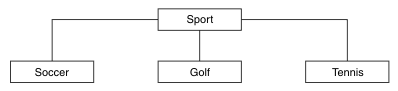
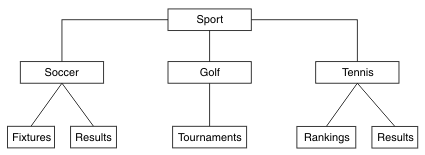
To create the topic tree illustrated, no administrative topic objects need be defined. Each of the nodes in this tree are defined by a topic string created in a publish or subscribe operation. Each topic in the tree inherits its attributes from its parent. Attributes are inherited from the parent topic object, because by default all attributes are set to ASPARENT. In this example, every topic has the same attributes as the Sport topic. The Sport topic has no administrative topic object, and inherits its attributes from SYSTEM.BASE.TOPIC.
Note, that it is not good practice to give authorities for non-mqm users at the root node of the topic tree, which is SYSTEM.BASE.TOPIC, because the authorities are inherited but cannot be restricted. Therefore, by giving authorities at this level, you are giving authorities to the whole tree. You should give the authority at a lower topic level in the hierarchy.
Administrative topic objects can be used to define specific attributes for particular nodes in the topic tree. In the following example, the administrative topic object is defined to set the durable subscriptions property DURSUB of the soccer topic to the value NO:
DEFINE TOPIC(FOOTBALL.EUROPEAN)
TOPICSTR('Sport/Soccer')
DURSUB(NO)
DESCR('Administrative topic object to disallow durable subscriptions')
The topic tree can now be visualized as: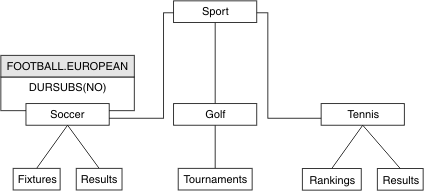
Any applications subscribing to topics beneath Soccer in the tree can still use the topic strings they used before the administrative topic object was added. However, an application can now be written to subscribe using the object name FOOTBALL.EUROPEAN, instead of the string /Sport/Soccer. For example, to subscribe to /Sport/Soccer/Results, an application can specify MQSD.ObjectName as FOOTBALL.EUROPEAN and MQSD.ObjectString as Results.
With this feature, we can hide part of the topic tree from application developers. Define an administrative topic object at a particular node in the topic tree, then application developers can define their own topics as children of the node. Developers must know about the parent topic, but not about any other nodes in the parent tree.
Inheriting attributes
If a topic tree has many administrative topic objects, each administrative topic object, by default, inherits its attributes from its closest parent administrative topic. The previous example has been extended in Figure 4: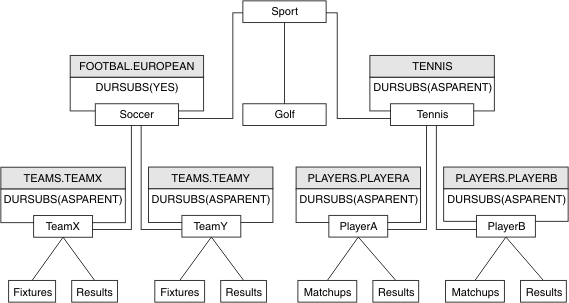
For example use inheritance to give all the child topics of /Sport/Soccer the property that subscriptions are non-durable. Change the DURSUB attribute of FOOTBALL.EUROPEAN to NO.
This attribute can be set using the following command:ALTER TOPIC(FOOTBALL.EUROPEAN) DURSUB(NO)
All the administrative topic objects of child topics of Sport/Soccer have the property DURSUB set to the default value ASPARENT. After changing the DURSUB property value of FOOTBALL.EUROPEAN to NO, the child topics of Sport/Soccer inherit the DURSUB property value NO. All child topics of Sport/Tennis inherit the value of DURSUB from SYSTEM.BASE.TOPIC object. SYSTEM.BASE.TOPIC has the value of YES.
