IBM BPM, V8.0.1, All platforms > Programming IBM BPM > Enterprise Service Bus programming > Service Component Architecture
SCA implementation in Integration Designer
You can build SCA modules within Integration Designer. Modules contain all the artifacts required to create a complete SCA application and they can be organized into projects. Additionally SCA libraries can be created in Integration Designer. You can build libraries to store artifacts, and you can share them between multiple SCA modules. Libraries are detailed later on in the chapter.
There are two types of modules that are supported by Integration Designer:
- A business module that contains a choice of many component types, often used to support a business process.
- A mediation module, which contains one or more mediation flow components. It is not necessary for a mediation module to contain any Java components, but there is no limit to the number of Java components that it can contain. Java components augment the mediation flow component. The mediation module acts as a gateway to existing external services, which is common in ESB architectures.
A business module is deployed to an IBM BPM server. A mediation module is deployed to either an IBM BPM server or a WebSphere ESB server. Both types of modules support imports and exports.
Mediation Modules
Mediation modules are SCA modules that can change the format, content, or target of service requests. Mediation modules operate on messages that are in-flight between service requesters and service providers. Mediation modules can route messages to different service providers and can also transform the message content or structure. Mediation modules can provide functions such as message logging, and error processing that are tailored to your requirements. You can change certain properties of mediation modules, from the WebSphere ESB administrative console, without having to redeploy the module. Figure 1 shows a simplified example of a mediation module. The mediation module contains one mediation flow component.
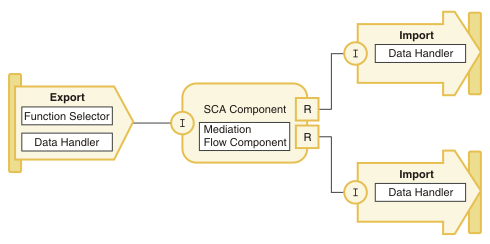
Module imports and exports
The mechanisms used for invocations from module to module and module to external services, are called imports and exports. Imports and exports are represented from the point of view of the module. The module is a self-contained bundle of components that perform a specific business function. A module invokes this capability using an import if it is required to use the business function from another service to call a function (external service or other module).
Exports provide the ability to make a service available over a number of different transport protocols. The export is associated to a particular component within the module.
Imports and exports also have the ability to interact with service providers across a variety of protocols and Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), such as:
- Web services
- HTTP
- JMS
- MQ
- EJB
- WebSphere Adapters
- SCA
Data handlers
Data handlers are reusable transformation logic in WebSphere ESB, which can be used by exports and imports. Data handlers transform native formats into business data and from business data into native formats required by external services.
In your SOA implementation, business data can flow between service providers and service requesters over a variety of protocols (HTTP, JMS, MQ, and so on), in a variety of data formats such as comma separated value, delimited, fixed width, COBOL and so on. Different protocols can have the same mechanisms for carrying the business data in their relevant protocol envelope.
For example, a HTTP message can encode its data using a comma delimited format, which can also be used in a JMS message. The data handler interface is protocol neutral, which enables data handlers to be usable across all of the protocols supported.
WebSphere ESB supplies a number of built in data handlers including:
- Atom feed format
- Delimited format
- Fixed width format
- JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) format
- SOAP data handler
- WTX Invoker Data Handler
- WTX MapSelection Data Handler
- XML Data Handler
Function selector
The function selector determines which operation defined on the associated interface is invoked. When a message arrives at an export it will include raw transport header information and encoded data for the body of the message. The function selector can use header data, body data, or both, to determine which of the operations on the associated interface can be invoked. As this mechanism is likely to be dependent on the protocol headers, the implementation of the function selector will be protocol specific.
For example, a JMS message header can specify the operation name and a function selector can use this JMS message header to determine the operation that is called.
SCA components
SCA components are building blocks for mediation modules. There are two types of SCA components, which are allowed within a mediation module:
- Mediation flow component
- Java component
Mediation flow component
Mediation modules contain a specific type of SCA component called a mediation flow component. A mediation flow component manipulates the message as it flows through the mediation module. A mediation flow component can be associated with several interfaces. A mediation flow is the process that occurs for a particular operation on the interface. There is at least one mediation flow for each operation on the interface.
An interface can have two types of operation:
- One way (request only), with a single request flow that holds the logic for the request message.
- Two way (request/response) with a request flow and a response flow. The request flow holds the logic for the request message. The response flow holds the logic for the response message.
A mediation flow can contain any number of mediation primitives. Mediation primitives are reusable blocks of function that are wired together to build a mediation flow. These mediation primitives can route and transform the message. WebSphere ESB supplies a set of mediation primitives that provide functionality for message processing. You can also contribute your own primitives. If the mediation module will only transform from one protocol to another, a mediation flow component is not required.
For example, a service request might be received using SOAP/JMS but might need transforming to SOAP/HTTP before sending on. In this instance, a Web Service Export (SOAP/JMS) and Web Service Import (SOAP/HTTP) is required.
Java component
The Java component provides an alternative implementation option for creating SCA components within WebSphere ESB. You can use Java code, instead of the mediation flow component to manipulate the messages as they pass through the system. This can provide additional flexibility in the solutions you implement. Service Component Architecture