Trying to make a durable subscription to the topic Sport/Soccer/TeamX/Results would now fail; however, trying to make a durable subscription to Sport/Tennis/PlayerB/Results would succeed.
Controlling wildcard usage with the WILDCARD property
Use the MQSC Topic WILDCARD property or the equivalent PCF Topic WildcardOperation property to control the delivery of publications to subscriber applications that use wildcard topic string names. The WILDCARD property can have one of two possible values:
- WILDCARD
- The behavior of
wildcard subscriptions with respect to this topic.
- PASSTHRU
- Subscriptions made to a wildcarded topic less specific than the topic string at this topic object receive publications made to this topic and to topic strings more specific than this topic.
- BLOCK
- Subscriptions made to a wildcarded topic less specific than the topic string at this topic object do not receive publications made to this topic or to topic strings more specific than this topic.
The value of this attribute is used when subscriptions are defined. If you alter this attribute, the set of topics covered by existing subscriptions is not affected by the modification. This scenario applies also if the topology is changed when topic objects are created or deleted; the set of topics matching subscriptions created following the modification of the WILDCARD attribute is created using the modified topology. If you want to force the matching set of topics to be re-evaluated for existing subscriptions, you must restart the queue manager.
In the example, Example: Create the Sport publish/subscribe cluster, we can follow the steps to create the topic tree structure shown in Figure 5.
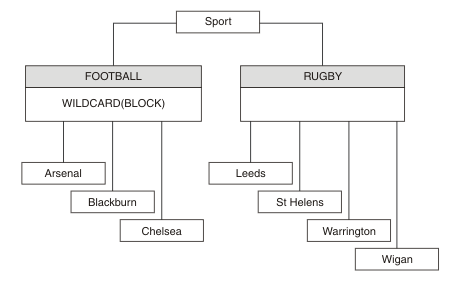
A subscriber using the wildcard topic string # receives all publications to the Sport topic and the Sport/Rugby subtree. The subscriber receives no publications to the Sport/Football subtree, because the WILDCARD property value of the Sport/Football topic is BLOCK.
PASSTHRU is the default setting. We can set the WILDCARD property value PASSTHRU to nodes in the Sport tree. If the nodes do not have the WILDCARD property value BLOCK, setting PASSTHRU does not alter the behavior observed by subscribers to nodes in the Sports tree.
In the example, create subscriptions to see how the wildcard setting affects the publications that are delivered; see Figure 9. Run the publish command in Figure 12 to create some publications.
pub QMA
The results are shown in Table 1. Notice how setting the WILDCARD property value BLOCK, prevents subscriptions with wildcards from receiving publications to topics within the scope of the wildcard.
| Subscription | Topic string | Publications received | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPORTS | Sports/# |
Sports Sports/Rugby Sports/Rugby/Leeds |
All publications to Football subtree blocked by WILDCARD(BLOCK) on Sports/Football |
| SARSENAL | Sports/#/Arsenal | - | WILDCARD(BLOCK) on Sports/Football prevents wildcard subscription on Arsenal |
| SLEEDS | Sports/#/Leeds |
Sports/Rugby/Leeds |
Default WILDCARD on Sports/Rugby does not prevent wildcard subscription on Leeds. |
Suppose a subscription has a wildcard that matches a topic object with the WILDCARD property value BLOCK. If the subscription also has a topic string to the right of the matching wildcard, the subscription never receives a publication. The set of publications that are not blocked are publications to topics that are parents of the blocked wildcard. Publications to topics that are children of the topic with the BLOCK property value are blocked by the wildcard. Therefore subscription topic strings that include a topic to the right of the wildcard never receive any publications to match.
Set the WILDCARD property value to BLOCK does not mean we cannot subscribe using a topic string that includes wildcards. Such a subscription is normal. The subscription has an explicit topic that matches the topic with a topic object having a WILDCARD property value BLOCK. It uses wildcards for topics that are parents or children of the topic with the WILDCARD property value BLOCK. In the example in Figure 5, a subscription such as Sports/Football/# can receive publications.
Wildcards and cluster topics
Cluster topic definitions are propagated to every queue manager in a cluster. A subscription to a cluster topic at one queue manager in a cluster results in the queue manager creating proxy subscriptions. A proxy subscription is created at every other queue manager in the cluster. Subscriptions using topics strings containing wildcards, combined with cluster topics, can give hard to predict behavior. The behavior is explained in the following example.
In the cluster set up for the example, Example: Create the Sport publish/subscribe cluster, QMB has the same set of subscriptions as QMA, yet QMB received no publications after the publisher published to QMA, see Figure 6. Although the Sports/Football and Sports/Rugby topics are cluster topics, the subscriptions defined in fullsubs.tst do not reference a cluster topic. No proxy subscriptions are propagated from QMB to QMA. Without proxy subscriptions, no publications to QMA are forwarded to QMB.
Some of the subscriptions, such as Sports/#/Leeds, might seem to reference a cluster topic, in this case Sports/Rugby. The Sports/#/Leeds subscription actually resolves to the topic object SYSTEM.BASE.TOPIC.
The rule for resolving the topic object referenced by a subscription such as, Sports/#/Leeds is as follows. Truncate the topic string to the first wildcard. Scan left through the topic string looking for the first topic that has an associated administrative topic object. The topic object might specify a cluster name, or define a local topic object. In the example, Sports/#/Leeds, the topic string after truncation is Sports, which has no topic object, and so Sports/#/Leeds inherits from SYSTEM.BASE.TOPIC, which is a local topic object.
To see how subscribing to clustered topics can change the way wildcard propagation works, run the batch script, upsubs.bat. The script clears the subscription queues, and adds the cluster topic subscriptions in fullsubs.tst. Run puba.bat again to create a batch of publications; see Figure 6.
Table 2 shows the result of adding two new subscriptions to the same queue manager that the publications were published on. The result is as expected, the new subscriptions receive one publication each, and the numbers of publications received by the other subscriptions are unchanged. The unexpected results occur on the other cluster queue manager; see Table 3.
| Subscription | Topic string | Publications received | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPORTS | Sports/# |
Sports Sports/Rugby Sports/Rugby/Leeds |
All publications to Football subtree blocked by WILDCARD(BLOCK) on Sports/Football |
| SARSENAL | Sports/#/Arsenal | - | WILDCARD(BLOCK) on Sports/Football prevents wildcard subscription on Arsenal |
| SLEEDS | Sports/#/Leeds |
Sports/Rugby/Leeds |
Default WILDCARD on Sports/Rugby does not prevent wildcard subscription on Leeds. |
| FARSENAL | Sports/Football/Arsenal | Sports/Football/Arsenal | Arsenal receives a publication because the subscription does not have a wildcard. |
| FLEEDS | Sports/Rugby/Leeds | Sports/Rugby/Leeds | Leeds would receive a publication in any event. |
Table 3 shows the results of adding the two new subscriptions on QMB and publishing on QMA. Recall that QMB received no publications without these two new subscriptions. As expected, the two new subscriptions receive publications, because Sports/FootBall and Sports/Rugby are both cluster topics. QMB forwarded proxy subscriptions for Sports/Football/Arsenal and Sports/Rugby/Leeds to QMA, which then sent the publications to QMB.
The unexpected result is that the two subscriptions Sports/# and Sports/#/Leeds that previously received no publications, now receive publications. The reason is that the Sports/Football/Arsenal and Sports/Rugby/Leeds publications forwarded to QMB for the other subscriptions are now available for any subscriber attached to QMB. Consequently the subscriptions to the local topics Sports/# and Sports/#/Leeds receive the Sports/Rugby/Leeds publication. Sports/#/Arsenal continues not to receive a publication, because Sports/Football has its WILDCARD property value set to BLOCK.
| Subscription | Topic string | Publications received | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| SPORTS | Sports/# |
Sports/Rugby/Leeds |
All publications to Football subtree blocked by WILDCARD(BLOCK) on Sports/Football |
| SARSENAL | Sports/#/Arsenal | - | WILDCARD(BLOCK) on Sports/Football prevents wildcard subscription on Arsenal |
| SLEEDS | Sports/#/Leeds |
Sports/Rugby/Leeds |
Default WILDCARD on Sports/Rugby does not prevent wildcard subscription on Leeds. |
| FARSENAL | Sports/Football/Arsenal | Sports/Football/Arsenal | Arsenal receives a publication because the subscription does not have a wildcard. |
| FLEEDS | Sports/Rugby/Leeds | Sports/Rugby/Leeds | Leeds would receive a publication in any event. |
In most applications, it is undesirable for one subscription to influence the behavior of another subscription. One important use of the WILDCARD property with the value BLOCK is to make the subscriptions to the same topic string containing wildcards behave uniformly. Whether the subscription is on the same queue manager as the publisher, or a different one, the results of the subscription are the same.
Wildcards and streams
For a new application written to the publish/subscribe API, the effect is that a subscription to * receives no publications. To receive all the Sports publications you must subscribe to Sports/*, or Sports/#, and similarly for Business publications.
The behavior of an existing queued publish/subscribe application does not change when the publish/subscribe broker is migrated to IBM MQ Version 7 and later versions. The StreamName property in the Publish, Register Publisher, or Subscriber commands is mapped to the name of the topic the stream has been migrated to.
Wildcards and subscription points
For a new application written to the publish/subscribe API, the effect of the migration is that a subscription to * receives no publications. To receive all the Sports publications you must subscribe to Sports/*, or Sports/#, and similarly for Business publications.
The behavior of an existing queued publish/subscribe application does not change when the publish/subscribe broker is migrated to IBM MQ Version 7 and later versions. The SubPoint property in the Publish, Register Publisher, or Subscriber commands is mapped to the name of the topic the subscription has been migrated to.
Example: Create the Sport publish/subscribe cluster
The steps that follow create a cluster, CL1, with four queue managers: two full repositories, CL1A and CL1B, and two partial repositories, QMA and QMB. The full repositories are used to hold only cluster definitions. QMA is designated the cluster topic host. Durable subscriptions are defined on both QMA and QMB. Note: The example is coded for Windows. You must recode Create qmgrs.bat and create pub.bat to configure and test the example on other platforms.- Create the script files.
- Run Create qmgrs.bat to create the configuration.
qmgrs
DELETE TOPIC ('Sports')
DELETE TOPIC ('Football')
DELETE TOPIC ('Arsenal')
DELETE TOPIC ('Blackburn')
DELETE TOPIC ('Chelsea')
DELETE TOPIC ('Rugby')
DELETE TOPIC ('Leeds')
DELETE TOPIC ('Wigan')
DELETE TOPIC ('Warrington')
DELETE TOPIC ('St. Helens')
DEFINE TOPIC ('Sports') TOPICSTR('Sports')
DEFINE TOPIC ('Football') TOPICSTR('Sports/Football') CLUSTER(CL1) WILDCARD(BLOCK)
DEFINE TOPIC ('Arsenal') TOPICSTR('Sports/Football/Arsenal')
DEFINE TOPIC ('Blackburn') TOPICSTR('Sports/Football/Blackburn')
DEFINE TOPIC ('Chelsea') TOPICSTR('Sports/Football/Chelsea')
DEFINE TOPIC ('Rugby') TOPICSTR('Sports/Rugby') CLUSTER(CL1)
DEFINE TOPIC ('Leeds') TOPICSTR('Sports/Rugby/Leeds')
DEFINE TOPIC ('Wigan') TOPICSTR('Sports/Rugby/Wigan')
DEFINE TOPIC ('Warrington') TOPICSTR('Sports/Rugby/Warrington')
DEFINE TOPIC ('St. Helens') TOPICSTR('Sports/Rugby/St. Helens')
DEFINE QLOCAL(QSPORTS) REPLACE
DEFINE QLOCAL(QSARSENAL) REPLACE
DEFINE QLOCAL(QSLEEDS) REPLACE
CLEAR QLOCAL(QSPORTS)
CLEAR QLOCAL(QSARSENAL)
CLEAR QLOCAL(QSLEEDS)
DELETE SUB (SPORTS)
DELETE SUB (SARSENAL)
DELETE SUB (SLEEDS)
DEFINE SUB (SPORTS) TOPICSTR('Sports/#') DEST(QSPORTS)
DEFINE SUB (SARSENAL) TOPICSTR('Sports/+/Arsenal') DEST(QSARSENAL)
DEFINE SUB (SLEEDS) TOPICSTR('Sports/+/Leeds') DEST(QSLEEDS)
The delimiter, /, is automatically inserted between the topic string referenced by TOPICOBJ, and the topic string defined by TOPICSTR.
The definition, DEFINE SUB(FARSENAL) TOPICSTR('Sports/Football/Arsenal') DEST(QFARSENAL) creates the same subscription. TOPICOBJ is used as a quick way to reference topic string we have already defined. The subscription, when created, no longer refers to the topic object.
DEFINE QLOCAL(QFARSENAL) REPLACE
DEFINE QLOCAL(QRLEEDS) REPLACE
CLEAR QLOCAL(QFARSENAL)
CLEAR QLOCAL(QRLEEDS)
DELETE SUB (FARSENAL)
DELETE SUB (RLEEDS)
DEFINE SUB (FARSENAL) TOPICOBJ('Football') TOPICSTR('Arsenal') DEST(QFARSENAL)
DEFINE SUB (RLEEDS) TOPICOBJ('Rugby') TOPICSTR('Leeds') DEST(QRLEEDS)
On other platforms, write a similar script, or type all the commands. Using a script makes it quick to delete everything and start again with an identical configuration.
@echo off
set port.CL1B=1421
set port.CLIA=1420
for %%A in (CL1A CL1B QMA QMB) do call :createQM %%A
call :configureQM CL1A CL1B %port.CL1B% full
call :configureQM CL1B CL1A %port.CL1A% full
for %%A in (QMA QMB) do call :configureQM %%A CL1A %port.CL1A% partial
for %%A in (topics.tst wildsubs.tst) do runmqsc QMA < %%A
for %%A in (wildsubs.tst) do runmqsc QMB < %%A
goto:eof
:createQM
echo Configure Queue manager %1
endmqm -p %1
for %%B in (dlt crt str) do %%Bmqm %1
goto:eof
:configureQM
if %1==CL1A set p=1420
if %1==CL1B set p=1421
if %1==QMA set p=1422
if %1==QMB set p=1423
echo configure %1 on port %p% connected to repository %2 on port %3 as %4 repository
echo DEFINE LISTENER(LST%1) TRPTYPE(TCP) PORT(%p%) CONTROL(QMGR) REPLACE | runmqsc %1
echo START LISTENER(LST%1) | runmqsc %1
if full==%4 echo ALTER QMGR REPOS(CL1) DEADQ(SYSTEM.DEAD.LETTER.QUEUE) | runmqsc %1
echo DEFINE CHANNEL(TO.%2) CHLTYPE(CLUSSDR) TRPTYPE(TCP) CONNAME('LOCALHOST(%3)') CLUSTER(CL1) REPLACE | runmqsc %1
echo DEFINE CHANNEL(TO.%1) CHLTYPE(CLUSRCVR) TRPTYPE(TCP) CONNAME('LOCALHOST(%p%)') CLUSTER(CL1) REPLACE | runmqsc %1
goto:eof
Update the configuration by adding the subscriptions to the cluster topics.
@echo off for %%A in (QMA QMB) do runmqsc %%A < wildsubs.tst for %%A in (QMA QMB) do runmqsc %%A < upsubs.tst
Run pub.bat, with a queue manager as a parameter, to publish messages containing the publication topic string. Pub.bat uses the sample program amqspub.
@echo off @rem Provide queue manager name as a parameter set S=Sports set S=6 Sports/Football Sports/Football/Arsenal set S=6 Sports/Rugby Sports/Rugby/Leeds for %%B in (6) do echo %%B | amqspub %%B %1